Configuring Lotus Notes optimization
You can enable and modify Lotus Notes optimization settings in the Optimization > Protocols: Lotus Notes page.
Lotus Notes is a client/server collaborative application that provides email, instant messaging, calendar, resource, and file sharing. RiOS provides latency and bandwidth optimization for Lotus Notes 6.0 and later traffic across the WAN, accelerating email attachment transfers and server-to-server or client-to-server replications.
RiOS saves bandwidth by automatically disabling socket compression, which makes SDR more effective. It also saves bandwidth by decompressing Huffman-compressed attachments and LZ-compressed attachments when they’re sent or received and recompressing them on the other side. Lotus Notes optimization allows SDR to recognize attachments that have previously been sent in other ways (such as over CIFS, HTTP, or other protocols), and also allows SDR to optimize the sending and receiving of attachments that are slightly changed from previous sends and receives.
Enabling Lotus Notes provides latency optimization regardless of the compression type (Huffman, LZ, or none).
Before enabling Lotus Notes optimization, be aware that it automatically disables socket-level compression for connections going through SteelHeads that have this feature enabled.
For appliances with feature-tier licensing, you can configure and enable Lotus Notes optimization even if the feature is not licensed; however, the feature needs to be both enabled and licensed to work. If the feature is not licensed, the interface displays an alert. For more information, see
Feature-tier licensing.To configure Lotus Notes optimization
1. Choose Optimization > Protocols: Lotus Notes to display the Lotus Notes page.
Lotus Notes page
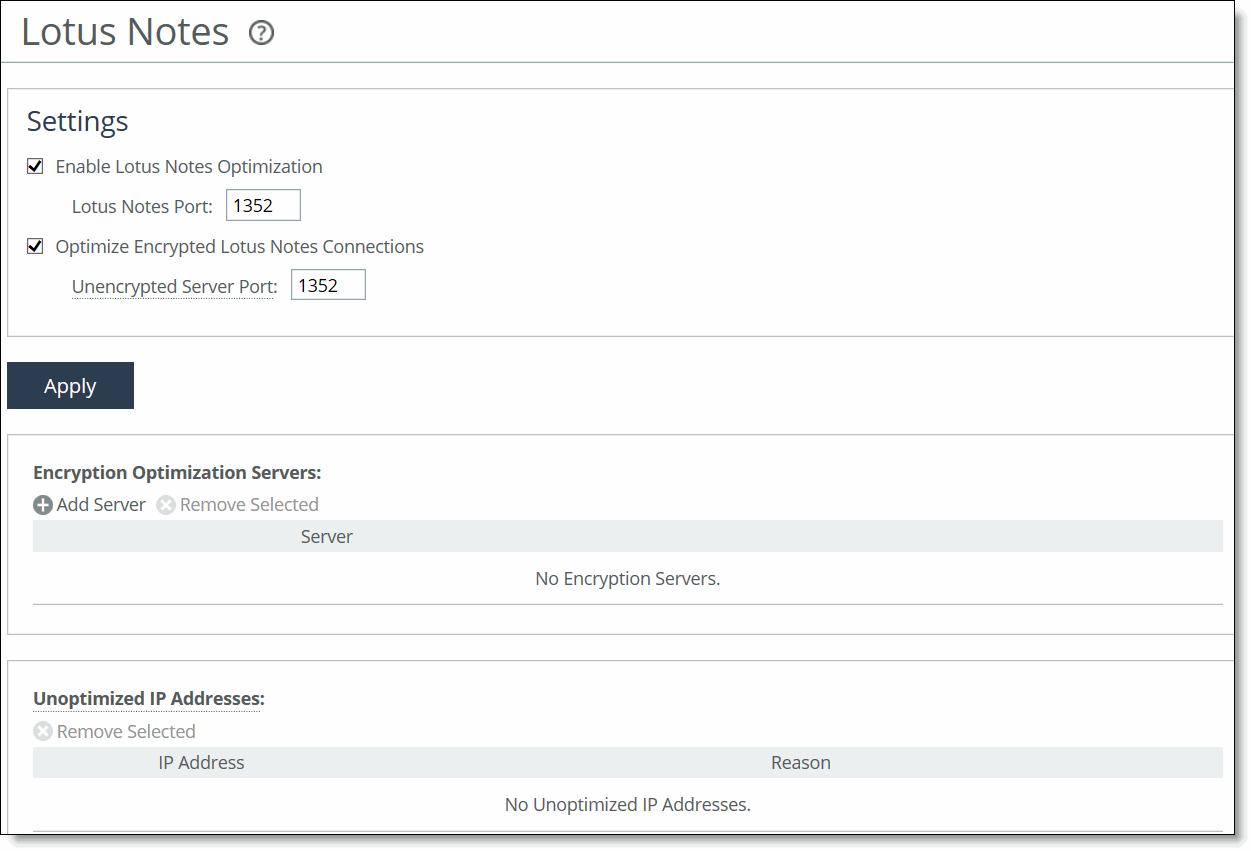
2. Under Settings, complete the configuration as described in this table.
Control | Description |
Enable Lotus Notes Optimization | Enable this control on the client-side SteelHead to provide latency and bandwidth optimization for Lotus Notes 6.0 and later traffic across the WAN. This feature accelerates email attachment transfers and server-to-server or client-to-server replications. By default, Lotus Notes optimization is disabled. |
Lotus Notes Port | On the server-side SteelHead, specify the Lotus Notes port for optimization. Typically, you don’t need to modify the default value 1352. |
Optimize Encrypted Lotus Notes Connections | Enables Lotus Notes optimization for connections that are encrypted. By default, encrypted Lotus Notes optimization is disabled. Perform these steps: 1. Configure an alternate unencrypted port on the Domino server to accept unencrypted connections in addition to accepting connections on the standard TCP port 1352. For details, see
Configuring an alternate port. If the standard port isn’t configured to require encryption, you can use it instead of configuring an alternate port. 2. Select the Optimize Encrypted Lotus Notes Connections check box on both the client-side and server-side SteelHeads. 3. Specify the alternate unencrypted port number on the server-side SteelHead. 4. Click Apply on both the client-side and server-side SteelHeads. 5. Import the ID files of the servers for which you want to optimize the connections on the server-side SteelHead. 6. Under Encryption Optimization Servers, choose Add Server. Either browse to a local file or specify the server ID filename to upload from a URL. Specify the password for the ID file in the password field. If the ID file has no password, leave this field blank. Click Add. The server ID file is usually located in C:\Program Files\IBM\Lotus\Domino\data on Windows servers. 7. (Optional, but recommended unless another WAN encryption mechanism is in use) Enable secure peering to create a secure inner channel between the client-side and server-side SteelHeads. 8. Click Save to Disk on both the client-side and server-side SteelHeads. 9. Restart the optimization service on both the client-side and server-side SteelHeads. After the connection is authenticated, the server-side SteelHead resets the connection of the Notes client, but maintains the unencrypted connection with the Domino server on the auxiliary port. The Notes client now tries to establish a new encrypted connection, which the server-side SteelHead intercepts and handles as if it were the Domino server. The server-side SteelHead (acting as the Domino server) generates the necessary information used to encrypt the connection to the Notes client. The result is an encrypted connection between the Notes client and server-side SteelHead. The connection is unencrypted between the server-side SteelHead and the Domino server. |
Unencrypted Server Port | Specify the alternate unencrypted port number on the server-side SteelHead. You must preconfigure this port on the Domino server. If the standard port (typically 1352) doesn’t require encryption, you can enter the standard port number. |
10. Click Apply to apply your settings to the running configuration.
11. Click Save to Disk to save your settings permanently.
Encryption Optimization Servers table
The Encryption Optimization Servers table displays all of the servers for which server ID files were imported and optimization of encrypted connections is occurring.
If the secure vault is locked, this table doesn’t appear. Instead, a dialog box asks you to unlock the secure vault. After you type the password to unlock the secure vault, the Encrypted Optimization Server table appears.
A successful connection appears as NOTES-ENCRYPT in the Current Connections report.
Unoptimized IP address table
New connections to or from an IP address on this list don’t receive Lotus Notes encryption optimization.
If RiOS encounters a problem during client authentication that prevents the SteelHead from optimizing the encrypted traffic, it must drop the connection, because in the partially authenticated session the client expects encryption but the server doesn’t. (Note that the client transparently tries to reconnect with the server after the connection drops.) Whenever there’s a risk that the problem might reoccur when the client reconnects, the client IP address or server IP address or both appear on the unoptimized IP address table on the server-side SteelHead. The system disables Lotus Notes encryption optimization in future connections to or from these IP addresses, which in turn prevents the SteelHead from repeatedly dropping connections, which could block the client from ever connecting to the server.
The Unoptimized IP Address table displays the reason that the client or server isn’t receiving Lotus Notes encrypted optimization.
Configuring an alternate port
This section explains how to configure a Domino server to accept unencrypted connections on an alternative TCP port in addition to accepting connections on the standard TCP port 1352.
To configure a Domino server to accept unencrypted connections on an alternative TCP port
1. Open Domino Administrator and connect to the Domino server that you want to configure.
2. Choose Configuration > Server > Setup Ports to display the Setup Ports dialog box.
3. Click New.
4. Type a port name: for example, TCPIP_RVBD. Then select TCP in the Driver drop-down box and click OK.
5. Select the new port in the Setup Ports dialog box.
6. Ensure that Port enabled is selected and that Encrypt network data is cleared, and click OK.
7. Locate and open the Domino server’s notes.ini file.
8. Add a line of the format <port-name>_TCPIPAddress=0,<ip-address>:<port>. Use the IP address 0.0.0.0 to have Domino listen on all server IP addresses.
9. To start the server listening on the new port, restart the port or restart the server.


