MAPI page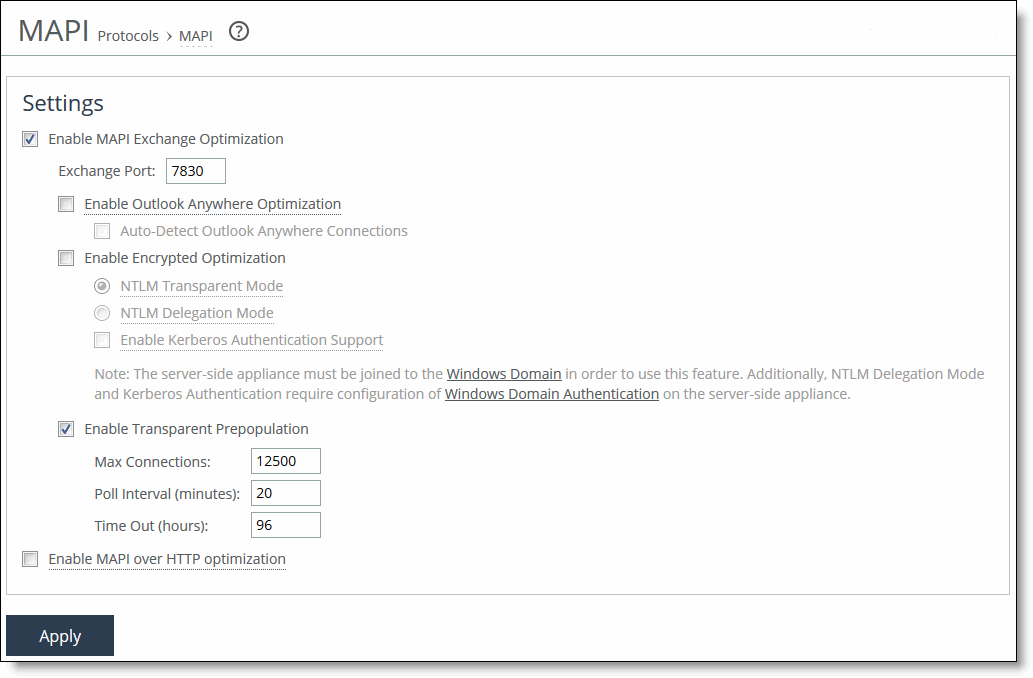


Control | Description |
Enable MAPI Exchange Optimization | Enables the fundamental component of the MAPI optimization module, which includes optimization for read, write (receive, send), and sync operations. By default, MAPI Exchange optimization is enabled. Only clear this check box to disable MAPI optimization. Typically, you disable MAPI optimization to troubleshoot problems with the system. For example, if you are experiencing problems with Outlook clients connecting with Exchange, you can disable MAPI latency acceleration (while continuing to optimize with SDR for MAPI). |
Exchange Port | Specify the MAPI Exchange port for optimization. Typically, you don’t need to modify the default value, 7830. |
Enable Outlook Anywhere Optimization | Enables Outlook Anywhere latency optimization. Outlook Anywhere is a feature of Microsoft Exchange Server 2003, 2007, and 2010 that allows Microsoft Office Outlook 2003, 2007, and 2010 clients to connect to their Exchange Servers over the Internet using the Microsoft RPC tunneling protocol. Outlook Anywhere allows for a VPN-less connection as the MAPI RPC protocol is tunneled over HTTP or HTTPS. RPC over HTTP can transport regular or encrypted MAPI. If you use encrypted MAPI, the server-side SteelHead must be a member of the Windows domain. Enable this feature on the client-side and server-side SteelHeads. By default, this feature is disabled. To use this feature, you must also enable HTTP Optimization on the client-side and server-side SteelHeads (HTTP optimization is enabled by default). If you are using Outlook Anywhere over HTTPS, you must enable SSL and the IIS certificate must be installed on the server-side SteelHead: • When using HTTP, Outlook can only use NTLM proxy authentication. • When using HTTPS, Outlook can use NTLM or Basic proxy authentication. • When using encrypted MAPI with HTTP or HTTPS, you must enable and configure encrypted MAPI in addition to this feature. Outlook Anywhere optimized connections can’t start MAPI prepopulation. After you apply your settings, you can verify that the connections appear in the Current Connections report as a MAPI-OA or an eMAPI-OA (encrypted MAPI) application. The Outlook Anywhere connection entries appear in the system log with an RPCH prefix. Outlook Anywhere creates twice as many connections on the SteelHead than regular MAPI. Enabling Outlook Anywhere latency optimization results in the SteelHead entering admission control twice as fast than with regular MAPI. For details, see Appendix A, “SteelHead MIB.” For details and troubleshooting information, see the SteelHead Deployment Guide - Protocols. For details about enabling Outlook Anywhere, see http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/bb123513(EXCHG.80).aspx. |
Auto-Detect Outlook Anywhere Connections | Automatically detects the RPC over HTTPS protocol used by Outlook Anywhere. This feature is dimmed until you enable Outlook Anywhere optimization. By default, these options are enabled. You can enable automatic detection of RPC over HTTPS using this option or you can set in-path rules. Autodetect is best for simple SteelHead configurations with only a single SteelHead at each site and when the IIS server is also handling websites. If the IIS server is only used as RPC Proxy, and for configurations with asymmetric routing, connection forwarding or Interceptor installations, add in-path rules that identify the RPC Proxy server IP addresses and select the Outlook Anywhere latency optimization policy. After adding the in-path rule, disable the autodetect option. On an Interceptor, add load-balancing rules to direct traffic for RPC Proxy to the same SteelHead. In-path rules interact with autodetect as follows: • When autodetect is enabled and the in-path rule doesn’t match, RiOS optimizes Outlook Anywhere if it detects the RPC over HTTPS protocol. • When autodetect is not enabled and the in-path rule doesn’t match, RiOS doesn’t optimize Outlook Anywhere. • When autodetect is enabled and the in-path rule matches with HTTP only, RiOS doesn’t optimize Outlook Anywhere (even if it detects the RPC over HTTPS protocol). • When autodetect is not enabled and the in-path rule doesn’t match with HTTP only, RiOS doesn’t optimize Outlook Anywhere. • When autodetect is enabled and the in-path rule matches with an Outlook Anywhere latency optimization policy, RiOS optimizes Outlook Anywhere (even if it doesn’t detect the RPC over HTTPS protocol). • When autodetect is not enabled and the in-path rule matches with Outlook Anywhere, RiOS optimizes Outlook Anywhere. |
Enable Encrypted Optimization | Enables encrypted MAPI RPC traffic optimization between Outlook and Exchange. By default, this option is disabled. The basic steps to enable encrypted optimization are: 1. Choose Networking > Active Directory: Domain Join and join the server-side SteelHead to the same Windows Domain that the Exchange Server belongs to and operates as a member server. An adjacent domain can be used (through cross-domain support). It is not necessary to join the client-side SteelHead to the domain. 2. Verify that Outlook is encrypting traffic. 3. Enable this option on all SteelHeads involved in optimizing MAPI encrypted traffic. 4. RiOS supports both NTLM and Kerberos authentication. To use Kerberos authentication, select Enable Kerberos Authentication support on both the client-side and server-side SteelHeads. Kerberos authentication does not work with Windows 7 clients that are configured to use NTLM authentication only. 5. Restart the service on all SteelHeads that have this option enabled. When this option is enabled and Enable MAPI Exchange 2007 Acceleration is disabled on either SteelHead, MAPI Exchange 2007 acceleration remains in effect for unencrypted connections. |
NTLM Transparent Mode | Provides encrypted MAPI with transparent NTLM authentication. By default, this setting is enabled with encrypted MAPI optimization. Transparent mode supports all Windows servers, including Windows 2008 R2 (assuming they’re not in domains with NTLM disabled). Transparent mode includes support for trusted domains, wherein users are joined to a different domain from the Exchange Server being accessed. Transparent mode doesn’t support Windows 2008 R2 domains and Windows 7 clients that have NTLM disabled; instead, use Kerberos Authentication Support mode. |
Enable Kerberos Authentication Support | Provides encrypted MAPI optimization with end-to-end authentication using Kerberos. The server-side SteelHead uses Kerberos to authenticate users. In addition to enabling this feature, you must also join the server-side SteelHead to a Windows Domain and add replication users on the Optimization > Active Directory: Service Accounts page. The server-side SteelHead must be joined to the same Windows Domain that the Exchange Server belongs to and operates as a member server. |
Enable Transparent Prepopulation | Enables a mechanism for sustaining Microsoft Exchange MAPI connections between the client and server even after the Outlook client has shut down. This method allows email data to be delivered between the Exchange Server and the client-side SteelHead while the Outlook client is offline or inactive. When a user logs into their Outlook client, the mail data is already prepopulated on the client-side SteelHead. This accelerates the first access of the client’s email, which is retrieved with LAN-like performance. Transparent prepopulation creates virtual MAPI connections to the Exchange Server for Outlook clients that are offline. When the remote SteelHead detects that an Outlook client has shut down, the virtual MAPI connections are triggered. The remote SteelHead uses these virtual connections to pull mail data from the Exchange Server over the WAN link. You must enable this control on the server-side and client-side SteelHeads. By default, MAPI transparent prepopulation is enabled. MAPI prepopulation doesn’t use any additional Client Access Licenses (CALs). The SteelHead holds open an existing authenticated MAPI connection after Outlook is shut down. No user credentials are used or saved by the SteelHead when performing prepopulation. The client-side SteelHead controls MAPI v2 prepopulation, which allows for a higher rate of prepopulated session, and enables the MAPI prepopulation to take advantage of the read-ahead feature in the MAPI optimization blade. If a user starts a new Outlook session, the MAPI prepopulation session terminates. If for some reason the MAPI prepopulation session doesn’t terminate (for example, the user starts a new session in a location that is different than the SteelHead that has the MAPI prepopulation session active), the MAPI prepopulation session eventually times-out per the configuration setting. MAPI transparent prepopulation is not started with Outlook Anywhere connections. |
Max Connections | Specify the maximum number of virtual MAPI connections to the Exchange Server for Outlook clients that have shut down. Setting the maximum connections limits the aggregate load on all Exchange Servers through the configured SteelHead. The default value varies by model. For example, on a 5520 the default is 3750. You must configure the maximum connections on both the client-side and server-side of the network. The maximum connections setting is only used by the client-side SteelHead. |
Poll Interval (minutes) | Sets the number of minutes you want the appliance to check the Exchange Server for newly arrived email for each of its virtual connections. The default value is 20. |
Time Out (hours) | Specify the number of hours after which to time-out virtual MAPI connections. When this threshold is reached, the virtual MAPI connection is terminated. The time-out is enforced on a per-connection basis. Time-out prevents a buildup of stale or unused virtual connections over time. The default value is 96. |
Enable MAPI over HTTP Optimization | Select on a client-side SteelHead to enable bandwidth and latency optimization for the MAPI over HTTP transport protocol. You must also create an in-path rule using the Exchange Autodetect latency optimization policy to differentiate and optimize MAPI over HTTP traffic. Microsoft implemented the MAPI over HTTP transport protocol in Outlook 2010 update, Outlook 2013 SP1, and Exchange Server 2013 SP1. You must enable SSL optimization and install the server SSL certificate on the server-side SteelHead. Both the client-side and server-side SteelHeads must be running RiOS 9.2 or later to receive full bandwidth and latency optimization. If you have SteelHeads running both RiOS 9.1 and 9.2, you will receive bandwidth optimization only. To view the MAPI over HTTP optimized connections, choose Reports > Networking: Current Connections. A successful connection appears as MAPI-HTTP in the Application column. |