SteelFusion Appliance Sizing
Every deployment of the SteelFusion product family differs due to variations in specific customer needs and types and sizes of IT infrastructure. The following information is intended to guide you to achieving optimal performance. However, these guidelines are general; for detailed worksheets for proper sizing, contact your Riverbed representative.
This chapter includes the following sections:
General sizing considerations
Accurate sizing typically requires a discussion between Riverbed representatives and your server, storage, and application administrators.
General considerations include but are not limited to:
• Storage capacity used by branch offices - How much capacity is currently used, or expected to be used, by the branch office. The total capacity might include the amount of used and free space.
• Input/output operations per second (IOPS) - What are the number and types of drives being used? This value should be determined early so that the SteelFusion-enabled SteelHead can provide the same or higher level of performance.
• Daily rate of change - How much data is the Edge expected to write back to the storage array through the Core? This value can be determined by studying backup logs.
• Branch applications - Which and how many applications are required to continue running during a WAN outage? This answer can impact disk capacity calculations.
Core sizing guidelines
The main considerations for sizing your Core deployment are as follows:
• Total data set size - The total space used across exports (not the size of the exports).
• Total number of exports - Each export adds five optimized connections to the SteelHead. Also, each branch office in which you have deployed Edge represents at least one export in the storage array.
• RAM requirements - You should have at least 700 MB of RAM per terabyte (TB) of used space in the data set. There is no specific setting on the Core to allocate memory on this basis, but in general this amount is how much the Core uses under normal circumstances if the memory is available. Each Core model has a fixed capacity of memory (see SteelFusion and SteelHead specification sheets for details) that it is shipped with. If the metric falls below the recommended value, performance of the Core can be affected, and the ability to efficiently perform prediction and prefetch operations.
Other potentially decisive factors include:
• Number of files and directories
• Type of file system, such as NTFS or VMFS
• File fragmentation
• Active working set of exports
• Number of misses seen from Edge
• Response time of the storage array
This table summarizes sizing recommendations for Core appliances based on the number of branches and data set sizes.
Model | Number of LUNs | Number of branches | Data set size | RAM |
1000U | 10 | 5 | 2 TB | VM guidelines |
1000L | 20 | 10 | 5 TB | VM guidelines |
1000M | 40 | 20 | 10 TB | VM guidelines |
1500L | 60 | 30 | 20 TB | VM guidelines |
1500M | 60 | 30 | 35 TB | VM guidelines |
2000L | 20 | 10 | 5 TB | 24 GB |
2000M | 40 | 20 | 10 TB | 24 GB |
2000H | 80 | 40 | 20 TB | 24 GB |
2000VH | 160 | 80 | 35 TB | 24 GB |
2500-C1 | 20 | 10 | 5TB | VM guidelines |
2500-C2 | 60 | 30 | 25 TB | VM guidelines |
2500-C3 | 60 | 30 | 50TB | VM guidelines |
2500-C4 | 60 | 30 | 75TB | VM guidelines |
3000L | 200 | 100 | 50 TB | 128 GB |
3000M | 250 | 125 | 75 TB | 128 GB |
3000H | 300 | 150 | 100 TB | 128 GB |
3500C1 | 150 | 75 | 25 TB | 256 GB |
3500C2 | 200 | 100 | 50 TB | 256 GB |
3500C3 | 300 | 150 | 100 TB | 256 GB |
Note: Core models 1000, 1500, and 2500 are virtual appliances. For minimum memory requirements, see the SteelFusion Core Installation and Configuration Guide.
Note: Core models 1000, 2000, and 3000 do not support NFS/file mode.
The above table assumes 2 x LUNs per branch; however, in SteelFusion 4.6 and earlier, there is no enforced limit for the number of LUNs per branch or number of branches, so long as the recommended number of LUNs and data set sizes are within limits.
SteelFusion Core version 5.0 and later include support for enforcement of Core specifications. This enforcement is designed to ensure the SteelFusion deployment performs to its optimum. When upgrading to Core version 5.0, or later, from a 4.x release, the Core will raise an alarm warning the administrator if the specifications have already been exceeded by a configuration that was applied prior to upgrading. However, the SteelFusion deployment will continue to operate normally.
In Core version 5.0 or later, if you are applying configuration changes where additional LUNs or Edges are in the process of being added, the Core will prevent the operation from being performed if the specification limits will be exceeded. The administrator will receive a warning message describing the problem.
Figure: Example warning messages shows two example messages. One for exceeding the maximum number of LUNs and one for exceeding the number of Edges.
Figure: Example warning messages
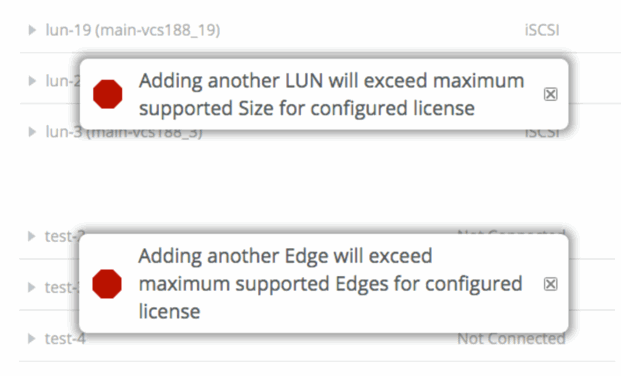
The specification enforcement does not apply to local LUNs. If an existing LUN is resized to a capacity that will exceed the specification limit for the Core, it will be allowed, but an alarm will be raised.
When a failover occurs in a Core HA deployment, the ActiveSolo Core will take control of serving the failed Core’s LUNs to the Edges it was connected to. This is normal behavior. Depending on the configuration in this scenario, if the Cores are running software version 5.0 or later, the ActiveSolo Core could be in a situation where the total number of LUNs and/or Edges exceed the specification. This is due to it taking over from the failed Core. If the specification limits are exceeded, an alarm will be raised on the ActiveSolo Core but operations will continue. The alarm will clear automatically once the failed Core is recovered and back online.
There is currently no enforcement of specifications for Core appliances deployed in NFS/file mode and currently no enforcement for Edge devices deployed in block storage mode or NFS/file mode.
Edge sizing guidelines
The main considerations for sizing your Edge deployment are as follows:
• Disk size - What is the expected capacity of the Edge blockstore?
– Your calculations can be affected depending on if exports are pinned, unpinned, or local.
– During WAN outages when the Edge cannot synchronize write operations back through the Core to the exports in the data center, the Edge uses a
write reserve area on the blockstore to store the data. As described in
Pin the export and prepopulate the blockstore, this area is 10 percent of the blockstore capacity.
• Input/output operations per second (IOPS) - If you are replacing existing storage in the branch office, you can calculate this value from the number and types of drives in the devices you want to replace. Remember that the drives might not have been operating at their full performance capacity. So, if an accurate figure is required, consider using performance monitoring tools that might be included within the server OS: for example, perfmon.exe in Windows.
Other potentially decisive factors:
• HA requirements (PSU, disk, network redundancy)
• VSP CPU and memory requirements
• WAN optimization requirements (bandwidth and connection count)
See the SteelFusion Edge specification sheets for capacity and capabilities of each model.
When sizing the Edge appliance, you have the additional flexibility of choosing optimized WAN bandwidth (W0-W3) needed after you have completed sizing for disk size, IOPS, and CPU. The W0 model comes with 0 optimized WAN bandwidth for external traffic, but it still optimizes SteelFusion traffic. For more information, see
Rdisk traffic routing options.


