Managing SteelHeads
This chapter describes tasks you perform for routine management of the SteelHead. It includes these topics:
Starting and stopping the optimization service
You can start, stop, and restart the optimization service in the Administration > Maintenance: Services page. You can also use this page to reset the optimization service alarm after it has been triggered.
The optimization service is a daemon that executes in the background, performing operations when required.
Many of the optimization service commands are initiated at startup. It is important to restart the optimization service when you have made changes to your configuration.
Restarting the optimization service disrupts existing network connections that are proxied through the SteelHead.
To start, stop, or restart services
1. Choose Administration > Maintenance: Services to display the Services page.
2. Under Optimization Service click Stop, Start, or Restart.
3. Click Save to Disk to save your settings permanently.
To reset the optimization service alarm
1. Choose Administration > Maintenance: Services to display the Services page. The option to reset the optimization service alarm appears only after RiOS triggers the Reset Service alarm.
2. Under Reset Service alarm, click Reset Service alarm.
3. Click Save to Disk to save your settings permanently.
Configuring scheduled jobs
You can view completed, pending, inactive jobs, as well as jobs that were not completed because of an error in the Administration > Maintenance: Scheduled Jobs page. You can also delete a job, change its status, or modify its properties.
Jobs are commands that are scheduled to execute at a time you specify.
You can use the Management Console to:
•schedule an appliance reboot or shut down.
•generate multiple TCP trace dumps on a specific date and time.
To schedule all other jobs, you must use the Riverbed CLI.
For details about scheduling jobs using the CLI, see the Riverbed Command-Line Interface Reference Manual.
To configure scheduled jobs
1. Choose Administration > Maintenance: Scheduled Jobs to display the Scheduled Jobs page.
2. Select Enabled or Disabled from the drop-down list to enable or disable the job.
3. Select the Job ID number to display details about the job.
4. Under Details for Job <#>, complete the configuration as described in this table.
Control | Description |
Name | Specify a name for the job. |
Comment | Specify a comment. |
Interval (seconds) | Specify the number of seconds between job recurrences. Specify 0 to run the job one-time only. |
Executes on | Specify the start time and end time using the format YYYY/MM/DD HH:MM:SS. |
Enable/Disable Job | Select the check box to enable the job, clear the check box to disable the job. |
Interval (seconds) | Specify how often the job runs. The default value is 0, which runs the job once. |
Executes On | Specify the date on which the job runs. |
Enable/Disable Job | Select to enable the job to run at the specified date or clear to prevent the job from running. |
Apply Changes | Applies the changes to the current configuration. |
Cancel/Remove This Job | Cancels and removes the job. |
Execute Now | Runs the job. |
Remove Selected Jobs | Select the check box next to the name and click Remove Selected Jobs. |
5. Click Save to Disk to save your settings permanently.
Upgrading your software
You can upgrade or revert to a backup version of the software in the Administration > Maintenance: Software Upgrade page.
The bottom of the page displays the software version history of the SteelHead, which includes the version number and the software installation date.
To find allowed upgrades between RiOS versions and recommended upgrade paths, use the Software Upgrade tool on the Riverbed Support Site at. The tool includes all of the recommended intermediate RiOS versions.


You can upgrade software on the ESX SteelHead-c and the SteelHead (virtual edition) appliance using this procedure. To upgrade the software on the AWS SteelHead-c, use the Riverbed Cloud Portal. For details, see the
SteelHead (in the Cloud) User Guide.
Verifying your software image
Before you install a software upgrade, you can verify the integrity and authenticity of the software image and ensure it is an unmodified and approved Riverbed image. The feature requires a public key in a certificate to verify the digital signature of the software image. The certificate is automatically installed on the SteelHead, but you can import an updated version, if needed.
You can download the public key for Riverbed images from KB article
S33657.
During the verification process, the appliance compares the signature in the image with the Riverbed public certificate. If they match, the installation continues. If not, the system alerts you to a potential problem. As long as image signature verification is enabled, you cannot continue with an installation that cannot verify the image signature.
By default, image signature verification is on and should be disabled only when necessary. Riverbed recommends keeping the feature enabled at all times.
To enable software image verification
1. Choose Administration > Maintenance: Software Upgrade to display the Software Upgrade page.
2. Under Image Signature Verification, select Image Signature Verification.
If you clear the Image Signing Verification check box, you disable this feature and a warning message appears indicating images will not be verified.
3. Expand the Image Signing Certificate section and ensure the appliance has a valid certificate.
You can use the certificate that is installed by default or you can click the Import tab to replace an expired or revoked certificate. You can upload a PKCS-12, PEM, or DER format certificate or paste a PEM certificate. Click Import Image Signing Certificate to add the certificate to this appliance.
You can only use one certificate. The certificate information appears in the Details tab.
4. Click Apply.
5. Click Save to Disk to save your settings permanently.
Upgrading or reverting your software version
You can upgrade your software or revert to a backup version.
To upgrade the software
1. Download the software image from the Riverbed Support site to a location such as your desktop.
Optionally, you can download a delta image directly from the Riverbed Support site to the SteelHead. The downloaded image includes only the incremental changes. The smaller file size means a faster download and less load on the network. To download a delta image, skip to Step 2.
2. Choose Administration > Maintenance: Software Upgrade to display the Software Upgrade page.
3. Under Install Upgrade, complete the configuration as described in this table.
Control | Description |
From URL | Select this option and specify the URL. Use one of the following formats: http://host/path/to/file
https://host/path/to/file
ftp://user:password@host/path/to/file
scp://user:password@host/path/to/file |
From Riverbed Support Site | Select this option and select the target release number from the drop-down list. The system uploads and installs the new image immediately after you click Install. To upload and install the image later, schedule another date or time before you click Install. |
From Local File | Select this option and specify the path, or click Browse to go to the local file directory. If you specify a file to upload in the Local File text box, the image is uploaded immediately; however, the image is installed and the system is rebooted at the time you specify. |
Schedule Upgrade for Later | Schedules the upgrade process. Specify the date and time to run the upgrade: yyyy/mm/dd, hh:mm:ss. |
Install | Click to install the software upgrade on your system, unless you schedule it for later. The software image can be quite large; uploading the image to the appliance and installing it can take a few minutes. Downloading a delta image directly from the Riverbed Support site is faster because the downloaded image includes only the incremental changes. As the upgrade progresses, status messages appear. After the installation is complete, the system reminds you to reboot the appliance to switch to the new version of the software. |
Cancel | Cancels your changes. |
4. Choose Administration > Maintenance: Reboot/Shutdown and click Reboot.
The appliance can take a few minutes to reboot. This behavior is normal because the software is configuring the recovery flash device. Do not press Ctrl+C, unplug, or otherwise shut down the system during this first boot. There is no indication displayed during the system boot that the recovery flash device is being configured.
After the reboot, the Dashboard, Software Upgrade, and Help pages of the Management Console display the RiOS version upgrade.
To revert the RiOS version
1. Choose Administration > Maintenance: Software Upgrade to display the Software Upgrade page.
2. Under Software Upgrade, complete the configuration as described in this table.
Control | Description |
Switch to Backup Version | Switches to the backup version on the next reboot. |
Cancel | Cancels the software version switch on the next reboot. |
Related topic
Rebooting and shutting down the SteelHead
You can reboot or shut down the system in the Administration > Maintenance: Reboot/Shutdown page.
Rebooting the system disrupts existing network connections that are currently proxied through it. Rebooting can take a few minutes.
When you shut down the system, connections are broken and optimization ceases. Shutting down the appliance can take a few minutes.
To restart the system, you must manually power on the SteelHead.
To reboot or shut down the system
1. Choose Administration > Maintenance: Reboot/Shutdown to display the Reboot/Shutdown page.
2. To clear the RiOS data store of data, select the Clear Data Store check box. Clearing the data store degrades performance until the system repopulates the data.
3. Click Reboot. After you click Reboot, you are logged out of the system and RiOS reboots.
4. Click Shut Down to shut down the system. After you click Shut Down, the system is powered down. To restart the system, you must manually power on the SteelHead.
To schedule a reboot
1. Choose Administration > Maintenance: Reboot/Shutdown to display the Reboot/Shutdown page.
2. Select Schedule for Later and enter the date and time you would like the reboot to occur.
The reboot executes at the scheduled time.
Managing licenses and model upgrades
This section describes how to install, update, and remove a license. It also describes how to use flexible licensing to manage configurations and upgrades. This section includes these topics:
You perform all license management and SteelHead model upgrades in the Appliance > Licenses page.
SteelHead licenses can be permanent or temporary. Permanent licenses don’t display an expiration date in their Status column on the Licenses page; temporary licenses display an expiration date in their Status column. For example, evaluation licenses typically expire in 60 days and display a date within that range.
The system warns you two weeks before a license expires with the Expiring License alarm. After a license expires, the system warns with an Expired License alarm. You can add a license to extend the functionality of an expiring licenses. If multiple licenses exist for a feature, the system uses the license with the latest expiration date.
Flexible licensing overview
RiOS provides a flexible way to manage SteelHead licenses, model configurations, feature capabilities, and upgrades. Depending on the model of SteelHead, you follow one of these flexible licensing approaches:
•Feature-tier licensing, available only on SteelHead CX580, CX780, and CX3080 models, provides license tiers that define the available features. For details, see
Feature-tier licensing.
•Specification licensing, for all other SteelHead appliances, provides a license to define the appliance specifications, such as bandwidth capacity and number of optimized connections. For details, see
Specification licensing.
Feature-tier licensing
Feature-tier licensing is only available on SteelHead CX580, CX780, and CX3080 appliances.
Feature-tier licensing determines SteelHead appliance capabilities by feature categories. This licensing model provides three licensing tiers: Essentials, Standard, and Enterprise. The following table lists the features in each license tier.
Essentials | Standard | Enterprise |
•Scalable Data Referencing (SDR) optimization •Full LZ compression •Basic TCP optimization - transport optimizations (dual and single-ended, buffer settings, standard, HS-TCP, and bandwidth estimation) •MX-TCP and rate pacing •Hybrid networking (QoS, path-selection, secure transport) •IPSec peering •All network integration features (autodiscovery, network transparency, virtual in-path, WCCP/PBR, serial failover, parallel SteelHead with connection forwarding, host/port/domain labels) •Packet mode optimization (UDP) •IPv6 •DNS caching •HTTP prepopulation | All features in the Essentials tier plus: •Windows file server (SMB/CIFS) optimization •CIFS prepopulation •HTTP optimization (including SharePoint, WTA, UID, video caching, video stream splitting) •HTTPS •SSL/enhanced cryptography optimization •Web proxy (file caching, video caching, video stream splitting) •Microsoft Exchange (MAPI) optimization •SaaS Accelerator support •Legacy Cloud Accelerator (SCA) support •NetFlow export | All features in the Standard tier plus: •NFS optimization •Data replication (FCIP, SRDF, SnapMirror) •SCPS optimization •Federal Information Processing Standard (FIPS) •Lotus Notes protocol optimization •Citrix protocol optimization •Oracle Forms protocol optimization |
With feature-tier licensing, all license categories get the same specified number of connections and bandwidth capacity. The amount doesn’t change between licenses. (See the SteelHead Family Specification Sheet for these limits for your appliance.)
Although none of the feature tiers has differing bandwidth limits, service providers can continue to purchase a license to limit bandwidth.
You can upgrade from Essentials to Standard and from Standard to Enterprise. For details, see
Upgrading an appliance feature tier.
With feature-tier licensing, you can configure some functionality even if it is not licensed, but you cannot use that functionality until it is both licensed and enabled. Features and protocols that are not licensed display an alert on their configuration page in the user interface.
Any connections configured to use unlicensed capabilities will be passed through.
Licensing interoperability
Feature-tier licensing only ships with SteelHead models CX580, CX780, and CX3080. All other appliances maintain their existing licensing when communicating with feature-tier licensed appliances.
Dual-ended capabilities require a valid license at both peers and when two systems pair from different feature tiers or from different licensing models, only the smaller subset of features is allowed. For example, an Essentials client cannot optimize SMB/CIFS traffic, even if the server-side appliance has an Enterprise license. The opposite is true as well: If an Enterprise client communicates with an Essentials tier, only features in the Essentials tier will work.
SteelHead models that have specification licensing include the features in the Enterprise feature-license tier except SCPS and FIPS that each require a separate license on x70 and xx70 appliances. For details, see
Feature-tier licensing and the SCPS and FIPS documentation.
SaaS Accelerator and Legacy Cloud Accelerator require additional licenses, but the licenses are not installed on the SteelHead; they are installed on the SteelConnect Manager (for SaaS Accelerator) and Riverbed Cloud Portal (for Legacy Cloud Accelerator). In addition, SteelHead models CX580, CX780, and CX3080 require the Standard license tier or higher to accelerate SaaS traffic.
Specification licensing
RiOS provides specification licenses that configure specific performance characteristics of an appliance, such as bandwidth capacity and number of optimized connections. A specification license points to a specific, validated model and includes the required license and the hardware specification.
By activating a specification license on an appliance, you can transform the capabilities of the appliance to meet performance characteristics for any model within a platform family.
If a model upgrade requires additional hardware, the specification license determines which hardware is necessary to complete the upgrade. To upgrade, order a hardware kit that contains the additional hardware from Riverbed Support or Sales. For more information, see the Upgrade and Maintenance Guide.
SteelHead models that have specification licensing include the features in the Enterprise feature-license tier except SCPS and FIPS that each require a separate license on x70 and xx70 appliances. For details, see
Feature-tier licensing and the SCPS and FIPS documentation.
This table shows the appliances with specification licensing and their upgrade possibilities.
Source model | Destination model | Upgrade requirements | Minimum software version | Impact on data store | Impact on configuration | Reboot required |
CX255U | CX255L | License only | RiOS 8.0.3a,
8.5.0 | None | None | No |
CX255U | CX255M | License only | RiOS 8.0.3a,
8.5.0 | None | None | No |
CX255U | CX255H | License only | RiOS 8.0.3a,
8.5.0 | None | None | No |
CX255L | CX255M | License only | RiOS 8.0.3a,
8.5.0 | None | None | No |
CX255L | CX255H | License only | RiOS 8.0.3a,
8.5.0 | None | None | No |
CX255M | CX255H | License only | RiOS 8.0.3a,
8.5.0 | None | None | No |
CX570L | CX570M | License only | RiOS 8.0.6,
8.5.3, 8.6.1 | None | None | No |
CX570L | CX570H | License only | RiOS 8.0.6,
8.5.3, 8.6.1 | None | None | No |
CX570M | CX570H | License only | RiOS 8.0.6,
8.5.3, 8.6.1 | None | None | No |
CX770L | CX770M | License only | RiOS 8.0.6,
8.5.3, 8.6.1 | None | None | No |
CX770L | CX770H | License only | RiOS 8.0.6,
8.5.3, 8.6.1 | None | None | No |
CX770M | CX770H | License only | RiOS 8.0.6,
8.5.3, 8.6.1 | None | None | No |
CX3070L | CX3070M | License only | RiOS 8.6.2,
9.0.0a | None | None | No |
CX3070M | CX3070H | License only | RiOS 8.6.2,
9.0.0a | None | None | No |
CX5070M | CX5070H | License only | RiOS 8.6.2,
9.0.0a | None | None | No |
CX5080M | CX5080H | License only | 9.9.0 | None | None | No |
The CX7070 and CX7080 appliances don’t provide a model upgrade through a license. To upgrade these appliances, you need to exchange the appliance. During this upgrade, there is no data store migration. For more information about this upgrade, contact the Riverbed Sales Operations team.
For details about hardware specifications that require hardware upgrades, see the Upgrade and Maintenance Guide.
For more information
This table describes where to find more information on flexible licensing tasks.
Task | See |
Get a license and hardware kit. | Riverbed Support or Sales |
Install a license. | |
Update an expired license. | |
Remove a license. | |
Upgrade an appliance feature tier. | |
Upgrade an appliance model. | |
Although the types of flexible licenses differ between models, you follow the same steps to install, update, and remove licenses.
Installing a license
This section describes how to request a license from the Riverbed license portal or install a license manually after receiving it from Riverbed Support or Sales.
To install a license on a new SteelHead
•Connect a new SteelHead to the network.
The SteelHead automatically contacts the Riverbed license portal and downloads the licenses. The Licensing page displays a success message or the Alarm Status page reports an actionable error message.
After installing most new licenses, you must restart the optimization service. Consult the feature description for details.
To replace expired licenses
•Purchase new downloadable licenses to replace the expired license.
At the time of the next scheduled automatic license fetch, the SteelHead automatically contacts the Riverbed license portal and downloads the new licenses. The Licensing page displays a success message or the alarm Status page reports an actionable error message.
To fetch a license on demand
1. Choose Administration > Maintenance: Licenses to display the Licenses page.
2. Click Refresh Licenses.
On older appliances, the button is named Fetch Updates Now.
If you are upgrading licenses between feature tiers, for example moving from the Standard to the Enterprise tier, you need to stop the optimization service, refresh the license, and then restart the optimization service. For details, see
Upgrading an appliance feature tier.
The Licensing page displays a success message or the alarm Status page reports an actionable error message.
To manually obtain a license
2. Enter your appliance serial number or your unique product identifier.
The licensing portal requires a unique product identifier to retrieve a license. Depending on the product, the identifier can be a serial number, a license request key (activation code), or a token.
The serial number is on a label located on your appliance and it also appears in the Support tab of the Management Console.
3. Click Next.
4. Provide the contact information for the license, including your name and email.
5. Click Submit.
The Licensing Portal displays license information for all the products purchased with the serial number you specified.
6. Click a serial number to see license details.
7. Optionally, if you are behind a firewall, type the email address in the Email address text box and click Email Keys to have the license keys emailed to you.
8. Optionally, if you are behind a firewall, click Download XML to download an XML file. The XML file can be imported by the SteelCentral Controller for SteelHead.
To install a license
1. Choose Administration > Maintenance: Licenses to display the Licenses page.
The Licenses page includes a table of licenses with a column showing the date and time the license was installed and the approximate relative time it was installed. The next column shows whether the installation was done manually or automatically.
The names and positions of the buttons differ slightly on the Licenses page between x80/xx80 models and xx70/x70/x55 models.
2. Complete the configuration as described in this table.
Control | Description |
Add License | Displays the controls to add a new license. |
Licenses Text Box | Copy and paste the license key provided by Riverbed Support or Sales into the text box. Separate multiple license keys with a space, Tab, or Enter. |
Add | Adds the license. |
Refresh Licenses/Fetch Updates Now | Contacts the Riverbed license portal and downloads all applicable licenses for the SteelHead. |
3. Click Save to Disk to save your settings permanently.

If the Customer Key field displays on this page, you have a SteelHead-v model that uses a customer key. To register these models, enter your customer key and click
Set Customer Key. For details, see the
SteelHead (Virtual Edition) Installation Guide.
Upgrading an appliance feature tier
For appliances with feature-tier licensing, you can upgrade from Essentials to Standard and from Standard to Enterprise. This section describes how to upgrade an appliance feature tier.
To upgrade an appliance feature tier
1. Stop the optimization service.
2. Choose Administration > Maintenance: Licenses to display the Licenses page.
3. Install the new feature-tier license.
Or click
Refresh to retrieve the license from the Riverbed license server. For details, see
Installing a license.
4. Optionally, delete the previous feature-tier license.
For details, see
Removing a license. You can keep both licenses on the appliance without any problems: the interface simply lists both licenses and uses the higher license.
5. Restart the optimization service.
When the upgrade is installed, the new feature set is available.
Upgrading an appliance model
You can use a hardware specification license to upgrade some SteelHead models. Some model upgrades require additional hardware. When the appliance has the required hardware, activating the hardware specification upgrades the appliance to the new model number. When the existing hardware isn’t adequate, a hardware required message appears after the hardware specification description.
This section describes how to upgrade an appliance model.
To upgrade an appliance model
1. Install the upgrade license.
2. Stop the optimization service.
3. Choose Administration > Maintenance: Licenses to display the Licenses page.
The hardware model specifications appear at the bottom of the page. The current specification appears in bold.
4. Select the model specification you want to activate.
If a model specification requires an appliance reboot after activation, the message activation reboots appliance appears.
5. Click Apply.
Upgrades that require additional hardware automatically shut down the appliance after you activate the model upgrade specification. Install the new hardware and power on the system. The system reformats the drives and completes the upgrade.
6. If your model upgrade doesn’t require the installation of additional hardware, click the Restart icon to restart the optimization service.
When the upgrade is complete, the appliance is transformed into the new model. The model number appears on the appliance banner in the upper-right corner of the page. The appliance retains its original serial number.
Model downgrades based on the performance tier are not supported through the web interface; you need to use the CLI to downgrade the performance tier.
For more details, see the Upgrade and Maintenance Guide.
Removing a license
We recommend that you keep old licenses in case you want to downgrade to an earlier software version; however, in some situations you might want to remove a license.
To remove a license
1. Choose Administration > Maintenance: Licenses to display the Licenses page.
2. Select the license you want to delete.
3. Click Remove Licenses.
4. Click Save to Disk to save your settings permanently.
Viewing permissions
You can display your system permissions and add or change your login password in the My Account page.
To display system permissions
1. Choose Administration > System Settings: My Account to display the My Account page.
2. Under Password, complete the configuration as described in this table.
Control | Description |
Change Password | Allows you to add or change your login password. |
New Password/Confirm New Password | Specify a password in the text box. Retype the password in the Confirm New Password text box. |
Old Password | (Appears when password policy is enabled and the Minimum Character Difference Between Passwords value is greater than 0). Non-administrators must specify the old password. Administrators are never required to enter an old password when changing an account password. |
3. Click Apply to apply your changes to the running configuration.
The permissions list displays the roles and permissions assigned to your username.
The My Account page includes a way to clear user preferences if any user settings result in an unsafe state and the Management Console can’t display the page.
User preferences are set for individual users and don’t affect the appliance configuration.
To restore the user preferences for the current user
1. Choose My Account to display the My Account page.
2. Under User Preferences, click Restore Defaults.
Managing configuration files
You can save, activate, import, and revert configurations in the Administration > System Settings: Configurations page.
Each SteelHead has an active, running configuration and a written, saved configuration.
When you Apply your settings in the Management Console, the values are applied to the active running configuration, but the values aren’t written to disk and saved permanently.
When you Save your configuration settings, the values are written to disk and saved permanently. They take effect after you restart the optimization service.
Each time you save your configuration settings, they’re written to the current running configuration, and a backup is created. For example, if the running configuration is myconfig and you save it, myconfig is backed up to myconfig.bak and myconfig is overwritten with the current configuration settings.
The Configuration Manager is a utility that saves configurations as backups or active configuration backups.
The Configuration Manager also includes an Import Configuration utility to support these common use cases:
•Replacing a SteelHead appliance - If you are replacing one SteelHead for another, you can import all of the network information (although not the licenses) and disconnect the old SteelHead before you switch configurations on the new SteelHead.
•Configuration template for a large deployment - You can avoid entering the complete SteelHead configuration for every appliance in a large deployment by setting up a template SteelHead and importing template settings to the configuration list.
To manage configurations
1. Choose Administration > System Settings: Configurations to display the Configurations page.
2. Under Current Configuration: <filename>, complete the configuration as described in this table.
Control | Description |
Current Configuration: <configuration name> | View Running Config - Displays the running configuration settings in a new browser window. |
| Save - Saves settings that have been applied to the running configuration. |
| Revert - Reverts your settings to the running configuration. |
Save Current Configuration | Specify a new filename to save settings that have been applied to the running configuration as a new file, and then click Save. |
3. To import a configuration from another appliance, complete the configuration as described in this table.
Control | Description |
Import a New Configuration | Displays the controls to import a configuration from another appliance. |
IP/Hostname | Specify the IP address or hostname of the SteelHead from which you want to import the configuration. |
Remote Admin Password | Specify the administrator password for the remote SteelHead. |
Remote Config Name | Specify the name of the configuration you want to import from the remote SteelHead. |
New Config Name | Specify a new, local configuration name. |
Import Shared Data Only | Takes a subset of the configuration settings from the imported configuration and combines them with the current configuration to create a new configuration. Import shared data is enabled by default. |
Add | When the Import Shared Data Only check box is selected, activates the imported configuration and makes it the current configuration. This is the default. When the Import Shared Data Only check box is not selected, adds the imported configuration to the Configuration list. It doesn’t become the active configuration until you select it from the list and click Activate. |
Remove Selected | Select the check box next to the name and click Remove Selected. |
Change Active Configuration | Select the configuration to activate from the drop-down list. |
4. Click Activate.
Select the configuration name to display the configuration settings in a new browser window.
Configuring general security settings
You can prioritize local, RADIUS, and TACACS+ authentication methods for the system and set the authorization policy and default user for RADIUS and TACACS+ authorization systems in the Administration > Security: General Settings page.
Make sure to put the authentication methods in the order in which you want authentication to occur. If authorization fails on the first method, the next method is attempted, and so on, until all of the methods are attempted.
To set TACACS+ authorization levels (admin or read-only) to allow certain members of a group to log in, add this attribute to users on the TACACS+ server:
service = rbt-exec {
local-user-name = “monitor”
}
where you replace monitor with admin for write access.
For details about setting up RADIUS and TACACS+ servers, see the SteelHead Deployment Guide.
To set general security settings
1. Choose Administration > Security: General Settings to display the General Settings page.
2. Under Authentication Methods, complete the configuration as described in this table.
Control | Description |
Authentication Methods | Specifies the authentication method. Select an authentication method from the drop-down list. The methods are listed in the order in which they occur. If authorization fails on the first method, the next method is attempted, and so on, until all of the methods have been attempted. |
For RADIUS/TACACS+, fallback only when servers are unavailable | Select this check box to prevent local login if the RADIUS or TACACS+ server denies access, but allow local login if the RADIUS or TACACS+ server is not available. |
Safety Account | Creates a safety account so that admin or sys admin users can login to the SteelHead even if remote authentication servers are unreachable. A safety account increases security and conforms to US National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) requirements. Only the selected safety account will be allowed to login in cases where the AAA server isn’t reachable. (Only one user can be assigned to the safety account.) You can create a system administrator user in the Administrator > Security: User Permissions page. For details, see Managing user permissions. |
Safety Account User | Select the user from the drop-down list. |
Authorization Policy | Appears only for some Authentication Methods. Optionally, select one of these policies from the drop-down list: •Remote First - Checks the remote server first for an authentication policy, and only checks locally if the remote server doesn’t have one set. This is the default behavior. •Remote Only - Only checks the remote server. •Local Only - Only checks the local server. All remote users are mapped to the user specified. Any vendor attributes received by an authentication server are ignored. |
3. Click Apply to apply your changes to the running configuration.
4. Click Save to Disk to save your settings permanently.
Managing user permissions
You can change the administrator or monitor user passwords and define users in the Administration > Security: User Permissions page.
Accounts
The system uses these accounts based on what actions the user can take:
•Admin - The system administrator user has full privileges. For example, as an administrator you may set and modify configuration settings, add and delete users, restart the optimization service, reboot the SteelHead, and create and view performance and system reports. The system administrator role allows you to add or remove a system administrator role for any other user, but not for yourself.
•Monitor - A monitor user may view reports, view user logs, and change their password. A monitor user can’t make configuration changes, modify private keys, view logs, or manage cryptographic modules in the system.
You can also create users, assign passwords to the user, and assign varying configuration roles to the user.
An administrator role configures a system administrator role. Read-only permission isn’t allowed for this role. This role allows permission for all other RBM roles, including creating, editing and removing user accounts. The system administrator role allows you to add or remove a system administrator role for any other user, but not for yourself.
A user role determines whether the user has permission to:
•Read-only - With read-only privileges you can view current configuration settings but you can’t change them.
•Read/Write - With read and write privileges you can view settings and make configuration changes for a feature.
•Deny - With deny privileges you can’t view settings or save configuration changes for a feature.
As an example, you might have user Jane who can make configuration changes to QoS and SSL, whereas user John can only view these configuration settings; and finally, user Joe can’t view, change, or save the settings for these features.
Available menu items reflect the privileges of the user. For example, any menu items that a user doesn’t have permission to use are unavailable. When a user selects an unavailable link, the User Permissions page appears.
Combining permissions by feature
RiOS 9.0 and later require additional user permissions for path selection and QoS. For example, to change a QoS rule, a user needs read/write permission for the Network Settings role in addition to read/write permission for QoS.
This table summarizes the changes to the user permission requirements for RiOS 9.0 and later.
Management Console page | To configure this feature or change this section | Required read permission | Required read/write permission |
Networking > Topology: Sites & Networks | Networks | Network Settings Read-Only | Network Settings Read/Write |
| Sites | Network Settings Read-Only QoS Read-Only Path Selection Read-Only | Network Settings Read/Write QoS Read/Write Path Selection Read/Write |
Networking > App Definitions: Applications | Applications | Network Settings Read-Only | Network Settings Read/Write |
Networking > Network Services: Quality of Service | Enable QoS | Network Settings Read-Only | Network Settings Read/Write |
| Manage QoS Per Interface | Network Settings Read-Only | Network Settings Read/Write |
| QoS Profile | QoS Read-Only | QoS Read/Write |
| QoS Remote Site Info | Network Settings Read-Only QoS Read-Only | N/A |
Networking > Network Services: QoS Profile Details | Profile Name | QoS Read-Only | QoS Read/Write |
| QoS Classes | QoS Read-Only | QoS Read/Write |
| QoS Rules | QoS Read-Only | Network Settings Read/Write QoS Read/Write |
Path Selection | Enable Path Selection | Network Settings Read-Only | Network Settings Read/Write |
| Path Selection Rules | Network Settings Read-Only Path Selection Read-Only | Network Settings Read/Write Path Selection Read/Write |
| Uplink Status | Network Settings Read-Only Path Selection Read-Only Reports Read/Write | N/A |
Outbound QoS Report | | QoS Read-Only | QoS Read/Write |
Inbound QoS Report | | QoS Read-Only | QoS Read/Write |
Host Labels | | Network Settings Read-Only or QoS Read-Only | Network Settings Read/Write or QoS Read/Write |
Port Labels | | Network Settings Read-Only or QoS Read-Only | Network Settings Read/Write or QoS Read/Write |
To configure user permissions
1. Choose Administration > Security: User Permissions to display the User Permissions page.
2. Under Accounts, complete the configuration as described in this table.
Control | Description |
admin/monitor | Click the right arrow to change the password or to create a default user account. |
| Change Password - Enables password protection. Password protection is an account control feature that allows you to select a password policy for more security. When you enable account control on the Administration > Security: Password Policy page, a user must use a password. When a user has a null password to start with, the administrator can still set the user password with account control enabled. However, once the user or administrator changes the password, it can’t be reset to null as long as account control is enabled. Password - Specify a password in the text box. Password Confirm - Retype the new administrator password. Max Web Login Limit - Enter the maximum concurrent web interface sessions for this role or user. Max CLI Login Limit - Enter the maximum concurrent CLI sessions for this role or user. Enable Account - Select to enable or clear to disable the administrator or monitor account. When enabled, you may make the account the default user for Radius and TACACS+ authorization. You may only designate one account as the default user. Once enabled, the default user account may not be disabled or removed. The Accounts table displays the account as permanent. |
3. Under Accounts, complete the configuration as described in this table.
Control | Description |
Add a New Account | Click to display the controls for creating a new account. |
Account Name | Specify a name for the account. |
Password | Specify a password in the text box, and then retype the password for confirmation. |
Max Web Login Limit | Enter the maximum concurrent web interface sessions for this role or user. |
Max CLI Login Limit | Enter the maximum concurrent CLI sessions for this role or user. |
Enable Account | Select this check box to enable the new account. |
Administrator | Configures a system administrator role. This role allows permission for all other RBM roles, including creating, editing, and removing user accounts. The system administrator role allows you to add or remove a system administrator role for any other user, but not for yourself. Read-only permission is not allowed for this role. |
User | Configures a role that determines whether the user: •has permission to view current configuration settings but not change them (Read-Only). •has permission to view settings and make configuration changes for a feature (Read/Write). •is prevented from viewing or saving settings or configuration changes for a feature (Deny). |
General Settings | Configures per-source IP connection limit and the maximum connection pooling size. |
Network Settings | Configures these features: •Topology definitions •Site and network definitions •Application definitions •Host interface settings •Network interface settings •DNS cache settings •Hardware assist rules •Host labels •Port labels You must include this role for users configuring path selection or enforcing QoS policies in addition to the QoS and Path Selection roles. |
QoS | Enforces QoS policies. You must also include the Network Settings role. |
Path Selection | Configures path selection. You must also include the Network Settings role. |
Optimization Service | Configures alarms, performance features, SkipWare, HS-TCP, and TCP optimization. |
In-Path Rules | Configures TCP traffic for optimization and how to optimize traffic by setting in-path rules. This role includes WAN visibility to preserve TCP/IP address or port information. For details about WAN visibility, see the SteelHead Deployment Guide. |
CIFS Optimization | Configures CIFS optimization settings (including SMB signing) and overlapping open optimization. |
HTTP Optimization | Configures enhanced HTTP optimization settings: URL learning, Parse and Prefetch, Object Prefetch Table, keepalive, insert cookie, file extensions to prefetch, and the ability to set up HTTP optimization for a specific server subnet. |
Oracle Forms Optimization | Optimizes Oracle E-business application content and forms applications. |
MAPI Optimization | Optimizes MAPI and sets Exchange and NSPI ports. |
NFS Optimization | Configures NFS optimization. |
Notes Optimization | Configures Lotus Notes optimization. |
Citrix Optimization | Configures Citrix optimization. |
SSL Optimization | Configures SSL support and the secure inner channel. |
Replication Optimization | Configures the SRDF/A, FCIP, and SnapMirror storage optimization modules. |
Proxy File Service (PFS) | Configures the PFS. |
Storage Service | Configures branch storage services on SteelFusion Edge appliances (the branch storage services are only available on SteelFusion Edge). |
Security Settings | Configures security settings, including RADIUS and TACACS authentication settings and the secure vault password. |
Basic Diagnostics | Customizes system diagnostic logs, including system and user log settings, but doesn’t include TCP dumps. |
TCP Dumps | Customizes TCP dump settings. |
Reports | Sets system report parameters. |
Domain Authentication | Allows joining a Windows domain and configuring Windows domain authentication. |
Citrix Acceleration | Configures Citrix optimization. |
Add | Adds your settings to the system. |
Remove Selected Accounts | Select the check box next to the name and click Remove Selected. |
4. Click Save to Disk to save your settings permanently.
RiOS ignores the RBM user roles for SteelHead SaaS features. RiOS allows RBM users with DENY permissions in all roles access to SteelHead SaaS Management Console pages and GUI commands.
Managing password policy
You can change the password policy and strength in the Administration > Security: Password Policy page.
Selecting a password policy
You can choose one of these password policy templates, depending on your security requirements:
•Strong - Sets the password policy to more stringent enforcement settings. Selecting this template automatically prepopulates the password policy with stricter settings commonly required by higher security standards such as for the Department of Defense.
•Basic - Reverts the password policy to its predefined settings so you can customize your policy.
To set a password policy
1. Choose Administration > Security: Password Policy to display the Password Policy page.
2. Select the Enable Account Control check box to set a password policy. Enabling account control makes password use mandatory.
Passwords for all users expire as soon as account control is enabled. Account control forces all users to create new passwords that follow the password requirements defined in the password policy. All new passwords are then controlled by the password policy.
The passwords also expire after the number of days specified by the administrator in the Password Policy page. As a consequence of this change, when users try to log in to the Management Console and their password has expired, the Expired Password page asks them to change their password. After they change their password, the system automatically logs them in to the Management Console.
RiOS doesn’t allow empty passwords when account control is enabled.
3. Optionally, select either the Basic or Strong template.
When you select the basic template, the system prepopulates the page with the secure settings. Also, the system prompts a user logging into the SteelHead after 60 days to change their password. By default, RiOS locks out a user logging into the SteelHead after 300 days without a password change. After the system locks them out, an administrator must unlock the user account. For more details on unlocking user accounts, see
Unlocking an account.
4. Under Password Management, complete the configuration as described in this table.
Control | Description |
Login Attempts Before Lockout | Specify the maximum number of unsuccessful login attempts before temporarily blocking user access to the SteelHead. The user is prevented from further login attempts when the number is exceeded. The default for the strong security template is 3. The lockout expires after the amount of time specified in Timeout for User Login After Lockout elapses. |
Timeout for User Login After Lockout | Specify the amount of time, in seconds, that must elapse before a user can attempt to log in after an account lockout due to unsuccessful login attempts. The default for the strong security template is 300. |
Days Before Password Expires | Specify the number of days the current password remains in effect. The default for the strong security template is 60. To set the password expiration to 24 hours, specify 0. To set the password expiration to 48 hours, specify 1. Leave blank to turn off password expiration. |
Days to Warn User of an Expiring Password | Specify the number of days the user is warned before the password expires. The default for the strong security template is 7. |
Days to Keep Account Active After Password Expires | Specify the number of days the account remains active after the password expires. The default for the strong security template is 305. When the time elapses, RiOS locks the account permanently, preventing any further logins. |
Days Between Password Changes | Specify the minimum number of days before which passwords can’t be changed. |
Minimum Interval for Password Reuse | Specify the number of password changes allowed before a password can be reused. The default for the strong security template is 5. |
Enable Temporary Password Setting | Specify a temporary password to improve security and to conform to NIST requirements. A temporary password can be enabled only if Account Control is enabled. If a temporary password is set, then the password set by the Admin or Sys Admin for the new user shall expire on the first log in of the new user. A password expired page will appear for new users after the first login. If a temporary password is set and the Admin or Sys Admin resets the password for the existing user, the password will expire at the first log in after the reset. A password expired page will appear for existing users upon the first login after a password reset. |
5. Under Password Characteristics, complete the configuration as described in this table.
Control | Description |
Minimum Password Length | Specify the minimum password length. The default for the strong security template is 14 alphanumeric characters. |
Minimum Uppercase Characters | Specify the minimum number of uppercase characters required in a password. The default for the strong security template is 1. |
Minimum Lowercase Characters | Specify the minimum number of lowercase characters required in a password. The default for the strong security template is 1. |
Minimum Numerical Characters | Specify the minimum number of numerical characters required in a password. The default for the strong security template is 1. |
Minimum Special Characters | Specify the minimum number of special characters required in a password. The default for the strong security template is 1. |
Minimum Character Differences Between Passwords | Specify the minimum number of characters that must be changed between the old and new password. The default for the strong security template is 4. |
Maximum Consecutively Repeating Characters | Specify the maximum number of times a character can occur consecutively. |
Prevent Dictionary Words | Select to prevent the use of any word that is found in a dictionary as a password. By default, this control is enabled. |
6. Click Save to Disk to save your settings permanently.
Applying Session Management
Enable session management to limit the number of concurrent sessions on the appliance for all users regardless of role. Limiting the number of concurrent sessions adds a layer of security that helps to reduce the risk of Denial of Service (DoS) attacks.
Session management can be set for the appliance web interface and CLI access separately. Also, you can set a global limit and user-level limits. The default value (-1) is unlimited.
Concurrent session limitation is based on locally mapped users.
To enable session management and set global limits
1. Choose Administration > Security: Password Policy to display the Password Policy page.
2. Under Session Management, select Enable Session Management.
3. Enter the maximum number of concurrent sessions for all users.
To set user-level limits
1. Choose Administration > Security: User Permissions to display the User Permissions page.
2. Do one of these actions:
–Select Add New Account.
–Select a user account
3. Enter the maximum number of concurrent web interface sessions for this user or role.
4. Enter the maximum number of concurrent CLI interface sessions for this user or role.
Unlocking an account
RiOS temporarily locks out an account after a user exceeds the configured number of login attempts. Account lockout information appears on the Administration > Security: User Permissions page.
When an account is locked out, the lockout ends after:
•The configured lockout time elapses.
—or—
•The administrator unlocks the account. RiOS never locks out administrator accounts.
To unlock an account
1. Log in as an administrator (admin).
2. Choose Administration > Security: User Permissions page and click Clear Login Failure Details.
When users log in to their account successfully, RiOS resets the login failure count.
Resetting an expired password
RiOS temporarily locks out an account when its password expires. Passwords expire for one of these reasons:
•An administrator enables account control.
•The expiration time for a password elapses.
•An administrator disables a user account and then enables it.
•An administrator uses a CLI command to encrypt a password.
After a user password expires, users must update their password within the number of days specified in Days to Keep Account Active After Password Expires. The default value is 305 days. After the time elapses, RiOS locks the account permanently, preventing any further logins.
To reset the password and unlock the account
1. Log in as an administrator (admin).
2. Choose Administration > Security: User Permissions page and click Clear Login Failure Details.
3. Type and confirm the new password and click Change Password.
The password reset feature is separate from the account lockout feature.
Setting RADIUS servers
You set up RADIUS server authentication in the Administration > Security: RADIUS page.
RADIUS is an access control protocol that uses a challenge and response method for authenticating users.
Enabling this feature is optional.
You can prioritize local, RADIUS, and TACACS+ authentication methods for the system and set the authorization policy and default user for RADIUS and TACACS+ authorization systems in the Administration > Security: General Settings page.
For details about setting up RADIUS and TACACS+ servers, see the SteelHead Deployment Guide.
To set RADIUS server authentication
1. Choose Administration > Security: RADIUS to display the RADIUS page.
2. Under Default RADIUS Settings, complete the configuration as described in this table.
Control | Description |
Set a Global Default Key | Enables a global server key for the RADIUS server. |
Global Key | Specify the global server key. |
Confirm Global Key | Confirm the global server key. |
Timeout | Specify the time-out period in seconds (1 to 60). The default value is 3. |
Retries | Specify the number of times you want to allow the user to retry authentication. The default value is 1. |
3. Click Apply to apply your changes to the running configuration.
4. To add a new RADIUS server, complete the configuration as described in this table.
Control | Description |
Add a RADIUS Server | Displays the controls for defining a new RADIUS server. |
Hostname or IP Address | Specify the hostname or server IP address. RiOS doesn’t support IPv6 server IP addresses. |
Authentication Port | Specify the port for the server. |
Authentication Type | Select one of these authentication types: •PAP - Password Authentication Protocol (PAP), which validates users before allowing them access to the RADIUS server resources. PAP is the most flexible protocol but is less secure than CHAP. •CHAP - Challenge-Handshake Authentication Protocol (CHAP), which provides better security than PAP. CHAP validates the identity of remote clients by periodically verifying the identity of the client using a three-way handshake. This validation happens at the time of establishing the initial link and might happen again at any time. CHAP bases verification on a user password and transmits an MD5 sum of the password from the client to the server. •MS-CHAPv2 - The Microsoft version of the Challenge-Handshake Authentication Protocol. MS-CHAPv2 is a more secure authentication protocol than PAP or CHAP. |
Override the Global Default Key | Overrides the global server key for the server. Server Key - Specify the override server key. Confirm Server Key - Confirm the override server key. |
Timeout | Specify the time-out period in seconds (1 to 60). The default value is 3. |
Retries | Specify the number of times you want to allow the user to retry authentication. Valid values are from 0 to 5. The default value is 1. |
Enabled | Enables the new server. |
Add | Adds the RADIUS server to the list. |
Remove Selected | Select the check box next to the name and click Remove Selected. |
If you add a new server to your network and you don’t specify these fields at that time, RiOS applies the global settings.
5. Click Save to Disk to save your settings permanently.
To modify RADIUS server settings, click the server IP address in the list of Radius Servers. Use the Status drop-down list to enable or disable a server in the list.
Related topic
Configuring SAML
You set up SAML in the Administration > Security: SAML page.
Security Assertion Markup Language (SAML) 2.0 is an XML standard that acts as an authentication interface between a SteelHead and an identity provider (IdP). You can use the IdP to provide additional requirements for authentication, such as a multifactor authentication based on a common access card (CAC) or personal identity verification (PIV).
When a SteelHead receives a login request, it determines if SAML is enabled. If SAML is enabled, user authentication through AAA is disabled and the SteelHead redirects the authentication request to the IdP. The IdP authenticates the user and redirects the user to the SteelHead, which allows access.
SAML authentication process
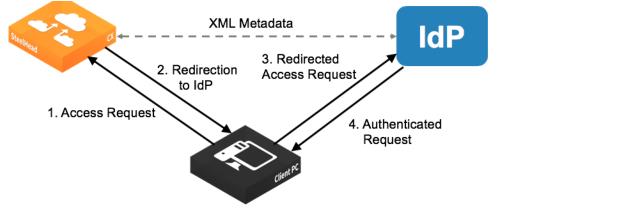
To enable IdP authentication, you configure the SteelHead and the IdP with XML metadata that provides detailed appliance identification. The metadata also establishes a trust relationship between the SteelHead and the IdP.
Administrators must add users to the IdP server to provide them login access, and those users need to correspond to SteelHead users. You can have one-to-one mapping of users between IdP and SteelHead, or you can have multiple users on IdP map to single account on the SteelHead, such as the admin account. (You have to create individual user accounts on the SteelHead for one-to-one mapping as the user accounts determine the access permissions.)
If a user who has not been set up in the IdP tries to log in to the SteelHead, the login fails on the IdP login page. (This failed login is not tracked in the SteelHead logs.) If the user has been set up but their user mapping has not been defined in the IdP, the login succeeds but the SteelHead displays an error page (instead of the dashboard).
SAML authentications are only available in the Management Console web interface; they are not available through the CLI. Users can log in to a SAML-enabled SteelHead through the CLI but they are authenticated using the local, RADIUS, or TACACS+ authentication methods.
If you cannot log in using SAML (for example, if the IdP server is unavailable), you can log in through the CLI and disable SAML using the no aaa saml command. Once SAML is disabled, you revert to the previously configured authentication method for the web interface. For command details, see the Riverbed Command-Line Interface Reference Manual.
You must be logged in as the administrator to enable or disable SAML.
To enable SAML
1. Choose Administration > Security: SAML to display the SAML page.
2. Under Appliance Metadata, click Download XML to download the SteelHead metadata in XML format.
The sp_metadata.xml file downloads to your local machine.
3. Configure the appliance in your IdP.
Refer to the documentation for your IdP for specific instructions. In general, you complete these steps:
–Log in to the IdP website.
–Upload the metadata from the sp_metadata.xml file and provide any other required details.
–When the configuration is complete, download the IdP metadata.
4. In the management console, under SAML > IdP Configuration, configure the SAML settings as described in this table.
Control | Description |
IdP Metadata | Paste the IdP metadata you copied or received from the IdP website. |
Security Settings Note: These setting should match the IdP settings. | Sign Authentication Request - Select this option to have SteelHead sign the SAML authentication request sent to the identity provider. Signing the initial login request sent by SteelHead allows the identity provider to verify that all login requests originate from a trusted service provider. |
Requires Signed Assertions - Select if the IdP signs the assertion response. Some SAML configurations require signed assertions to improve security. |
Requires Encrypted Assertions - Select this option if the SAML identity provider encrypts the assertion section of the SAML responses. Even though all SAML traffic to and from SteelHead is already encrypted by the use of HTTPS, this option adds another layer of encryption. |
Attribute | Username Attribute - Enter the name of the IdP variable that carries the username. The Username attribute is mandatory and must be sent by your identity provider in the SAML response to align the login with a configured SteelHead account. |
Member of Attribute - Enter the name of the IdP variable that carries the role of the user. The role must match with a local SteelHead user. This setting is mandatory. Note: If you use the default memberOf attribute, the SteelHead only attempts to match against the first entry in the IdP memberOf attribute list. If you require more control, we recommend creating a custom attribute. For details, see Knowledge Base article S33447. |
5. Click Apply to save your configuration settings.
6. Under Validate the IdP Configuration, click Validate.
The IdP Validation window appears.
7. Click Go to IdP.
The IdP login page opens.
8. Log in to the IdP website.
The page indicates if your IdP configuration was successful.
9. After successful validation, return to the SAML page in the management console and select the Enable SAML check box and click Apply.
Tip: If the validation status on the SteelHead page does not update after a successful validation, reload the page to refresh the status.
With SAML enabled, all web login requests are redirected to the IdP.
10. Click Save to Disk to save your settings permanently.
If you make changes to the SAML settings after you validate the IdP configuration, you need to validate again with the new settings and enable SAML again.
Configuring TACACS+ access
You set up TACACS+ server authentication in the Administration > Security: TACACS+ page.
TACACS+ is an authentication protocol that allows a remote access server to forward a login password for a user to an authentication server to determine whether access is allowed to a given system.
Enabling this feature is optional.
You can prioritize local, RADIUS, and TACACS+ authentication methods for the system and set the authorization policy and default user for RADIUS and TACACS+ authorization systems in the Administration > Security: General Settings page.
For details about configuring RADIUS and TACACS+ servers to accept login requests from the SteelHead, see the SteelHead Deployment Guide.
To set a TACACS+ server
1. Choose Administration > Security: TACACS+ to display the TACACS+ page.
2. Under Default TACACS+ Settings, complete the configuration as described in this table.
Control | Description |
Set a Global Default Key | Enables a global server key for the server. |
Global Key | Specify the global server key. |
Confirm Global Key | Confirms the global server key. |
Timeout | Specify the time-out period in seconds (1 to 60). The default value is 3. |
Retries | Specify the number of times you want to allow the user to retry authentication. Valid values are from 0 to 5. The default is 1. |
3. Click Apply to apply your changes to the running configuration.
4. To add or remove a TACACS+ server, complete the configuration as described in this table.
Control | Description |
Add a TACACS+ Server | Displays the controls for defining a new TACACS+ server. |
Hostname or IP Address | Specify the hostname or server IP address. |
Authentication Port | Specify the port for the server. The default value is 49. |
Authentication Type | Select either PAP or ASCII as the authentication type. The default value is PAP. |
Override the Global Default Key | Specify this option to override the global server key for the server. |
Server Key | Specify the override server key. |
Confirm Server Key | Confirm the override server key. |
Timeout | Specify the time-out period in seconds (1 to 60). The default is 3. |
Retries | Specify the number of times you want to allow the user to retry authentication. Valid values are from 0 to 5. The default is 1. |
Enabled | Enables the new server. |
Add | Adds the TACACS+ server to the list. |
Remove Selected | Select the check box next to the name and click Remove Selected. |
If you add a new server to your network and you don’t specify these fields, the system automatically applies the default settings.
5. Click Save to Disk to save your settings permanently.
Related topic
Unlocking the secure vault
You can unlock and change the password for the secure vault in the Administration > Security: Secure Vault page.
The secure vault contains sensitive information from your SteelHead configuration, including SSL private keys, the RiOS data store encryption key, and replication or delegate user configuration details. RiOS encrypts and secures these configuration settings on the disk at all times using AES 256-bit encryption.
Initially the secure vault is keyed with a default password known only to RiOS. This default password allows the SteelHead to automatically unlock the vault during system start up. You can change the password, but the secure vault doesn’t automatically unlock on start up. To optimize SSL connections or to use RiOS data store encryption, the secure vault must be unlocked.
To unlock or change the password of the secure vault
1. Choose Administration > Security: Secure Vault to display the Secure Vault page.
2. Under Unlock Secure Vault, complete the configuration as described in this table.
Control | Description |
Password | Specify a password and click Unlock Secure Vault. Initially the secure vault is keyed with a default password known only to RiOS. The default password allows the SteelHead to automatically unlock the vault during system start up. You can change the password, but the secure vault doesn’t automatically unlock on start up. To optimize SSL connections, use RiOS data store encryption, or replication or delegate users, you must unlock the secure vault. |
Unlock Secure Vault | Unlocks the vault. |
3. Under Change Password, complete the configuration as described in this table.
Control | Description |
Current Password | Specify the current password. If you are changing the default password that ships with the product, leave the text box blank. |
New Password | Specify a new password for the secure vault. |
New Password Confirm | Confirm the new password for the secure vault. |
Change Password | Changes the password for the secure vault. |
4. Click Save to Disk to save your settings permanently.
Related topic
Configuring a management ACL
You can secure access to a SteelHead using an internal management access control list (ACL) in the Security: Management ACL page.
SteelHeads are subject to the network policies defined by a corporate security policy, particularly in large networks. Using an internal management ACL, you can:
•restrict access to certain interfaces or protocols of a SteelHead.
•restrict inbound IP access to a SteelHead, protecting it from access by hosts that don’t have permission without using a separate device (such as a router or firewall).
•specify which hosts or groups of hosts can access and manage a SteelHead by IP address, simplifying the integration of SteelHeads into your network.
The management ACL provides these safeguards to prevent accidental disconnection from the SteelHead and the SCC:
•It detects the IP address you are connecting from and displays a warning if you add a rule that denies connections to that address.
•It always allows the default SteelHead ports 7800, 7801, 7810, 7820, and 7850.
•It always allows a previously connected SCC to connect and tracks any changes to the IP address of the SCC to prevent disconnection.
•It converts well-known port and protocol combinations such as SSH, Telnet, HTTP, HTTPS, SNMP, and SOAP into their default management service and protects these services from disconnection. For example, if you specify protocol 6 (TCP) and port 22, the management ACL converts this port and protocol combination into SSH and protects it from denial.
•It tracks changes to default service ports and automatically updates any references to changed ports in the access rules.
To set up a management ACL
1. Choose Administration > Security: Management ACL to display the Management ACL page.
2. Under Management ACL Settings, complete the configuration as described in this table.
Control | Description |
Enable Management ACL | Secures access to a SteelHead using a management ACL. |
3. Click Apply to apply your changes to the running configuration.
4. Click Save to Disk to save your settings permanently.
If you add, delete, edit, or move a rule that could disconnect connections to the SteelHead, a warning message appears. Click Confirm to override the warning and allow the rule definition. Use caution when overriding a disconnect warning.
ACL management rules
The management ACL contains rules that define a match condition for an inbound IP packet. You set a rule to allow or deny access to a matching inbound IP packet. When you add a rule on a SteelHead, the destination specifies the SteelHead itself, and the source specifies a remote host.
The ACL rules list contains default rules that allow you to use the management ACL with DNS caching. These default rules allow access to certain ports required by this feature. The list also includes default rules that allow access to the SCC. If you delete a default ACL rule and need to restore it, see
To restore the default ACL management rule for DNS caching.
To add an ACL management rule
1. Under Management ACL Settings, complete the configuration as described in this table.
Control | Description |
Add a New Rule | Displays the controls for adding a new rule. |
Action | Select one of these rule types from the drop-down list: •Allow - Allows a matching packet access to the SteelHead. This is the default action. •Deny - Denies access to any matching packets. |
Service | Optionally, select Specify Protocol, or HTTP, HTTPS, SOAP, SNMP, SSH, Telnet. When specified, the Destination Port is dimmed. |
Protocol | (Appears only when Service is set to Specify Protocol.) Optionally, select All, TCP, UDP, or ICMP from the drop-down list. The default setting is All. When set to All or ICMP, the Service and Destination Ports are dimmed. |
Source Network | Optionally, specify the source subnet of the inbound packet: for example, 1.2.3.0/24. |
Destination Port | Optionally, specify the destination port of the inbound packet, either a single port value or a port range of port1-port2, where port1 must be less than port2. Leave it blank to specify all ports. |
Interface | Optionally, select an interface name from the drop-down list. Select All to specify all interfaces. |
Description | Optionally, describe the rule to facilitate administration. |
Rule Number | Optionally, select a rule number from the drop-down list. By default, the rule goes to the end of the table (just above the default rule). SteelHeads evaluate rules in numerical order starting with rule 1. If the conditions set in the rule match, then the rule is applied, and the system moves on to the next packet. If the conditions set in the rule don’t match, the system consults the next rule. For example, if the conditions of rule 1 don’t match, rule 2 is consulted. If rule 2 matches the conditions, it’s applied, and no further rules are consulted. Note: The default rule, Allow, which allows all remaining traffic from everywhere that has not been selected by another rule, can’t be removed and is always listed last. |
Log Packets | Tracks denied packets in the log. By default, packet logging is enabled. |
Add | Adds the rule to the list. The Management Console redisplays the Rules table and applies your modifications to the running configuration, which is stored in memory. |
Remove Selected | Select the check box next to the name and click Remove Selected. |
Move Selected | Moves the selected rules. Click the arrow next to the desired rule position; the rule moves to the new position. |
2. Click Save to Disk to save your settings permanently.
Usage notes
•When you change the default port of services such as SSH, HTTP, HTTPS, on either the client-side or server-side SteelHead and create a management ACL rule denying that service, the rule will not work as expected. The SteelHead on the other end (either server or client) of an in-path deployment doesn’t know that the default service port has changed, and consequently optimizes the packets to that service port. To work around this problem, add a pass-through rule to the client-side SteelHead for the management interfaces. The pass-through rule prevents the traffic from coming from the local host when optimized.
•A management ACL rule that denies access from port 20 on the server-side SteelHead in an out-of-path deployment prevents data transfer using active FTP. In this deployment, the FTP server and client can’t establish a data connection because the FTP server initiates the SYN packet and the management rule on the server-side SteelHead blocks the SYN packet. To work around this problem:
—or—
–add a rule to either allow source port 20 on the server-side SteelHead or allow the IP address of the FTP server.
To restore the default ACL management rule for DNS caching
1. Under Management ACL Settings, add a DNS Caching ACL rule with these properties.
Property | Value |
Type | Allow |
Protocol | UDP |
Destination Port | 53 |
Rule Number | 1 |
Description | DNS Caching |
2. Click Add.
Configuring web settings
You can modify Management Console web user interface and certificate settings in the Administration > Security: Web Settings page.
To modify web settings
1. Choose Administration > Security: Web Settings to display the Web Settings page.
2. Under Web Settings, complete the configuration as described in this table.
Control | Description |
Default Web Login ID | Specify the username that appears in the authentication page. The default value is admin. |
Web Inactivity Timeout | Specify the number of idle minutes before time-out. The default value is 15. A value of 0 disables time-out. |
Allow Session Timeouts When Viewing Auto-Refreshing Pages | By default, session time-out is enabled, which stops the automatic updating of the report pages when the session times out. Clear the Allow box to disable the session time-out, remain logged-in indefinitely, and automatically refresh the report pages. Note: Disabling this feature poses a security risk. |
3. Click Apply to apply your changes to the running configuration.
4. Click Save to Disk to save your settings permanently.
Managing web SSL certificates
RiOS provides these security features to manage SSL certificates used by the SteelHead appliance Management Console through HTTPS:
•Generate the certificate and key pairs on the SteelHead. This method overwrites the existing certificate and key pair regardless of whether the previous certificate and key pair was self-signed or user added. The new self-signed certificate lasts for one year (365 days).
•Create certificate signing requests from the certificate and key pairs.
•Replace a signed certificate with one created by an administrator or generated by a third-party certificate authority.
To modify web certificates
1. Choose Administration > Security: Web Settings to display the Web Settings page.
2. Under Web Certificate, select the Details tab.
The SteelHead identity certificate details appear, as described in this table.
Control | Description |
Issued To/Issued By | Common Name - Specifies the common name of the certificate authority. Email - Specifies the email address of the certificate administrator. Organization - Specifies the organization name (for example, the company). Locality - Specifies the city. State - Specifies the state. Country - Specifies the country. Serial Number - Specifies the serial number (Issued To, only). |
Validity | Issued On - Specifies the date the certificate was issued. Expires On - Specifies the date the certificate expires. |
Fingerprint | Specifies the SSL fingerprint. |
Key | Type - Specifies the key type. Size - Specifies the size in bytes. |
3. To replace an existing certificate, under Web Certificate, select the Replace tab and complete the configuration as described in this table.
Control | Description |
Import Certificate and Private Key | Imports the certificate and key. The page displays controls for browsing to and uploading the certificate and key files. Or, you can use the text box to copy and paste a PEM file. The private key is required regardless of whether you are adding or updating the certificate. |
Certificate | Upload - Browse to the local file in PKCS-12, PEM, or DER formats. Paste it here (PEM) - Copy and then paste the contents of a PEM file. |
Private Key | Select the private key origin. •The Private Key is in a separate file (see below) - You can either upload it or copy and paste it. •This file includes the Certificate and Private Key •The Private Key for this Certificate was created with a CSR generated on this appliance. |
Separate Private Key | Upload (PEM or DER formats) - Browse to the local file in PEM or DER formats. Paste it here (PEM only) - Paste the contents of a PEM file. Decryption Password - Specify the decryption password, if necessary. Passwords are required for PKCS-12 files, optional for PEM files, and never needed for DER files. |
4. To generate a CSR, under Web Certificate, select the Generate CSR tab and complete the configuration as described in this table.
Control | Description |
Common Name | Specify the common name (hostname). |
Organization Name | Specify the organization name (for example, the company). |
Organization Unit Name | Specify the organization unit name (for example, the section or department). |
Locality | Specify the city. |
State | Specify the state. Do not abbreviate. |
Country | Specify the country (2-letter code only). |
Email Address | Specify the email address of the contact person. |
Generate CSR | Generates the Certificate Signing Request. |
5. Click Apply to apply your changes to the running configuration.
6. Click Save to Disk to save your settings permanently.
7. Click Add.
Enabling REST API access
You enable access to the Riverbed REST API in the Administration > Security: REST API Access page. REST API is enabled by default.
Representational State Transfer (REST) is a framework for API design. REST builds a simple API on top of the HTTP. It is based on generic facilities of the standard HTTP protocol, including the six basic HTTP methods (GET, POST, PUT, DELETE, HEAD, INFO) and the full range of HTTP return codes. You can discover REST APIs by navigating links embedded in the resources provided by the REST API, which follow common encoding and formatting practices.
You can invoke the REST API to enable communication from one Riverbed appliance to another through REST API calls, for example, a SteelCentral NetProfiler retrieving a QoS configuration from a SteelHead.
For all uses you must preconfigure an access code to authenticate communication between parties and to authorize access to protected resources.
The REST API calls are based on the trusted application flow, a scenario where you download and install an application on some host, such as your own laptop. You trust both the application and the security of the host onto which the application is installed.
For example, suppose you install a Python script on a Linux box that queries QoS policies on a SteelHead and prints a summary as text output. You install the script under your home directory and configure the script with credentials to access the SteelHead. Once set up, you can simply log in to the Linux box and run the script. Because you already preconfigured credentials with the SteelHead, you can run the script without any user interaction after logging in. This trusted application flow enables you to schedule execution through cron or chain it with other scripts that process the text data and combine it with other functionality.
This basic authentication sequence assumes you have already downloaded the Python script and installed it on a Linux box:
REST API Access Authentication Sequence
To enable REST API access
1. Choose Administration > Security: REST API Access to display the REST API Access page.
2. Under REST API Access Settings, select the Enable REST API Access check box.
3. Click Apply to apply your changes to the running configuration.
4. Click Save to Disk to save your settings permanently.
Before an appliance can access the REST API, you must preconfigure an access code for the system to use to authenticate access.
To preconfigure the access code
1. Choose Administration > Security: REST API Access to display the REST API Access page.
2. Click Add Access Code.
3. Under Access Codes, type a description such as the hostname or IP address of the appliance you are using.
4. To create a code, select Generate New Access Code.
To use an existing code, select Import Existing Access Code.
5. Click Add.
The access code description appears in the access code table along with the name of the user who created it.
6. Click the access code description to display the access code.
7. Copy the access code from the text field into a text editor such as Notepad.
To use the access code in your external script
•Copy the access code copied from the Management Console REST API Access page into the configuration file of your external script. The script uses the access code to make a call to the appliance or system to request an access token. The appliance/system validates the access code and returns an access token for use by the script. Generally the access token is kept by the script for a session only (defined within your script), but note that the script can make many requests using the same access token. These access tokens have some lifetime—usually around an hour—in which they’re valid. When they expire, the access code must fetch a new access token. The script uses the access token to make REST API calls with the appliance or system.

