About host settings
Host settings are under Networking > Networking: Host Settings.
Host settings
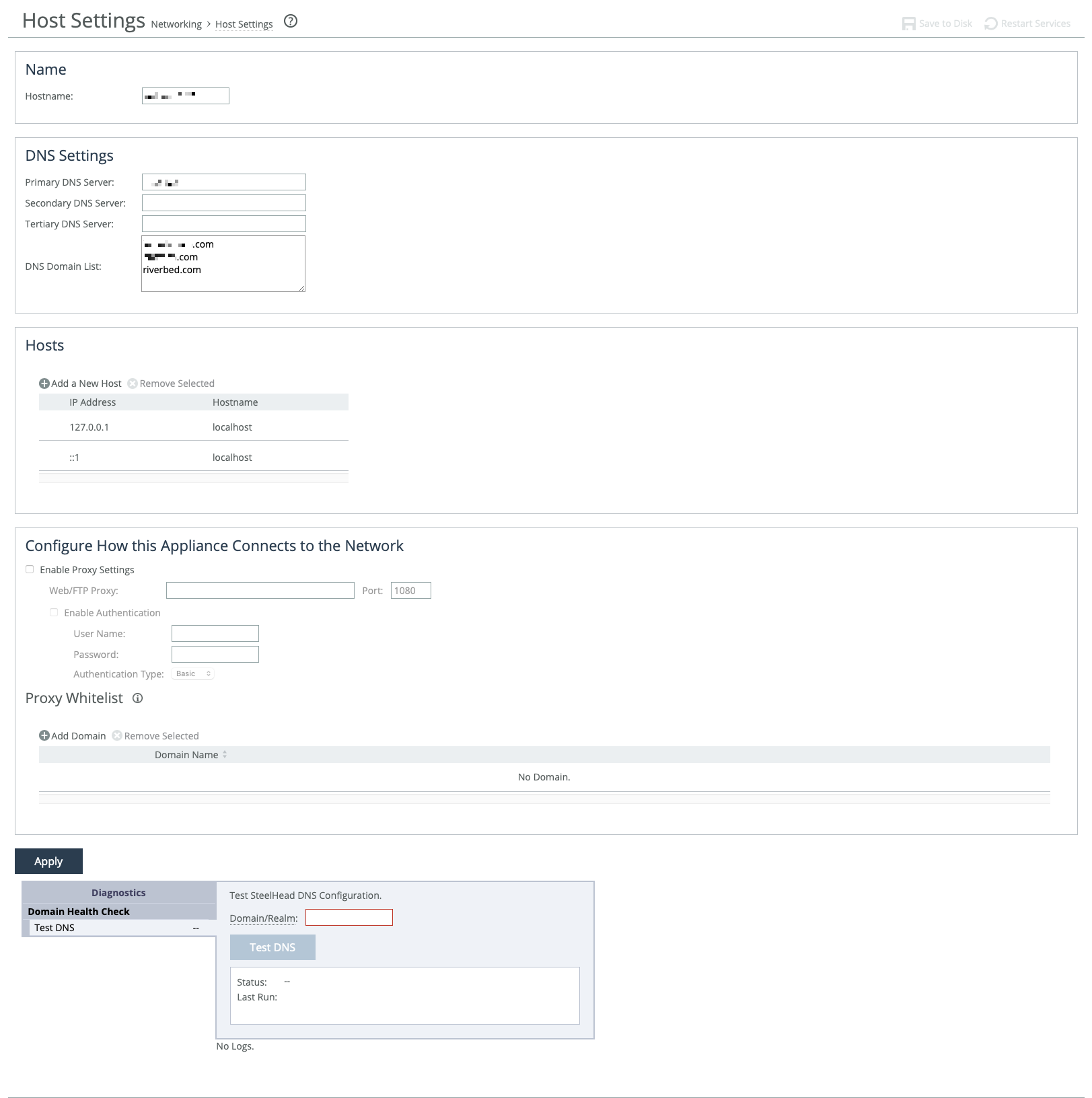
Typically, host settings, which include base (primary, auxiliary) and in-path interface settings, are configured during initial configuration of the appliance. Change these settings only when necessary, and only when you are sure about the changes you need to make.
We recommend using DNS resolution whenever possible. If your organization doesn’t use DNS, or if the appliance host doesn’t have a DNS entry, create a host-to-IP address resolution map under Hosts.
Use the proxy settings to configure web or FTP proxy access to the appliance. Whitelist domains traffic from which you do not want redirected through the proxy.
At the bottom of the page, you’ll find a handy tool for quickly testing the appliance’s DNS configuration.
DNS
You can specify the IP addresses for your primary DNS server and, optionally, secondary and tertiary ones. IPv6 addresses are allowed.
You can also create a centralized DNS domain list. This ordered list provides a single, central location for you to define the domain suffixes used in your organization so that you don’t need to always enter host or server fully-qualified domain names (FQDN) when configuring other aspects of the appliance; you can just use short names. The appliance completes those short names as needed by applying entries from the list in order until a match is found.
For example, let’s say that the appliance’s email notification SMTP server has been set as simply exchange, and let’s assume your organization’s email server is exchange.mydomain2.com. By adding entries to the DNS domain list, you enable the appliance to apply those domains to exchange, in order until a match is found. So, if the first entry is mydomain1.com and the second is mydomain2.com, the appliance looks for exchange within mydomain1.com. When it doesn’t find it there, it tries mydomain2.com. Finding a match, it resolves the hostname to exchange.mydomain2.com.
Proxy
Use the settings under Configure How This Appliance Connects to the Network to globally enable web or FTP proxy access to the appliance. Proxy access is disabled by default. IPv6 addresses supported. Default port is 1080.
When enabled, the appliance can securely contact the Riverbed licensing portal and fetch licenses, and it can securely contact a SaaS Accelerator Manager (SAM) for registration and management. Connection errors are reported in the appliance logs.
If you are configuring proxy settings to interoperate with SaaS Accelerator Manager (SAM), we recommend that you do not configure the system to perform SSL/TLS inspection of TCP traffic between the proxy and the SAM.
You can optionally require user credentials to communicate with the proxy, and you can set the method used to authenticate and negotiate user credentials. These methods are available:
• Basic authenticates user credentials by requesting a valid username and password. This is the default setting.
• NTLM authenticates user credentials based on an authentication challenge and response.
• Digest provides the same functionality as basic authentication, but with improved security because the system sends the credentials across the network as a Message Digest 5 (MD5) hash.
Allow direct communication between the appliance and specific domains by adding the domains to the whitelist. Traffic between the appliance and whitelisted domains bypass the proxy.
If you are using SteelCentral Controller for SteelHead (SCC) to manage your appliances, we recommend that you add the SCC’s domain to the whitelist. Otherwise, appliance backups to SCC are blocked if a proxy is enabled.


