Using Applications
This topic describes how to classify network traffic using application definitions and groups. It includes these sections:
Application overview
Applications are networked services that run in the internal network or on the internet. Application definitions are a way to attach a business relevancy to all traffic that goes through your network. A separate application definition allows you to configure multiple rules using the same application.
Application definitions also let you group applications, so that you can configure and reuse a single rule for multiple applications with similar characteristics and requirements. Using an application group means that you don’t have to repeat the application definition for each rule, which can reduce the number of rules significantly.
You can regulate access to applications using policy rules, as described in
Policy controls.
Because an application can act as a target or a destination in a rule, you need to add the application definition in both directions. A rule with a source IP address looks only at the source IP address, so you need to create a rule that uses the destination IP for the reverse direction.
Application groups
For convenient traffic rule and security policy creation, SCM predefines a number of application groups like Business or Web Services. When you use an application group in a traffic rule, a single rule can handle many applications based on similar properties. For example, the Business Voice application group classifies all traffic that requires low latency and a high queue priority.
Application groups simplify the configuration and minimize the number of rules needed, providing better scalability.
For details on traffic rules, see
To create a traffic rule.
To view the complete list of application groups
• Choose Applications > Groups.
Application groups page
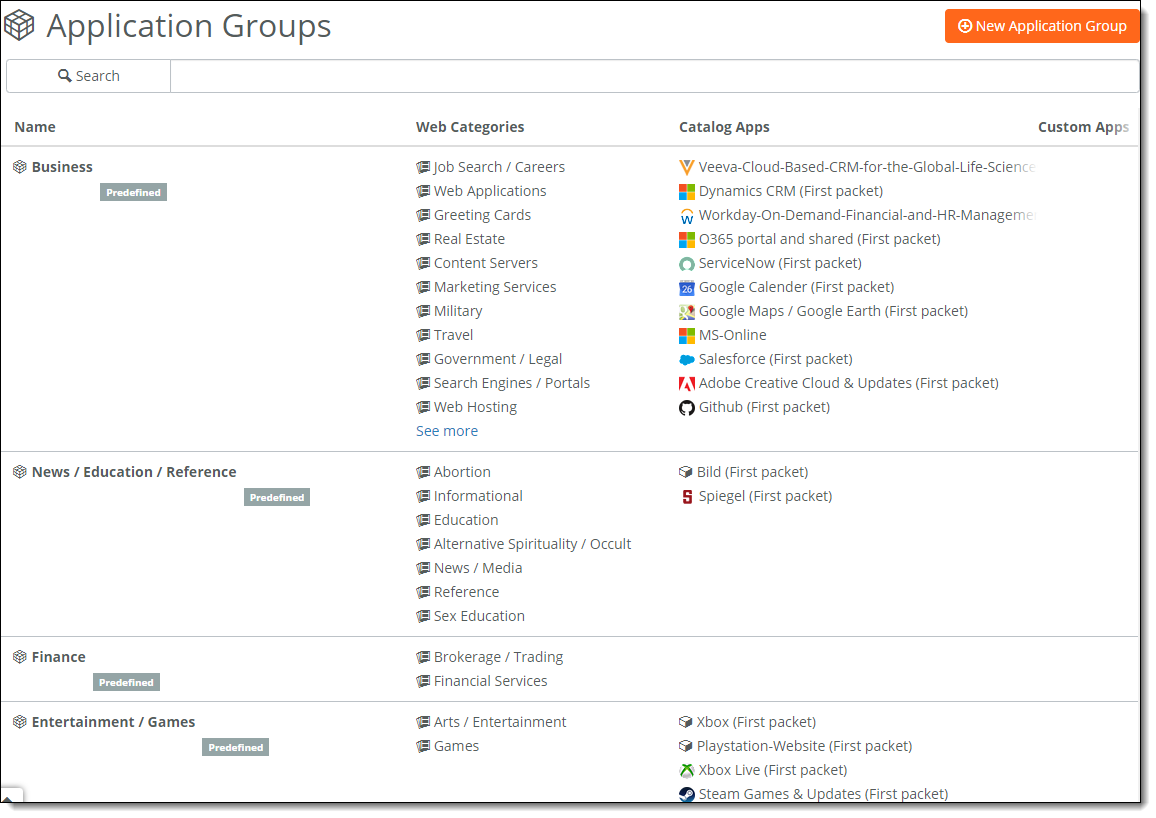
A web category catalog is available to include sites that aren’t covered by a specific application. You can add web categories to application groups.
To view a complete list of web categories
1. Choose Applications > Groups.
2. Select an application group.
3. Select the Web categories tab for that group.
This table describes some default application groups, web categories, and sample applications, but it does not provide an exhaustive list. See the Applications Group page for the most up-to-date app groups, web categories, and apps associated with a group.
Group | Web categories | Content types | Sample applications and protocols |
Business | Business / Economy Government / Legal Military Political / Activist Groups Computers / Internet Search Engines / Portals Job Search / Careers Real Estate Restaurants / Dining / Food Travel Vehicles Web Applications Web Hosting Translation Content Servers Greeting Cards Marketing Services Ecology / Nature Animals / Pets | Includes a wide range of applications focused on business use. | Captures apps such as Google Calendar, Google Maps / Google Earth, Salesforce, Wunderlist, DATEV. |
Images/Photography | Open Image / Media Search Photo Searches | Includes photo and image searches, online photo albums, digital photo exchange, and image hosting. | Captures applications such as Flickr, Picasa, 500px. |
Social Networking | Social Networking Personal Pages / Blogs | Includes websites that enable people to connect with others to form an online community. Instant messaging, file sharing and blogs are common features of social networking sites. | Captures applications such as Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, LinkedIn, Tinder, MySpace. |
Video/Media/TV | Media Sharing TV / Video Streams | Includes websites that allow sharing of media and have a low risk of including objectionable content such as adult or pornographic material. Also includes websites that provide streams or downloads of television, movie, webcam, or other video content that exceeds 15 minutes. | Captures content such as Twitch, Hulu, Netflix, YouTube, Vimeo, Sky / SkyGo, Amazon Instant Video / Lovefilm, Online TV Recorder (OTR), Maxdone, Plex Media, MyVideo, SAVE.TV, and Zattoo TV. |
Application catalog
SCM provides a constantly updated catalog of public applications that are available on the internet. For example, Facebook or Salesforce. Every catalog application is assigned to a default predefined application group.
The catalog provides an efficient and accurate way to identify applications for advanced classification of network traffic.
To determine the default predefined group for a specific application
1. Choose Applications > Applications Catalog.
2. Start typing the application name in the search field to narrow the list.
Custom applications
Creating a custom application means that you group together a set of criteria to match certain traffic. You define custom applications to set up access policies for internal services, or specific internet-based services. Internal applications are typically related to a registered server device or device group; however, you can also define applications based on zones, IP addresses, ports, or host/domain names.
If you configure a hostname-based custom application with a large number of entries, it will have an impact on performance.
To define custom applications
1. Choose Applications > Custom.
2. Click Add Application.
3. Complete the name and description.
4. Select the application type from the drop-down list: Device, Device Group, Zones, IP/Ports, or Hostnames (Internet Only). The traffic characteristics change according to the type of application.
Target devices must be preregistered, either manually or through the self-registration portal. For details, see
To register a device.
5. Complete the application characteristics as needed for the app type.
Custom apps appear in the Custom Apps column of the Application Group page.
To create a remote desktop application for a Windows 2012 Active Directory server in a data center
1. Choose Application > Custom.
2. Click Add Application.
3. Name the application RDP_AD.
4. Describe the application as RDP to Active Directory in DC.
5. Select Device as the application type.
6. Select the relevant server from the device list. For example, AD on W3K12 Server in DC.
7. Click On to limit the TCP/UDP ports.
8. Add port 3389.
9. Click Submit.
Custom application for an Active Directory server using port 3389

After defining the application, you can use it in a rule that defines the policy for internal users and devices. In this example, you define a rule to allow the laptop administrator access to the RDP Active Directory server in the data center. For details, see
Outbound and internal rules.
Traffic flow classification
The Riverbed Deep Packet Inspection (DPI) engine can identify and classify business-critical and nonessential network traffic beginning with the first packet of the traffic flow. Some applications can be detected on the first packet; these applications are identified in the application catalog with “1st packet.” Other applications can only be detected after some data have been exchanged, usually on the fourth or fifth packet.
Traffic flow classification for firewalled connections
SteelHead SD appliances, SDI-2030 gateways, and SDI-5030 gateways take longer to apply security firewall rules using DPI. The TCP RST packet for a firewalled connection is sent only after DPI is complete. This ensures that a higher priority DPI-based firewall rule is honored correctly, rather than matching a lower priority IP/port-based firewall rule and incorrectly denying the connection. The DPI can take a while (up to 20 packets in SCM 2.11.1 and later) before SteelConnect applies the firewall rule for a given connection.
Traffic flow classification for custom applications
SteelHead SD appliances, SDI-2030 gateways, and SDI-5030 gateways have different traffic flow classification behavior than the SDI-130, SDI-330, and SDI-1030 gateways.
• On SDI gateways, flows are classified as the first matching application. Classification stops after the first match. Custom applications, such as IP/port based applications, have a higher priority than catalog applications.
• On SteelHead SD appliances and SDI-2030/SDI-5030 gateways, each flow can be classified as multiple applications at once.



