Inbound QoS
This section explains how Riverbed inbound QoS works and how you configure it. It includes the following topics:
Introduction to Inbound QoSAssigning an Inbound QoS Profile to a SiteThis section requires that you be familiar with
QoS Concepts.
Introduction to Inbound QoS
Inbound QoS enables you to allocate bandwidth and prioritize traffic flowing from the WAN into the LAN network behind the SteelHead. This configuration provides the benefits of QoS for environments that cannot meet their QoS requirements with only outbound QoS.
Reasons to configure inbound QoS include the following:
Many business applications, such as VoIP and desktop video conferencing, now run over any-to-any mesh topologies.The traffic generated by these applications typically travels directly from one branch office to another; for example, if a user in Branch Office A calls a user in Branch Office B, the VoIP call is routed directly, without having to traverse the data center. This traffic might compete with other traffic that is coming from the data center, or from other sites, but it bypasses any QoS that is deployed at those sites. As a result, there is no network location from which you can use outbound QoS to control all incoming traffic going to Branch Office B. The only place where you can control all incoming traffic is at the branch itself. You can use inbound QoS at Branch Office B to guarantee bandwidth for critical applications and slow down traffic from other, less critical applications.
Software as a Service (SaaS) applications and public cloud services that are accessed over the Internet.These applications compete with recreational Internet traffic for bandwidth at the branch office. When users watch online videos or browse social networking sites, business applications can struggle to get the resources they need. With inbound QoS, you can ensure that business applications have enough room to get through.
Inbound QoS is used the same way as outbound QoS—to prioritize traffic from sites and types of traffic using rules and classes. You define the applications on the local SteelHead and then create a QoS profile corresponding to the shaping and prioritization policies.
For information about how to configure inbound QoS, see the SteelHead Management Console User’s Guide.
Inbound QoS applies the HFSC shaping policies to the ingress traffic. This addresses environments in which bandwidth constraints exist at the downstream location. When this occurs, the downstream SteelHead (where inbound QoS is enabled) dynamically communicates the bandwidth constraints to the client transmitting the traffic. The client slows down the throughput and the traffic adheres to the configured inbound QoS rule. Inbound QoS, just like outbound QoS, is not a dual ended SteelHead solution. A single SteelHead can control inbound WAN traffic on its own.
For information about the HFSC queueing technology, see
Overview of Riverbed QoS and the
SteelHead Management Console User’s Guide.
Unlike earlier RiOS versions, RiOS v9.0 allows for applying inbound QoS per site (hierarchical inbound).
Assigning an Inbound QoS Profile to a Site
You configure an inbound QoS profile the same way as an outbound QoS profile. Assigning an inbound QoS profile to a site requires you to think backwards. For example, you want to restrict certain traffic coming into the data center. When you configure the SteelHead that is located in the data center for inbound QoS, you need to assign a QoS profile to that site. Do not assign a QoS profile for inbound QoS to the data center SteelHead.
To assign a QoS profiles for inbound QoS to a site
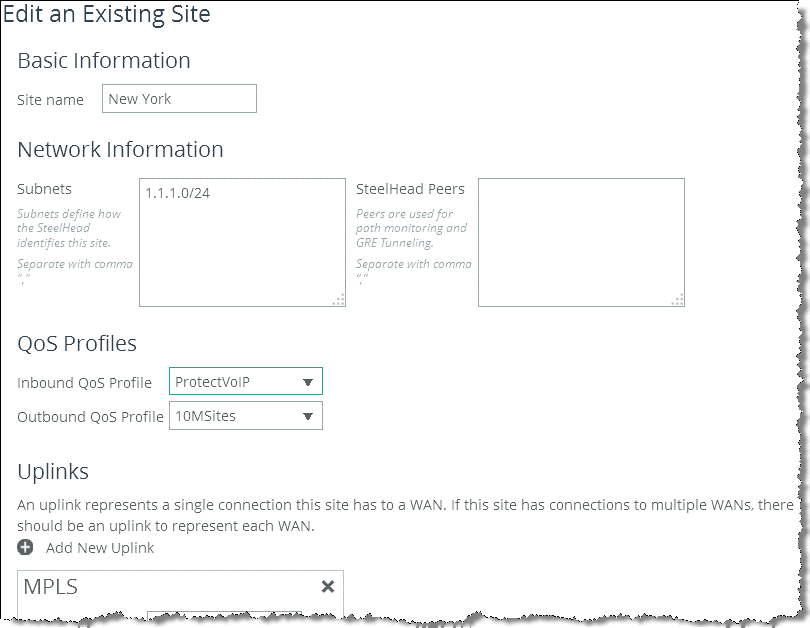
Choose go to Networking > Topology: Sites & Networks.
Click Edit Site in the Sites section.
In the QoS Profiles section of the configuration page, open the Inbound QoS Profile drop-down menu and select the profile for this site (
Figure 6‑11).
Figure 6‑11. Edit an Existing Site