Figure: Modifying the Base Interfaces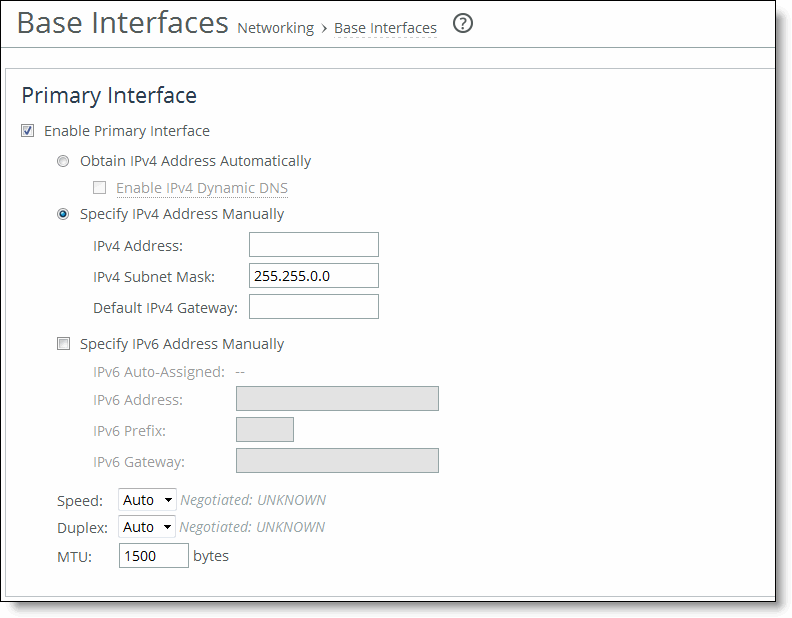


Control | Description |
Enable Primary Interface | Enables the appliance management interface, which can be used for both managing the SteelHead and serving data for a server-side out-of-path (OOP) configuration. |
Obtain IPv4 Address Automatically | Select this option to automatically obtain the IP address from a DHCP server. A DHCP server must be available so that the system can request the IP address from it. Note: The primary and in-path interfaces can share the same network subnet. The primary and auxiliary interfaces cannot share the same network subnet. |
Enable IPv4 Dynamic DNS | Select this option to send the hostname with the DHCP request for registration with Dynamic DNS. The hostname is specified in the Networking > Networking: Host Settings page. |
Specify IPv4 Address Manually | Select this option if you do not use a DHCP server to set the IPv4 address. Specify these settings: • IPv4 Address - Specify an IP address. • IPv4 Subnet Mask - Specify a subnet mask. • Default IPv4 Gateway - Specify the default gateway IPv4 address. The default gateway must be in the same network as the primary interface. You must set the default gateway for in-path configurations. |
Do Not Assign An IPv4 Address | Enables the interface without assigning an IP address. Use this option if all traffic on this interface is for VSP. |
Specify IPv6 Address Manually | Select this option and specify these settings to set an IPv6 address. • IPv6 Auto-Assigned - Displays the link-local address that is automatically generated when IPv6 is enabled on the base interfaces. • IPv6 Address - Specify an IP address using this format: eight 16-bit hexadecimal strings separated by colons, 128-bits. For example: 2001:38dc:0052:0000:0000:e9a4:00c5:6282 You do not need to include leading zeros. For example: 2001:38dc:52:0:0:e9a4:c5:6282 You can replace consecutive zero strings with double colons (::). For example: 2001:38dc:52::e9a4:c5:6282 • IPv6 Prefix - Specify a prefix. The prefix length is 0 to 128, separated from the address by a forward slash (/). In this example, 60 is the prefix: 2001:38dc:52::e9a4:c5:6282/60 • IPv6 Gateway - Specify the gateway IP address. The gateway must be in the same network as the primary interface. Note: You cannot set an IPv6 address dynamically using a DHCP server. |
Speed and Duplex | Speed - Select a speed from the drop-down list. The default value is Auto. Duplex - Select Auto, Full, or Half from the drop-down list. The default value is Auto. If your network routers or switches do not automatically negotiate the speed and duplex, be sure to set them manually. The speed and duplex must match (LAN and WAN) in an in-path configuration. If they do not match, you might have a large number of errors on the interface when it is in bypass mode, because the switch and the router are not set with the same duplex settings. |
MTU | Specify the MTU value. The MTU is the largest physical packet size, measured in bytes, that a network can send. The default value is 1500. |
Control | Description |
Enable Aux Interface | Enables an auxiliary interface, which can be used only for managing the SteelHead. It cannot be used for an out-of-path (OOP) SteelHead data service. Typically this is used for device-management networks. |
Obtain IPv4 Address Automatically | Select this option to automatically obtain the IP address from a DHCP server. A DHCP server must be available so that the system can request the IP address from it. Note: The primary and in-path interfaces can share the same subnet. The primary and auxiliary interfaces cannot share the same network subnet. |
Enable IPv4 Dynamic DNS | Select this option to send the hostname with the DHCP request for registration with Dynamic DNS. The hostname is specified in the Networking > Networking: Host Settings page. |
Specify IPv4 Address Manually | Select this option if you do not use a DHCP server to set the IPv4 address. Specify these settings: • IPv4 Address - Specify an IP address. • IPv4 Subnet Mask - Specify a subnet mask. |
Do Not Assign An IPv4 Address | Enables the interface without assigning an IP address. Use this option if all traffic on this interface is for VSP. |
Specify IPv6 Address Manually | Select this option and specify these settings to set an IPv6 address. • IPv6 Auto-Assigned - Displays the link-local address that is automatically generated when IPv6 is enabled on the base interfaces. • IPv6 Address - Specify an IP address, using this format: eight 16-bit hexadecimal strings separated by colons, 128-bits. For example: 2001:38dc:0052:0000:0000:e9a4:00c5:6282 You do not need to include leading zeros: for example 2001:38dc:52:0:0:e9a4:c5:6282 You can replace consecutive zero strings with double colons (::). For example, 2001:38dc:52::e9a4:c5:6282 • IPv6 Prefix - Specify a prefix. The prefix length is 0 to 128, separated from the address by a forward slash (/). In this example, 60 is the prefix: 2001:38dc:52::e9a4:c5:6282/60 Note: You cannot set an IPv6 address dynamically using a DHCP server. |
Speed and Duplex | Speed - Select the speed from the drop-down list. The default value is Auto. Duplex - Select Auto, Full, or Half from the drop-down list. The default value is Auto. If your network routers or switches do not automatically negotiate the speed and duplex, be sure to set them on the device manually. The speed and duplex must match (LAN and WAN) in an in-path configuration. To avoid a speed and duplex mismatch, configure your LAN external pair to match the WAN external pair. |
MTU | Specify the MTU value. The MTU is the largest physical packet size, measured in bytes, that a network can send. The default value is 1500. |
Apply | Applies your settings to the running configuration. |
Control | Description |
Add a New Route | Displays the controls for adding a new route. |
Destination IPv4 Address | Specify the destination IP address for the out-of-path appliance or network management device. |
IPv4 Subnet Mask | Specify the subnet mask. |
Gateway IPv4 Address | Specify the IP address for the gateway. The gateway must be in the same network as the primary or auxiliary interface you are configuring. |
Interface | Select an interface for the IPv4 route from the drop-down list. |
Add | Adds the route to the table list. |
Remove Selected | Select the check box next to the name and click Remove Selected. |
Control | Description |
Add a New Route | Displays the controls for adding a new route. |
Destination IPv6 Address | Specify the destination IP address. |
IPv6 Prefix | Specify a prefix. The prefix length is from 0 to 128 bits, separated from the address by a forward slash (/). |
Gateway IPv6 Address | Specify the IP address for the gateway. The gateway must be in the same network as the primary or auxiliary interface you are configuring. |
Interface | Select an interface for the IPv6 route from the drop-down list. |
Add | Adds the route to the table list. |
Remove Selected | Select the check box next to the name and click Remove Selected. |