Configuring SRDF optimization
You can enable and modify Symmetrix Remote Data Facility (SRDF) storage module optimization settings in the Optimization > Data Replication: SRDF page.
EMC’s Symmetrix Remote Data Facility/Asynchronous (SRDF/A) is a SAN replication product. It performs the data replication over GigE (instead of the Fibre Channel), using gateways that implement the SRDF protocol.
SRDF storage optimization provides support for environments using storage technology that originates traffic through Symmetrix GigE ports. For details on storage technologies that originate traffic through GigE RE ports, see the SteelHead Deployment Guide.
To increase the data reduction LAN-to-WAN ratio with either equal or greater data throughput in environments with SRDF traffic, RiOS separates the SRDF headers from the application data workload written to storage. The SRDF headers contain changing protocol state information, such as sequence numbers. These headers interrupt the network stream and reduce the ability of scalable data replication (SDR) to match large, contiguous data patterns. After isolating the header data, the SteelHead performs SDR network deduplication on the larger, uninterrupted storage data workload and LZ compression on the headers. RiOS then optimizes, reassembles, and delivers the data to the TCP consumer as originally presented to the SteelHead network.
Traffic originated through Symmetrix GigE ports (RE ports) requires configuration of the RiOS SRDF storage optimization module. Environments with SRDF traffic originated through Symmetrix FC ports (RF ports) require configuration of the RiOS FCIP storage optimization module.
You configure the SRDF storage optimization module on the SteelHead closest to the Symmetrix array that opens the SRDF TCP connection by sending the initial SYN packet. The SteelHead location can vary by environment. If you are unsure which array initiates the SYN, configure SRDF on both the client-side and server-side SteelHeads.
By default, SRDF optimization is disabled.
For details about data replication deployments, see the SteelHead Deployment Guide.
To configure SRDF optimization
1. Choose Optimization > Data Replication: SRDF to display the SRDF page.
SRDF page
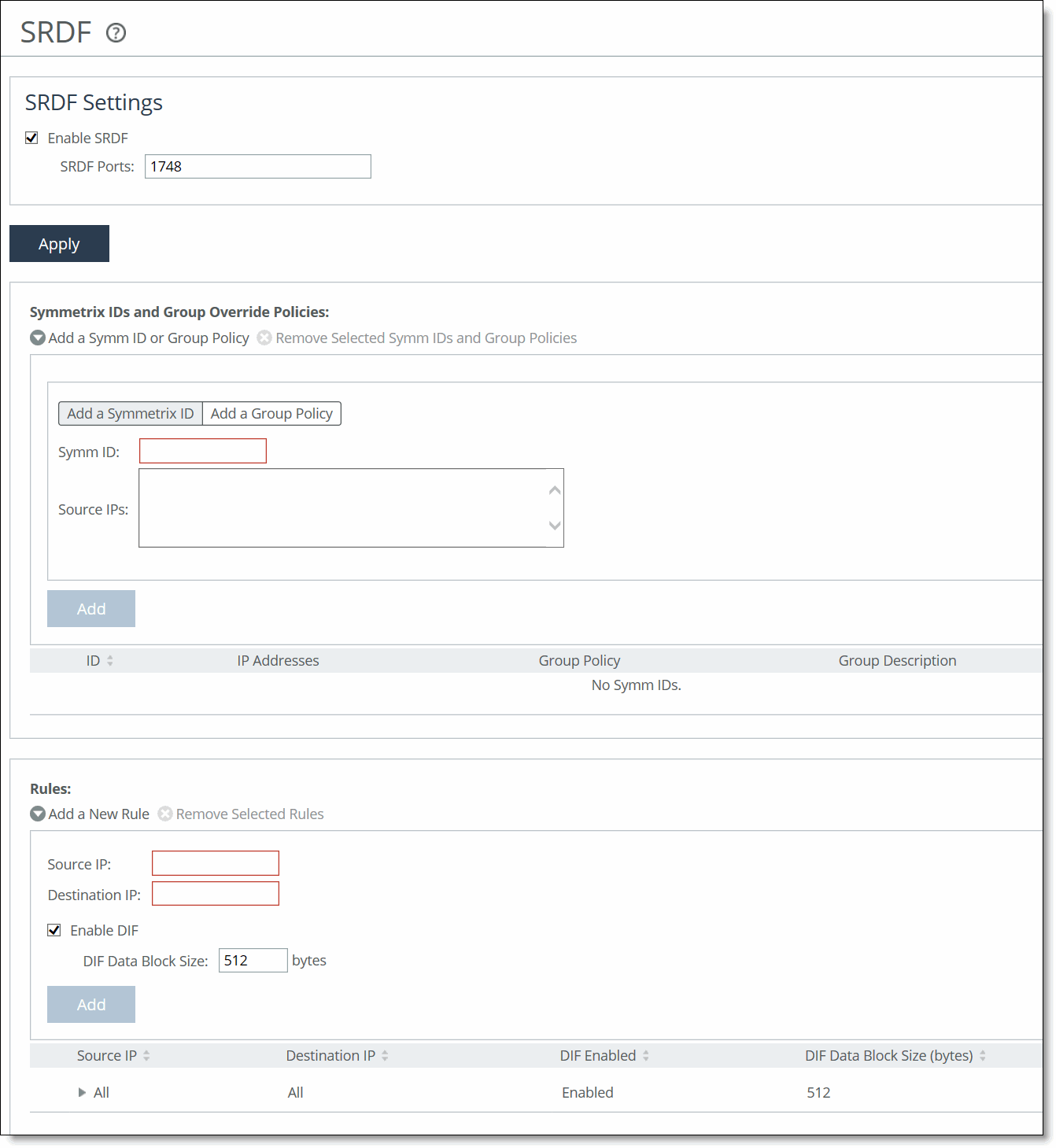
2. Under SRDF Settings, select Enable SRDF. By default, RiOS directs all traffic on the standard port 1748 through the SRDF module for enhanced SRDF header isolation. For most environments, the configuration is complete and you can skip to Step 4.
3. Optionally, specify nonstandard individual SRDF port numbers separated by commas. Do not specify a port range.
The SRDF ports field must always contain at least one port.
4. Click Apply to save your settings to the running configuration.
5. Click Save to Disk to save your settings permanently.
Viewing SRDF connections
After completing the SRDF configuration on both SteelHeads and restarting the optimization service, you can view the SRDF connections in the Current Connections report.
• If the report lists a connection as TCP instead of SRDF, RiOS isn’t optimizing the connection. You must verify the configuration.
• If the report lists a connection as SRDF but a red protocol error icon appears in the Notes column, click the connection to view the reason for the error. A SRDF protocol error can occur when attempting to optimize traffic originating from the LAN side of the SteelHead. Check the LAN-side Symmetrix array for compatibility.
• If a protocol error doesn’t appear next to the SRDF connection on the client-side SteelHead, RiOS is optimizing the connection normally.
Setting a custom data reduction level for an RDF group
This section describes how to apply custom data reduction levels to remote data facility (RDF) groups.
You can base the data reduction level on the compression characteristics of the data associated with an RDF group to provide SRDF selective optimization. Selective optimization enables you to find the best optimization setting for each RDF group, maximizing the SteelHead use. Selective optimization depends on an R1 Symmetrix array running VMAX Enginuity microcode levels newer than 5874.
For example, you can customize the data reduction level for applications associated with an RDF group when excess WAN bandwidth is available and the application data associated with the group isn’t reducible. For applications with reducible data, getting maximum reduction might be more important, requiring a more aggressive data reduction level.
You can configure the optimization level from no compression to full scalable data replication (SDR). SDR optimization is the default, and includes LZ compression on the cold, first-pass of the data. You can also configure LZ-compression alone with no SDR.
Consider an example with these types of data:
• Oracle logs (RDF group 1)
• Encrypted check images (RDF group 2)
• Virtual machine images (RDF group 3)
In this example, you can assign LZ-only compression to the Oracle logs, no optimization to the encrypted check images, and default SDR to the virtual machine images. To assign these levels of optimization, you configure the SteelHead to associate specific RE port IP addresses with specific Symmetrix arrays, and then assign a group policy to specific RDF groups to apply different optimization policies.
The data reduction level within a group policy overrides the current default data reduction setting for the storage resources an RDF group represents. This override is distinct per Symmetrix ID.
To configure a custom data reduction group policy for a Symmetrix ID:
1. Choose Optimization > Data Replication: SRDF to display the SRDF page.
2. Under Symmetrix IDs and Group Override Policies, complete the configuration as described in this table.
Control | Description |
Add a Symm ID or Group Policy | Displays the tabs for adding a Symmetrix ID or group policy. |
Add a Symmetrix ID | Select to display the controls for adding a Symmetrix ID. |
Symm ID | Specify the Symmetrix ID. The Symmetrix ID is an alphanumeric string that can contain hyphens and underscores (for example, a standard Symmetrix serial number is 000194900363). Do not use spaces or special characters. Each Symmetrix ID can have 0 to 254 group override policies. |
Source IPs | Specify the connection source IP address of the Symmetrix DMX or VMAX GigE ports (RE ports) originating the replication. |
Add a Group Policy | Select to display the controls for adding a group policy. |
RDF Group | Specify the RDF group number. Symmetrix arrays that are serving Open Systems hosts and are using EMC Solutions Enabler report RDF group numbers in decimal, ranging from 1 to 255 (this is the RiOS default). Mainframe-attached Symmetrix arrays report RDF group numbers in hexadecimal, ranging from 0 to 254. You can’t add an RDF group until a Symmetrix ID exists. |
Symmetrix ID | Specify an IP address of the Symmetrix DMX or VMAX GigE ports (RE ports) originating the replication. |
Data Reduction Policy | By default, SDR uses the in-path rule data reduction policy. Select one of these data reduction policies from the drop-down list to override the in-path rule data reduction policy: • Default—Performs LZ compression and SDR. • LZ—Performs LZ compression; doesn’t perform SDR. • None—Disables SDR and LZ compression. |
Description | Describe the policy to facilitate administration: for example, Oracle 1 DB. |
Add | Adds the ID or policy to the list. The Management Console redisplays the list and applies your modifications to the running configuration, which is stored in memory. |
Remove Selected | Select the check box next to the name and click Remove Selected. |
Creating SRDF rules (VMAX-to-VMAX traffic only)
Environments with GigE-based (RE port) originated SRDF traffic between VMAX arrays must isolate data integrity field (DIF) headers within the data stream. These DIF headers interrupt the data stream. When the R1 Symmetrix array is running Enginuity microcode version 5875 or newer, manual SRDF rules aren’t necessary. In 5875+ environments, RiOS automatically detects the presence of DIF headers and DIF blocksize for GigE-based (RE port) SRDF traffic. To manually isolate the DIF headers when the R1 Symmetrix array is running Enginuity microcode version 5874 or older, you add SRDF rules by defining a match for source or destination IP traffic.
Automatically detected SRDF settings in Enginuity 5875 and later environments override any manually configured SRDF rules.
SRDF default rule
The default rule optimizes all remaining traffic that has not been selected by another rule. It always appears as the last in the list. You can’t remove the default rule; however, you can change the DIF setting of the default rule. The default rule uses 0.0.0.0 in the source and destination IP address fields, specifying all IP addresses. You can’t specify 0.0.0.0 as the source or destination IP address for any other rule.
To add an SRDF rule
1. Choose Optimization > Data Replication: SRDF to display the SRDF page.
2. Under Rules, complete the configuration as described in this table.
Control | Description |
Add a New Rule | Displays the controls for adding a manual rule. Use this control when the R1 Symmetrix array is running Enginuity microcode version 5874 or earlier. |
Source IP | Specify the connection source IP address of the Symmetrix DMX or VMAX GigE ports (RE ports) originating the replication. The source IP address can’t be the same as the destination IP address. |
Destination IP | Specify the connection destination IP address of the Symmetrix DMX or VMAX GigE ports (RE ports) receiving the replication. |
Enable DIF | Isolates and optimizes the Data Integrity Fields embedded within the SRDF data workload. |
DIF Data Block Size | Specify the size of a standard block of storage data, in bytes, after which a DIF header begins. The valid range is from 1 to 2048 bytes. The default value is 512, which is a standard block size for Open System environments. When you enable DIF, RiOS SRDF optimization looks for a DIF header after every 512 bytes of storage data unless you change the default setting. Open System environments (such as Windows, UNIX, and Linux) inject the DIF header into the data stream after every 512 bytes of storage data. IBM iSeries (AS/400) host environments inject the DIF header into the data stream after every 520 bytes. Do not add a manual rule isolating DIF headers in mainframe environments, as SRDF environments that replicate mainframe traffic don’t currently include DIF headers. This field is required when you enable DIF. |
Add | Adds the manual rule to the list. The Management Console redisplays the Rules table and applies your modifications to the running configuration, which is stored in memory. |
Remove Selected | Select the check box next to the name and click Remove Selected. |
Move Selected | Moves the selected rules. Click the arrow next to the desired rule position; the rule moves to the new position. |
3. Click Apply to save your settings to the running configuration.
4. Click Save to Disk to save your settings permanently.
To edit an SRDF rule
1. Choose Optimization > Data Replication: SRDF to display the SRDF page.
2. Select the rule number in the rule list.
3. Edit the rule.
4. Click Save to Disk to save your settings permanently.
Related topics


