Figure: Host Settings Page



Control | Description |
Primary DNS Server | Specify the IP address for the primary name server. |
Secondary DNS Server | Optionally, specify the IP address for the secondary name server. |
Tertiary DNS Server | Optionally, specify the IP address for the tertiary name server. |
DNS Domain List | Specify an ordered list of domain names. If you specify domains, the system automatically finds the appropriate domain for each of the hosts that you specify in the system. |

Control | Description |
Add a New Host | Displays the controls for adding a new host. |
IP Address | Specify the IP address for the host. |
Hostname | Specify a hostname. |
Add | Adds the host. |
Remove Selected | Select the check box next to the name, and then click Remove Selected. |
Control | Description |
Enable Web Proxy | Select the check box to enable the web proxy. |
Web/FTP Proxy | Specify the IP address for the web/FTP proxy. |
Port | Specify the port for the web/FTP proxy. |
Enable Authentication | Optionally, select this feature to enable authentication. Specify the following authenticate the users: • User Name - Specify a username. • Password - Specify a password. • Authentication Type- Select an authentication method from the drop-down list: – Basic - Authenticates user credentials by requesting a valid username and password. This is the default setting. – NTLM - Authenticates user credentials based on an authentication challenge and response – Digest - Provides the same functionality as basic authentication; however, digest authentication improves security because the system sends the user credentials across the network as a Message Digest 5 (MD5) hash. |
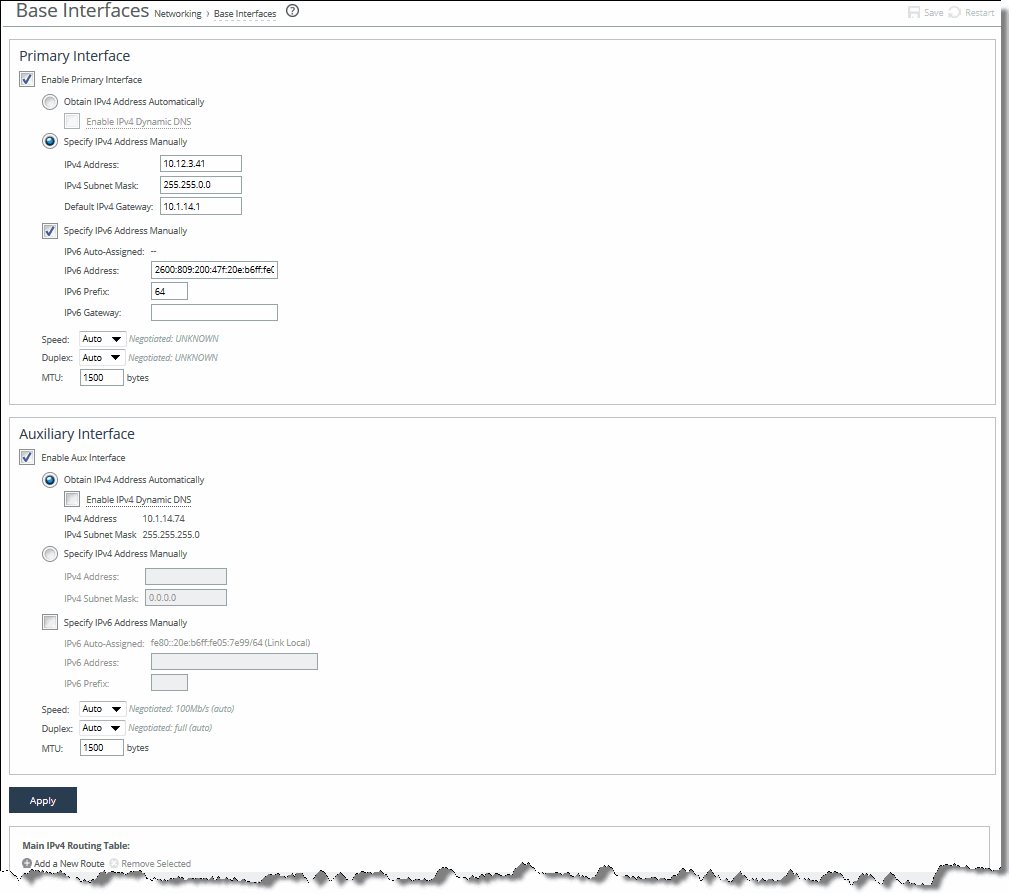
Control | Description |
Enable Primary Interface | Select the check box to enable the primary interface. |
Obtain IPv4 Address Automatically | Select this option to automatically obtain the IP address from a DHCP server. A DHCP server must be available so that the system can request the IP address from it. Optionally, select Enable IPv4 Dynamic DNS to include the appliance hostname with the DHCP request. Note: The primary and in-path interfaces can share the same subnet. The primary and auxiliary interfaces cannot share the same network subnet. |
Specify IPv4 Address Manually | Select this option if you do not use a DHCP server to set the IP address. Specify the following settings: • IPv4 Address - Specify an IP address. • IPv4 Subnet Mask - Specify a subnet mask. • Default IPv4 Gateway - Specify the primary gateway IP address. The primary gateway must be in the same network as the primary interface. You must set the primary gateway for in-path configurations. |
Specify IPv6 Address Manually | Select this option and specify the following settings to set an IPv6 address: • IPv6 Auto-Assigned - Displays the link-local address that is automatically generated when IPv6 is enabled on the base interfaces. • IPv6 Address - Specify an IP address using the following format: eight 16-bit hexadecimal strings separated by colons, 128-bits. For example: 2001:38dc:0052:0000:0000:e9a4:00c5:6282 You do not need to include leading zeros. For example: 2001:38dc:52:0:0:e9a4:c5:6282 You can replace consecutive zero strings with double colons (::). For example: 2001:38dc:52::e9a4:c5:6282 • IPv6 Prefix - Specify a prefix. The prefix length is 0 to 128, separated from the address by a forward slash (/). In the following example, 60 is the prefix: 2001:38dc:52::e9a4:c5:6282/60 • IPv6 Gateway - Specify the default gateway IP address. The gateway must be in the same network as the primary interface. Note: You cannot set an IPv6 address dynamically using a DHCP server. |
Speed | Select a speed from the drop-down list. The default value is Auto. |
Duplex | Select a choice from the drop-down list. The default value is Auto. If your network routers or switches do not automatically negotiate the speed and duplex, be sure to set them manually. The speed and duplex must match (LAN and WAN) in an in-path configuration. If they do not match, you might have a large number of errors on the interface when it is in bypass mode, because the switch and the router are not set with the same duplex settings. |
MTU (Bytes) | Specify the MTU value. The MTU is the largest physical packet size, measured in bytes, that a network can send. The default value is 1500. |
Control | Description |
Enable Aux Interface | Enables an auxiliary interface. |
Obtain IPv4 Address Automatically | Select this option to set the appliance to automatically obtain the IP address. Optionally, select Enable IPv4 Dynamic DNS to include the appliance hostname with the DHCP request. Caution: The primary and auxiliary interfaces cannot share the same network subnet. The auxiliary and in-path interfaces cannot share the same subnet. You cannot use the auxiliary port for out-of-path SteelHead Interceptors. |
Specify IPv4 Address Manually | Specify the following settings: • IPv4 Address - Specify an IP address. • IPv4 Subnet Mask - Specify a subnet mask. Select this option if you do not use a DHCP server to set the IP address. |
Specify IPv6 Address Manually | Specify the following settings: • IPv6 Auto-Assigned - Specify an automatic IP address. • IPv6 Address - Specify an IP address. • IPv6 Prefix - Specify a prefix. |
Speed | Select the speed from the drop-down list. The default value is Auto. |
Duplex | Select a choice from the drop-down list. The default value is Auto. If your network routers or switches do not automatically negotiate the speed and duplex, be sure to set them on the device manually. The speed and duplex must match (LAN and WAN) in an in-path configuration. To avoid a speed and duplex mismatch, configure your LAN external pair to match the WAN external pair. |
MTU (Bytes) | Specify the MTU value. The MTU is the largest physical packet size, measured in bytes, that a network can send. The default value is 1500. |
Control | Description |
Add a New Route | Displays the controls for adding a new route. |
Destination IPv4 Address | Specify the destination IPv4 address for the out-of-path appliance or network management device. |
IPv4 Subnet Mask | Specify the IPv4 subnet mask. |
Gateway IPv4 Address | Specify the IPv4 address for the gateway. |
Interface | Select the interface for routing from the drop-down list. |
Add | Adds the route to the table list. |
Remove Selected | Select the check box next to the name and click Remove Selected. |
Control | Description |
Add a New Route | Displays the controls for adding a new route. |
Destination IPv6 Address | Specify the destination IPv6 address for the out-of-path appliance or network management device. |
IPv6 Prefix | Specify the prefix. |
Gateway IPv6 Address | Specify the IPv6 address for the gateway. |
Interface | Select the interface for routing from the drop-down list. |
Add | Adds the route to the table list. |
Remove Selected | Select the check box next to the name and click Remove Selected. |

Control | Description |
IPv4 Address | Specify an IP address. This IP address is the in-path main interface. |
IPv4 Subnet Mask | Specify the subnet mask. |
IPv4 Gateway | Specify the IP address for the in-path gateway. If you have a router (or a Layer-3 switch) on the LAN side of your network, specify this device as the in-path gateway. Note: If there is a routed network on the LAN-side of the in-path appliance, the router that is the default gateway for the appliance must not have the ACL configured to drop packets from the remote hosts as its source. The in-path appliance uses IP masquerading to appear as the remote server. |
Enable Bypass | Select this option to enable bypass on this interface. Caution: By enabling bypass, you disable load balancing on this interface. |
LAN Speed and Duplex WAN Speed and Duplex | Specify the following settings for the LAN and WAN ports: • Speed - Select a speed from the drop-down list. The default value is Auto. • Duplex - Select a choice from the drop-down list. The default value is Auto. If your network routers or switches do not automatically negotiate the speed and duplex, be sure to set them on the device manually. The speed and duplex must match (LAN and WAN) in an in-path configuration. To avoid a speed and duplex mismatch, configure your LAN external pair to match the WAN external pair. To avoid speed and duplex mismatches, see Avoiding Speed and Duplex Mismatches. |
MTU (Bytes) | Specify the MTU value. The MTU is the largest physical packet size, measured in bytes, that a network can send. Applies to optimized traffic only. The default value is 1500. |
VLAN Tag ID | Specify a numeric VLAN Tag ID. When you specify the VLAN Tag ID for the MIP interface, all packets originating from the SteelHead Interceptor are tagged with that identification number. Specify the VLAN tag that the appliance uses to communicate with other SteelHead Interceptors in your network. The VLAN Tag ID might be the same value or a different value than the VLAN tag used on the client. A zero (0) value specifies nontagged (or native VLAN) and is the correct setting if there are no VLANs present. For example, if the in-path interface is 192.168.1.1 in VLAN 200, you would specify tag 200. Note: When the SteelHead Interceptor communicates with a client or a server, it uses the same VLAN tag as the client or the server. If the SteelHead Interceptor cannot determine which VLAN the client or server is in, it uses its own VLAN until it is able to determine that information. You must also define in-path rules to apply to your VLANs. |
Failure Condition | Select the failure condition from the drop-down list: • Block - Enables fail-to-block mode. A failed SteelHead Interceptor blocks any network traffic on its path, as opposed to passing it through. • Bypass - Enables fail-to-wire mode. A failed SteelHead Interceptor passes through network traffic. The default value is Bypass. The SteelHead Interceptor supports the same concepts of fail-to-block and fail-to-wire as the SteelHead. In physical in-path deployments, the SteelHead Interceptor LAN and WAN ports that traffic flows through are internally connected by circuitry that can take special action in the event of a disk failure, a software crash, a runaway software process, or even loss of power to the SteelHead Interceptor. If a serious failure occurs on the SteelHead Interceptor, the appliance either passes traffic through (for fail-to-wire mode) or prevents traffic from passing (for fail-to-block mode). Note: In a parallel configuration, fail-to-block mode should be enabled to force all traffic through a cluster SteelHead Interceptor, thereby enabling optimization to continue. Note: In a serial, quad, or octal configuration, fail-to-wire mode should be enabled to pass all traffic through to the cluster or failover SteelHead Interceptor, thereby enabling optimization to continue. |
Apply | Click to apply your changes to the running configuration. After you apply your settings, you can verify whether changes have had the desired effect by reviewing related reports. When you have verified appropriate changes, you can write the active configuration that is stored in memory to the active configuration file, or save it as a file. For details about saving configurations, see Managing Configuration Files. |
Control | Description |
Add a New Route | Displays the controls to add a route. |
Destination IP Address | Specify the destination IP address. |
Subnet Mask | Specify the subnet mask. |
Gateway IP Address | Specify the IP address for the gateway. The gateway must be in the same network as the in-path interface. |
Add | Adds the route to the table list. |
Remove Selected | Select the check box next to the name and click Remove Selected. |
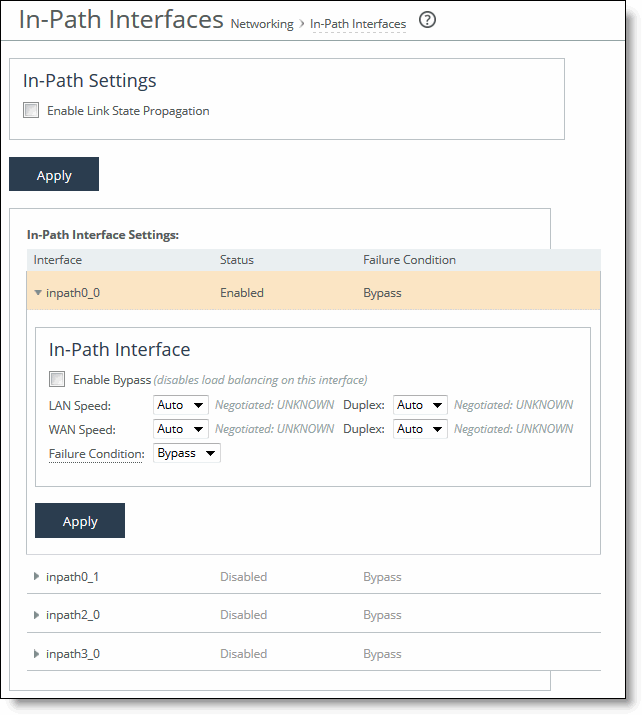
Control | Description |
Enable Bypass | Select this option to enable bypass on this interface. Caution: By enabling bypass, you disable load balancing on this interface. |
LAN Speed and Duplex WAN Speed and Duplex | Specify the following settings for the LAN and WAN ports: • Speed - Select a speed from the drop-down list. The default value is Auto. • Duplex - Select a choice from the drop-down list. The default value is Auto. If your network routers or switches do not automatically negotiate the speed and duplex, be sure to set them on the device manually. The speed and duplex must match (LAN and WAN) in an in-path configuration. To avoid a speed and duplex mismatch, configure your LAN external pair to match the WAN external pair. To avoid speed and duplex mismatches, see Avoiding Speed and Duplex Mismatches. |
Failure Condition | Select the failure condition from the drop-down list: • Bypass - Enables fail-to-wire mode. A failed SteelHead Interceptor passes through network traffic. • Block - Enables fail-to-block mode. A failed SteelHead Interceptor blocks any network traffic on its path, as opposed to passing it through. The default value is Bypass. The SteelHead Interceptor supports the same concepts of fail-to-block and fail-to-wire as the SteelHead. In physical in-path deployments, the SteelHead Interceptor LAN and WAN ports that traffic flows through are internally connected by circuitry that can take special action in the event of a disk failure, a software crash, a runaway software process, or even loss of power to the SteelHead Interceptor. If a serious failure occurs on the SteelHead Interceptor, the appliance either passes traffic through (for fail-to-wire mode) or prevents traffic from passing (for fail-to-block mode). Note: In a parallel configuration, fail-to-block mode should be enabled to force all traffic through a cluster SteelHead Interceptor, thereby enabling optimization to continue. Note: In a serial, quad, or octal configuration, fail-to-wire mode should be enabled to pass all traffic through to the cluster or failover SteelHead Interceptor, thereby enabling optimization to continue. |

Control | Description |
Enable for Load Balancing | Select this option to enable load balancing on this interface. Conversely, if this check box is selected, clear it to disable load balancing on this interface. If selected, specify the following settings: • IPv4 Address - Specify an IP address. This IP address is the in-path main interface. • IPv4 Subnet Mask - Specify the subnet mask. • IPv4 Gateway - Specify the IP address for the in-path gateway. If you have a router (or a Layer-3 switch) on the LAN side of your network, specify this device as the in-path gateway. • MTU - Specify the MTU value. The MTU is the largest physical packet size, measured in bytes, that a network can send. Applies to optimized traffic only. The default value is 1500. Note: If you change the MTU value of a VLAN in-path interface, the system propagates the value to the in-path interface and to the physical LAN/WAN interfaces. The system calculates the MTU from the maximum MTU of all the VLAN in-path interfaces (inpathx_y.v) for that in-path interface (inpathx_y). Note: If there is a routed network on the LAN-side of the in-path appliance, the router that is the default gateway for the appliance must not have the ACL configured to drop packets from the remote hosts as its source. The in-path appliance uses IP masquerading to appear as the remote server. |
Apply | Click to apply your changes to the running configuration. |
Control | Description |
Add a New Route | Displays the controls to add a route. |
Destination IP Address | Specify the destination IP address. |
Subnet Mask | Specify the subnet mask. |
Gateway IP Address | Specify the IP address for the gateway. The gateway must be in the same network as the in-path interface. |
Add | Adds the route to the table list. |
Remove Selected | Select the check box next to the name and click Remove Selected. |

