Figure: Configuring Legacy Path Selection Rules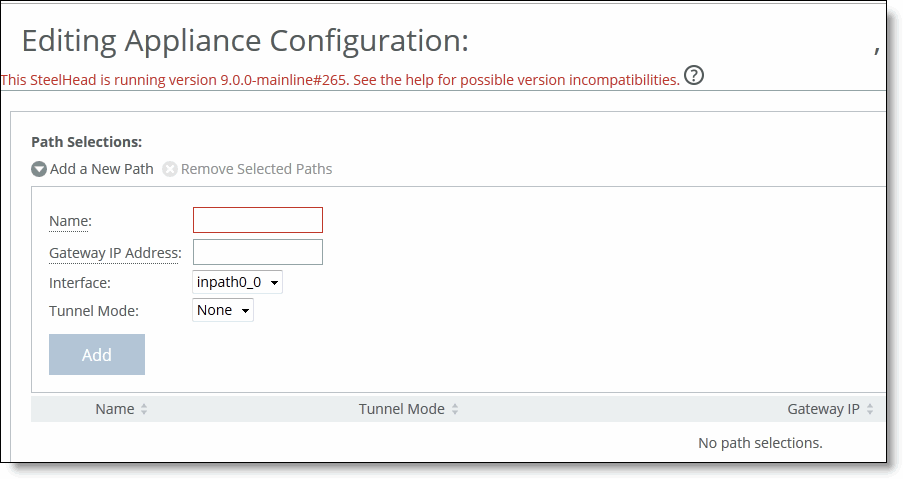


Control | Description |
Name | Specify the path selection name. Note: The path selection name is case sensitive and must match the path name in the policy being pushed to this appliance. If the names do not match, policy push will fail. |
Gateway IP Address | Specify the IP address for the gateway. The gateway must be in the same network as the in-path interface. Note: The gateway IP address must be in the same subnet (local network) as the in-path interface. |
Interface | Select a relay interface over which the appliance reaches the path. |
Tunnel Mode | Select the tunnel mode from the drop-down list: None or GRE. GRE provides IPv4 generic routing encapsulation (GRE) for direct uplinks. Direct uplinks using GRE become direct tunneled uplinks. You must create direct tunneled uplinks to steer traffic over any uplink that traverses a stateful firewall between the SteelHeads. Without GRE, traffic attempting to switch midstream to an uplink that traverses a stateful firewall might be blocked. The firewall needs to track the TCP connection state and sequence numbers for security reasons. Because the firewall has not logged the initial connection handshake, and has partial or no packet sequence numbers, it blocks the attempt to switch to the secondary uplink and might drop these packets. To traverse the firewall, path selection can encapsulate that traffic into a GRE tunnel. |
Add | Adds the path to the path table. The SCC redisplays the path table and applies your changes to the running configuration, that is stored in memory. |
Remove Selected | Select the check box next to the name and click Remove Selected. |