Powering, Connecting, and Configuring the Appliance
Before you power on, connect, and configure the appliance, you'll need to know how you plan to deploy it in your network's topology. For example, you'll need to know if you plan to deploy the appliance in an in-path or an out-of-path topology. For a brief overview of deployment scenarios, see
About connecting the appliance to the network. For more detailed information about deploying appliances, go to the deployment guide for your appliance.
It’ll also be helpful to know whether you plan to configure the appliance for fail-to-block or fail-to-wire in the event of a power outage or other disturbance to your network. For a brief overview of these failure modes, see
Installing Network Interface Cards.About appliance power cords
Depending on the model, some appliances require one power cord and some appliances require two power cords (see
Figure: Connecting the AC power). If your model has multiple power supplies, you must plug in all the power cords or you will hear an alarm.
Connecting the AC power
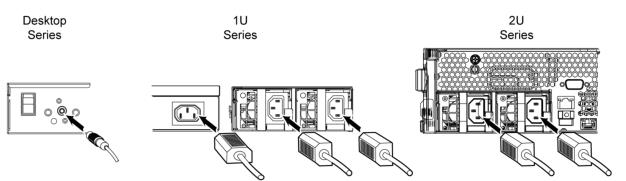
In European electrical environments you must ground (earth) the Green/Yellow tab on the power cord, or risk electrical shock.
Some desktop models include a power cord retention module. You can install the retention module to reduce the risk of accidentally unplugging the power. The retention module doesn’t prevent accidental pulls from removing the power cord, but it does provide increased protection.
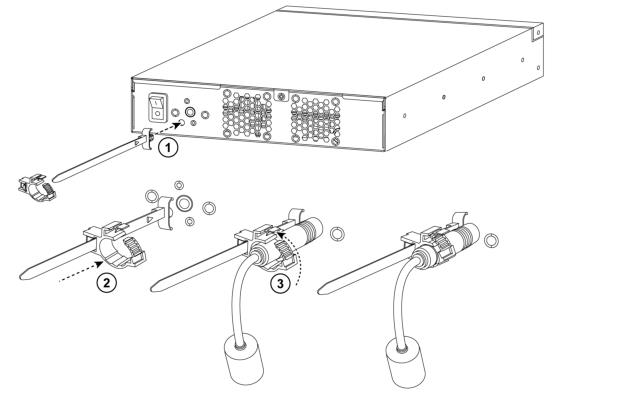
Attaching the retention fastener
Securing the power cord
1. Push the retention module into the socket near the power connection. The socket is left of the power supply.
2. Attach the retention fastener to the module and tighten it around the power cable.
Powering the appliance
1. If your system has a master power switch, ensure that the system and master power switch is in the off position on the rear of the appliance.
2. Plug the AC power cord into the appliance.
3. Plug the AC power cord into an uninterrupted AC power source.
4. Press the system power switch on. If the appliance doesn’t immediately power on, press the power switch off, and then press the power switch on again.
About connecting the appliance to the network
How you plan to deploy your appliance determines how you will connect it to your network. You have two deployment options: in-path and out-of-path.
In an in-path deployment, the appliance is in the direct path between clients and servers. The clients and servers continue to see client and server IP addresses. In-path configurations are suitable for any location where the total bandwidth is within the limits of the installed appliance.
You use standard Ethernet straight-through and crossover cables to connect to your network in an in-path configuration. Make sure that you use the correct cables to establish your network connections:
• Straight-through cables—Primary and LAN ports on the appliance to the LAN switch.
• Crossover cable—WAN port on the appliance to the WAN router.
In an out-of-path deployment, the appliance is not in the direct path between the client and the server. Servers see the IP address of the server-side appliance rather than the client-side IP address.
In an out-of-path configuration, the client-side SteelHead is configured as an in-path device and the server-side SteelHead is configured as an out-of-path device.
An out-of-path configuration is suitable for data center locations where in-path or logical in-path configurations aren’t possible.
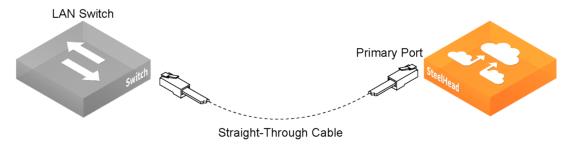
You use a standard Ethernet straight-through cable to connect the primary port of the appliance to the LAN switch in an out-of-path configuration.
Cabling in-path deployments
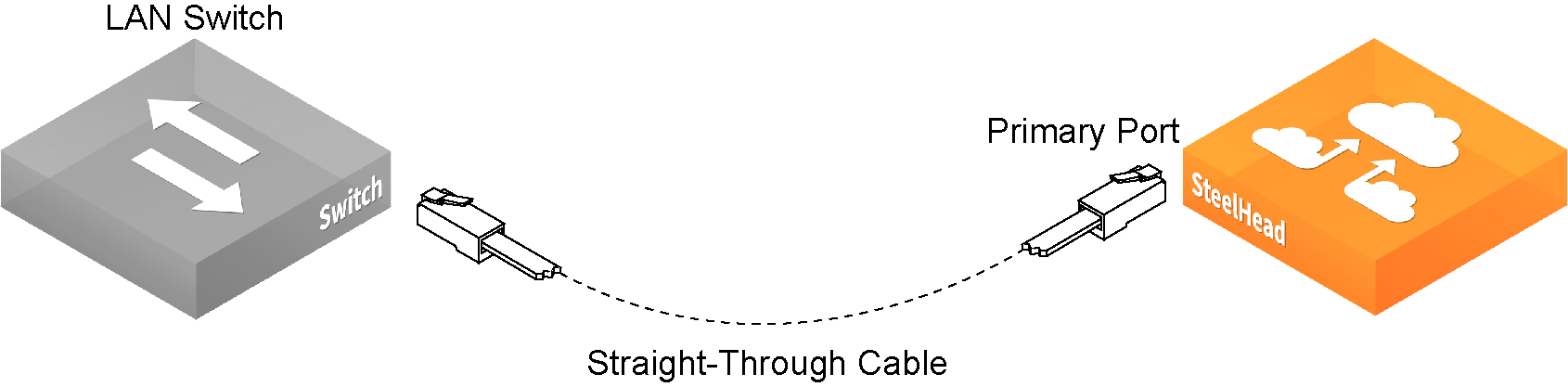
1. Plug the straight-through cable into the primary port of the appliance and the LAN switch. This can be any port on your LAN switch configured to connect to a host.
Connecting the primary port to the LAN switch
2. Identify the straight-through cable that connects your LAN switch to your WAN router. Unplug the end connected to the WAN router.
Disconnecting the WAN router
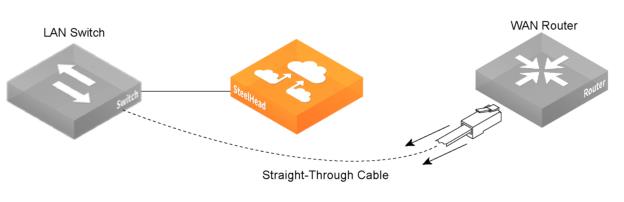
3. Plug the straight-through cable that you disconnected from the WAN router into the LAN port of the appliance.
Connecting the LAN switch to the LAN port
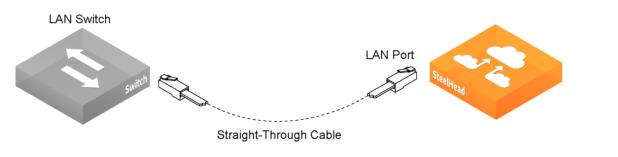
4. Using the provided crossover cable, plug the cable into the WAN port of the appliance and the WAN router. This must be a crossover cable.
Connecting the WAN port to the WAN router
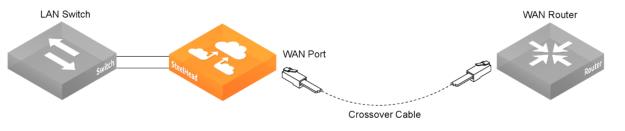
Cabling out-of-path deployments
Plug the straight-through cable into the primary port of the appliance and the LAN switch. This can be any port on your LAN switch that is configured to connect to a host.
Connecting the primary port and LAN switch
About first-time configuration
To get your appliance up and running, you’ll need to perform a one-time initial configuration. To do that, you’ll need to connect a monitor to the appliance and complete the configuration wizard. Completing the initial configuration will enable users to access the graphical user interface (GUI) or Management Console, where further configuration can be performed.
To access the configuration wizard and the appliance CLI, you’ll need to connect a monitor and establish a serial connection using a terminal emulator program. Depending on your appliance, the console port is either a DB9M port or an RJ45 port. The appropriate console cable ships with your appliance.
Connecting to the appliance console port
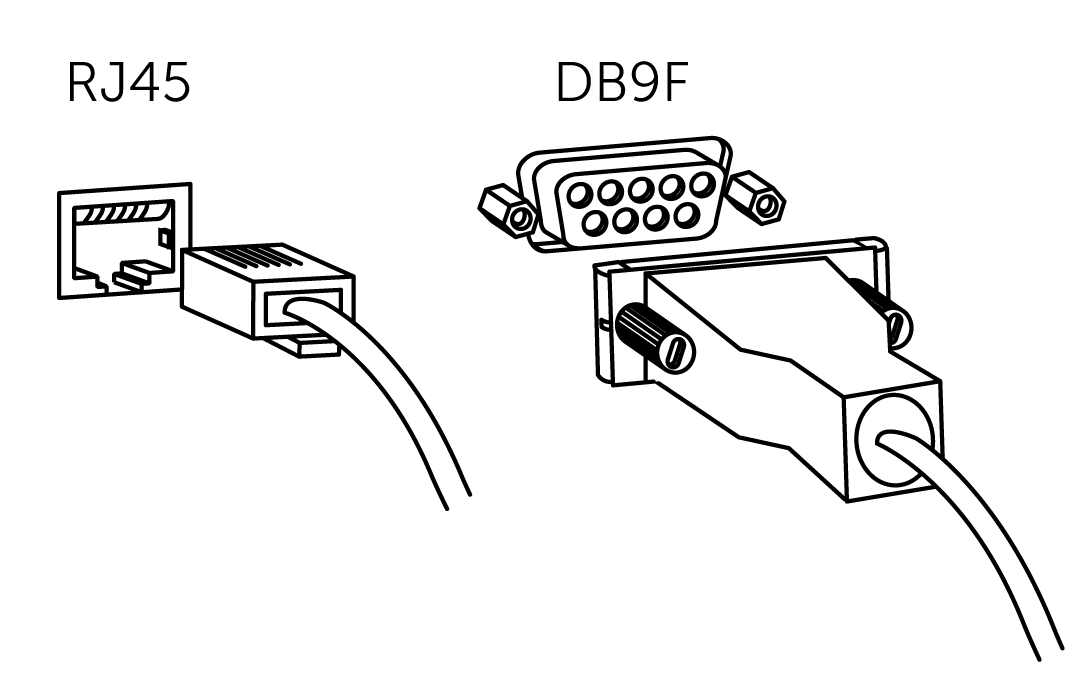
The terminal device must have these settings:
• Baud rate: 9600 bps
• Data bits: 8
• Parity: none
• Stop bits: 1
• VT100 emulation
• No flow control
If you are using the appliance with a terminal server, the terminal server must use hardware flow control for the port connected to the appliance.
We recommend that you connect the console port to a device that logs output. Even though this is not a requirement, it can help you to identify problems with the system.
The configuration wizard automatically starts when you log in to the CLI for the first time. This checklist lists the parameters you’ll need to specify to complete the initial configuration of the appliance. Be prepared to provide values for these parameters.
Appliance | Parameter | Your value |
SteelHead (the Primary Interface) | Host name | |
IP address | |
Netmask | |
Default gateway (the WAN gateway) | |
DNS IP address | |
Domain name for the system | |
Administrator password | |
SMTP server IP address | |
Events and failures notification email address | |
Primary interface speed | |
Primary interface duplex | |
In-Path Deployments | In-path interface IP address | |
In-path netmask | |
In-path gateway | |
In-path: LAN interface speed | |
In-path: LAN interface duplex | |
In-path: WAN interface speed | |
In-path: WAN interface duplex | |
While running the configuration wizard, you can restart the wizard if you make a mistake. Just enter the configuration jump-start command while in configuration mode. At each prompt, you can press Enter to enter the default value, press ? for help, or press Ctrl+B to return to the previous step.
After you complete the initial configuration, we recommend that you verify that the appliance is properly connected. See
Verifying the appliance connections.Running the initial configuration wizard
1. Plug the serial cable into the Console port and a terminal.
2. Start your terminal emulation program.
3. Log in to the appliance as the default administrator user admin and enter the default password password. The configuration wizard automatically starts.
4. If you have an SCC appliance installed in your network to manage multiple SteelHead appliances, you can use it to automatically configure them. If you answer yes, you are prompted for the SCC host name or IP address. The host name or IP address is used to contact the SCC. The default value is riverbedcmc. If you enter no, the wizard continues.
5. Complete the configuration wizard steps on the client-side and the server-side SteelHeads as described in this table.
Wizard prompt | Description |
Step 1: Host name? | Enter the host name for the SteelHead. |
Step 2: Use DHCP on the primary interface? | You are given the option to enable the DHCP to automatically assign an IP address to the primary interface for the SteelHead. We recommend that you don’t set DHCP. The default value is no. |
Step 3: Primary IP address? | Enter the IP address for the SteelHead. |
Step 4: Netmask? | Enter the netmask address. |
Step 5: Default gateway? | Enter the default gateway for the SteelHead. |
Step 6: Primary DNS server? | Enter the primary DNS server IP address. |
Step 7: Domain name? | Enter the domain name for the network where the SteelHead is to reside. If you set a domain name, you can enter host names in the system without the domain name. |
Step 8: Admin password? | We strongly recommend that you change the default administrator password at this time. The password must be a minimum of six characters. The default administrator password is password. |
Step 9: SMTP server? | Enter the name of the SMTP server. External DNS and external access for SMTP traffic is required for email notification of events and failures to function. Make sure that you provide a valid SMTP server to ensure that the email notifications for events and failures can be sent. |
Step 10: Notification email address? | Enter a valid email address to which notification of events and failures are to be sent. |
Step 11: Set the primary interface speed? | Enter the speed on the primary interface (that is, the SteelHead). Make sure that this value matches the settings on your router or switch. The default value is auto. |
Step 12: Set the primary interface duplex? | Enter the duplex mode on the primary interface. Make sure that this value matches the settings on your router or switch. The default value is auto. |
Step 13: Would you like to activate the in-path configuration? | Enter yes at the system prompt to configure in-path support. An in-path configuration is a configuration in which the SteelHead is in the direct path of the client and server. For detailed information about in-path configurations, see the SteelHead Deployment Guide. |
Step 14: In-Path IP address? | Enter the in-path IP address for the SteelHead. |
Step 15: In-Path Netmask? | Enter the in-path netmask address. |
Step 16: In-Path Default gateway? | Enter the in-path default gateway (the WAN gateway). |
Step 17: Set the in-path: LAN interface speed? | Enter the in-path, LAN interface speed. Make sure that this value matches the settings on your router or switch. The default value is auto. |
Step 18: Set the in-path: LAN interface duplex? | Enter the in-path, LAN duplex value. Make sure that this value matches the settings on your router or switch. The default value is auto. |
Step 19: Set the in-path: WAN interface speed? | Enter the in-path, WAN interface speed. Make sure that this value matches the settings on your router or switch. The default value is auto. |
Step 20: Set the in-path: WAN interface duplex? | Enter the in-path, WAN duplex speed. Make sure that this value matches the setting on your router or switch. The default value is auto. |
6. Press Enter to confirm and save your configuration settings.
7. Enter the exit command to log out of the system.
If you need to restart the wizard, enter these commands:
enable
configure terminal
configuration jump-start
Verifying the appliance connections
1. Check the status lights to verify that the appliance is connected properly.
2. From a remote LAN-side system, connect to the CLI.
ssh admin@<host>.<domain>
–or–
ssh admin@<ip-address>
3. Enter these ping commands to verify the connections:
ping -I <primary-ip-address> <primary-default-gateway>
ping -I <inpath-ip-address> <address-on-lan-side>
ping -I <inpath-ip-address> <address-on-wan-side>
Next steps
After you complete the initial configuration, you can configure the appliance through the Management Console. For details, see the user guide for your product.
You can also use the command-line interface. For details, see the Riverbed Command-Line Interface Reference Manual.



 Attaching the retention fastener
Attaching the retention fastener




