Configuring ASBR Routing Policies on SteelHead SD
This topic describes how to configure autonomous system boundary routers (ASBR) and route policies on SteelHead SD 2.0. It includes these sections:
Introducing ASBR-full route policies on SteelHead SD
SteelHead SD appliances act as a full ASBR when they are located at the branch. ASBR-full routing policies are supported on SteelHead SD 570-SD, 770-SD, 3070-SD appliances and the SteelConnect SDI-2030 gateway located at the branch. ASBR-full support is not available on SteelConnect SDI-130/330/1030 and virtual gateways.
An ASBR is a router that is connected to several autonomous systems (ASs) using multiple protocols. Typically, ASBRs are connected via an exterior routing protocol (for example, BGP). An ASBR can also connect LAN routers through an interior gateway protocol (IGP), such as OSPF within its own AS. Basically, with an ASBR you are distributing routes from BGP to OSPF and from OSPF to BGP. An ASBR can also distribute static and connected routes into these protocols.
For example, if you have a SteelHead SD on Branch-1 with eBGP configured on the WAN uplink and OSPF configured on the LAN zones. The SteelHead SD can distribute LAN routes to the WAN and WAN routes to the LAN. This method of redistributing routes received via one routing protocol through another protocol is called route redistribution or route injection.
ASBR deployment in branch 1
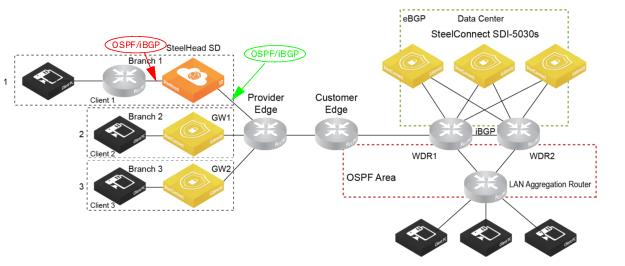
SteelHead SD provides:
•BGP redistribution - Support includes static and connected route redistribution, OSPF route redistribution, and default route redistribution to BGP neighbors.
•OSPF redistribution - Support includes static and connected route redistribution, OSPF route redistribution, and default route redistribution.
ASBR routing policies are available only on underlay branch networks.
What are routing policies?
Routing polices are rules that are applied when routes are distributed between the routers. Creating routing policies enables you to redistribute BGP, OSPF, static, and connected routes.
ASBR routing policies are not policy-based routing where routing decisions are made while directing the traffic.
Creating routing policies enables you to apply certain rules and route attributes while redistributing BGP, OSPF, static and connected routes. You can create route-maps for the following purposes:
•Route injection in OSPF.
•Default route origination in OSPF.
•Static and connected route injection BGP.
•OSPF route injection in BGP.
•Policies at the BGP neighbor level.
•Default route origination in BGP for a neighbor.
Each route map clause has two types of values:
•A match value selects routes to which the clause should be applied.
•A set value modifies information that will be redistributed into the target protocol.
For each route that is being redistributed, the router evaluates the match criteria of a clause in the route map. If the match criteria succeed, then the route is redistributed and some of the attributes may be modified by the set clause. If the route doesn’t match any clause in a route map, then the route redistribution is denied.
Once configured, the route-maps can be applied to satisfy the needs of these use-cases:
•Route Injection in OSPF - OSPF redistributes static, connected, and BGP routes. This route-map category contains only a match criteria. The route map depends on the following objects:
–IP prefix lists
–Interface (all zones/uplinks associated with SteelHead SD appliances in the given organization)
•Default Route Origination in OSPF - Redistributes the default route in OSPF. This category of route-map contains both match and set criteria. This is the simplest route-map category that is not dependent on other objects.
•Static and Connected Route Injection in BGP - Redistributes static and connected routes in BGP using a list of IPv4 prefixes. This route-map category contains both match and set criteria. Also dependent on the following objects:
–IPv4 prefix lists
–Interface
•OSPF Route Injection in BGP - Redistributes OSPF routes in BGP using a list of IPv4 prefixes. This category of route map contains both match and set criteria.
•Route-Policy for BGP Neighbor - Redistributes routes for BGP neighbors using a community list and list of IP next-hop prefixes. This route-map category contains both match and set criteria. The match criteria in this use case is dependent on:
–Community list
–Prefix list
•Default Route Origination in BGP -Redistributes the route in BGP. This route-map category contains both match and set criteria. There are not any dependent objects for this type of route map.
Basic steps
Perform these basic steps to configure ASBR routing polices.
You can’t create dynamic routing policies for SteelHead SD 570-SD, 770-SD, and 3070-SD appliances located at the branch.
5. Configure route maps by specifying the available use cases. For example, create a route map for a routing policy to establish BGP neighbors. For details, see
Creating routing IPv4 prefix lists 6. Configure inbound and outbound route maps and prefixes for BGP neighbors using the configured route maps. For details on configuring BGP neighbors, see
Configuring BGP on SteelHead SD.
Creating routing IPv4 prefix lists
An IPv4 prefix list contains a list of IPv4 prefixes and a name that is associated for each list.
To create a IPv4 prefix list
1. Choose Routing > IPv4 Prefix Lists.
2. Click New IPv4 Prefix List.
Creating an IPv4 prefix list
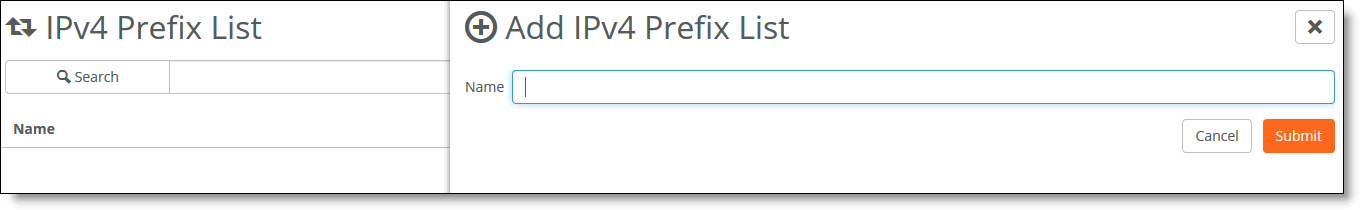
3. Specify the name of the IPV4 prefix list.
4. Click Submit.
5. To define the prefixes for the list, select the list in the IPv4 Prefix List page.
Defining IPv4 prefixes list
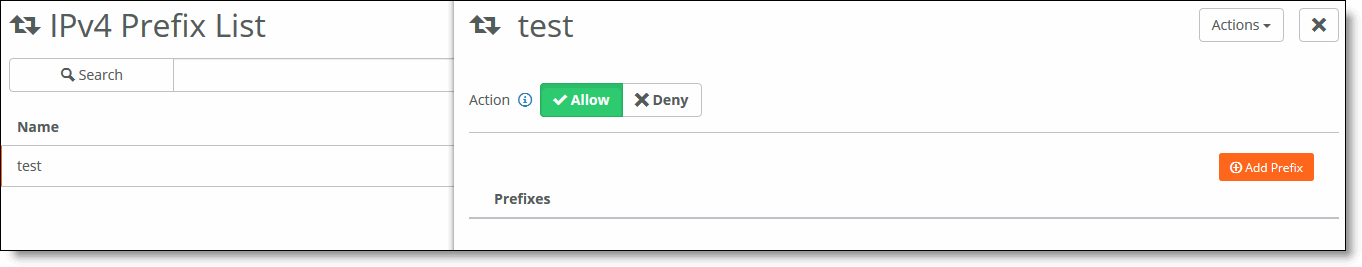
6. Click Allow to distribute only the specified prefixes and deny the rest. Click Deny to stop distribution of the prefixes specified and allow the rest.
7. Click Add Prefix.
Adding a prefix
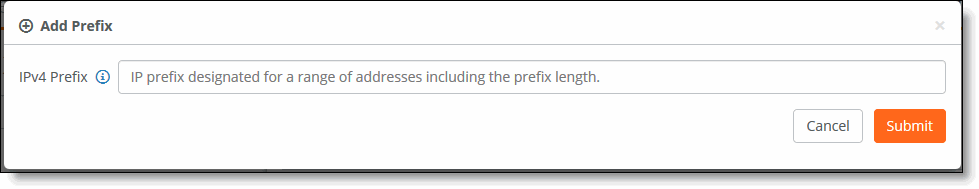
8. Enter the IP prefix designated for the range of addresses to distribute. Use the format: xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx/xx
9. Click Submit.
Click Actions to delete a list.
Creating routing community lists
A BGP community is a group of routes to which a BGP router applies the same policies. You specify the name of the community list and a string that contains values only from a predefined set of keywords and numbers.
To create a community list
1. Choose Routing > Community Lists.
2. Click Add Community List.
Creating a community list
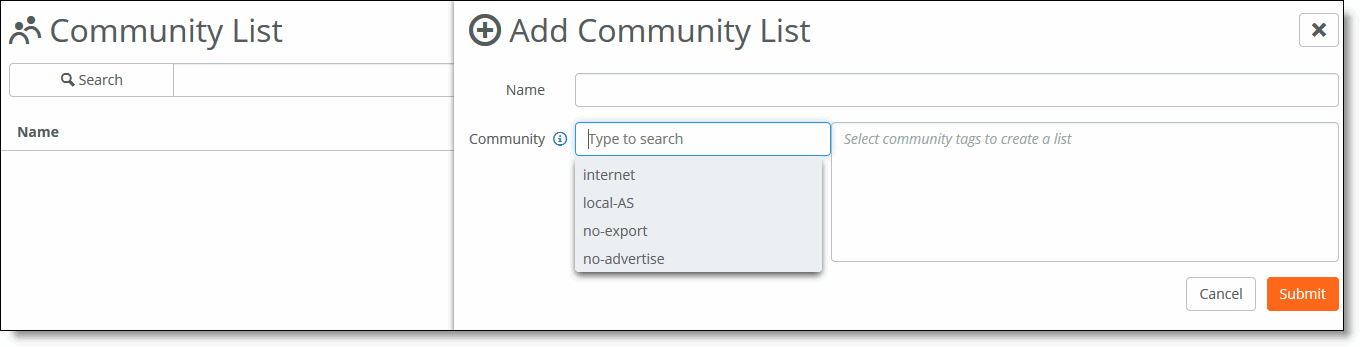
3. Enter a descriptive name for the community list.
4. Click the search selector for community list options. In addition to the keywords below, you can also configure numbers in the range from 1 to 65535 and numbers in AA:NN format where the range for AA and NN is 1 to 65535.
•internet - Advertises this route to the internet community; by default, all prefixes are members of the internet community.
•local-AS - Doesn’t advertise the route to any external peers.
•no-export - Instructs routers not to export a prefix to eBGP neighbors. For instance, subnets of a larger block can be advertised to influence external AS best-path selection, and those not required for this traffic engineering purpose may be tagged NO-EXPORT to prevent them from being leaked to the internet (and thus contributing to unnecessary global routing table growth).
•no-advertise - Instructs a BGP router not to advertise the tagged prefix to any other neighbor, including other iBGP or eBGP routers.
5. Click Submit.
6. To edit a community list, select the list in the Community List page, edit the expressions, and click Submit.
Editing an AS path list
Click Actions to delete a list.
Creating routing AS path lists
You specify the name of the AS path list and define a regular expression that defines the attributes of the AS path.
The AS path list can be used while applying route policies at the BGP neighbor level.
To create an AS path list
1. Choose Routing > AS Path List.
2. Click Add AS Path List to expand the page.
Creating an AS path list
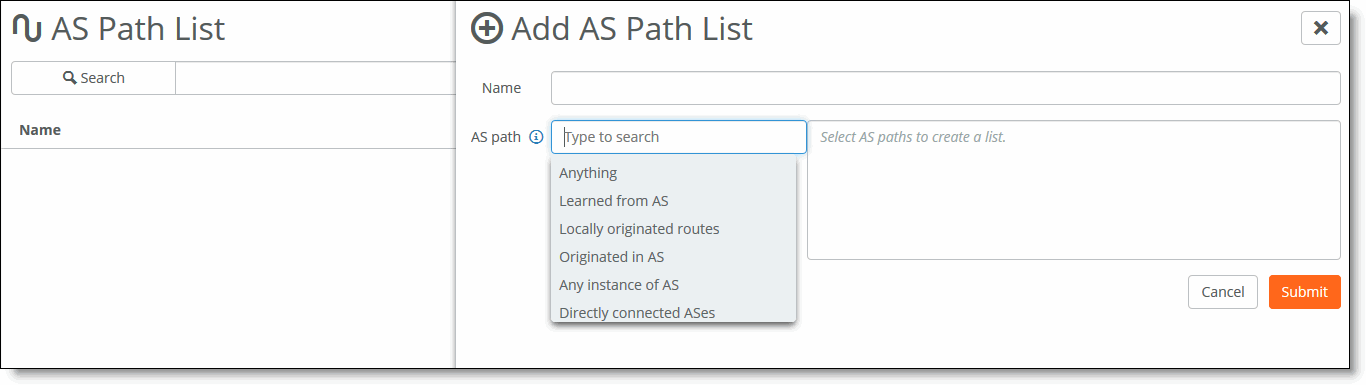
3. Enter a descriptive name for the AS path list.
4. Click the search selector for a list of AS list options. Enter one or more AS numbers from 1 to 4294967295. Separate multiple numbers with a space.
•Anything - Specifies the BGP expression “.*”, which matches anything. The “.*” matches any single character (“.”), and then finds zero or more instances of that single character (“*”).
•Learned from AS - Enter one or more AS numbers from 1 to 4294967295. Separate multiple numbers with a space.
•Locally originated routes - Specifies the BGP expression: “^$”, which matches locally originated routes. “^$” means that the string is null. Within the scope of BGP, the only time that the AS path is null is when you are looking at a route within your own AS that you or one of your iBGP peers has originated.
•Originated in AS - Enter one or more AS numbers from 1 to 4294967295. Separate multiple numbers with a space.
•Any instance of AS - Enter one or more AS numbers from 1 to 4294967295. Separate multiple numbers with a space.
•Directly connected to AS - Specifies the BGP expression “^[0-9]+$”, which matches all routes originated in any directly connected single AS. These are the routes directly originated by the peers of your AS.
5. Click Submit.
6. To edit an AS path list, select the list in the AS Path page, edit the expressions, and click Submit.
Editing an AS path list
Click Actions to delete a list.
Configuring use case route maps
After you configure the prefix list, AS list, and community lists, these lists can be applied to satisfy the needs of particular use cases.
To create use case route maps
1. Choose Routing > Route Maps.
2. Click New Route Map.
Creating route maps
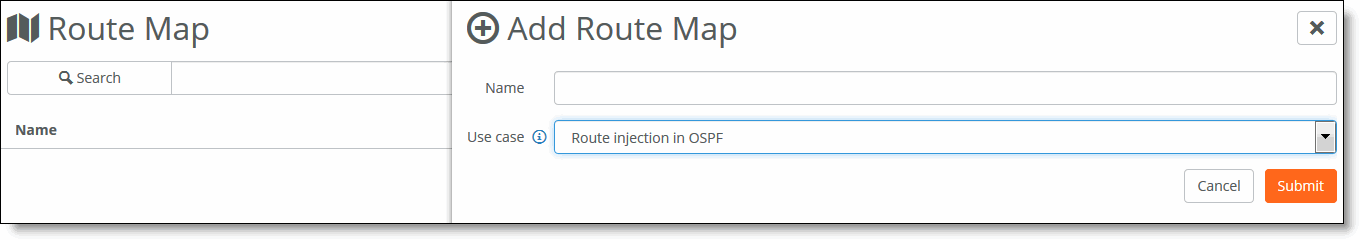
3. Specify the name of the route map.
4. Select a use case from the drop-down list:
•Route injection in OSPF - Allows the creation of match clauses that can be applied during BGP, static, and connected route injection in OSPF.
•Default route origination in OSPF - Allows the creation of match and set clauses that can be used during the default route origination in OSPF.
•Static and connected route injection in BGP - Allows the configuration of match and set clauses that can applied while redistributing static and connected routes in BGP.
•OSPF route injection in BGP - Allows the creation of match and set clauses that can be applied while redistributing OSPF routes in BGP.
•Policies at a BGP neighbor level - Allows the configuration of match and set clauses that can be applied while establishing a BGP neighbor.
•Default route origination in BGP for a neighbor - Allows the configuration of match and set clauses that can be applied while advertising a default route to a BGP neighbor.
5. Click Submit. The route map is displayed on the Route Map page.
6. In the Route map page. Match Criteria and Set Criteria tabs are displayed depending on the match and set requirements for each use case.
Match Criteria and Set Criteria tabs
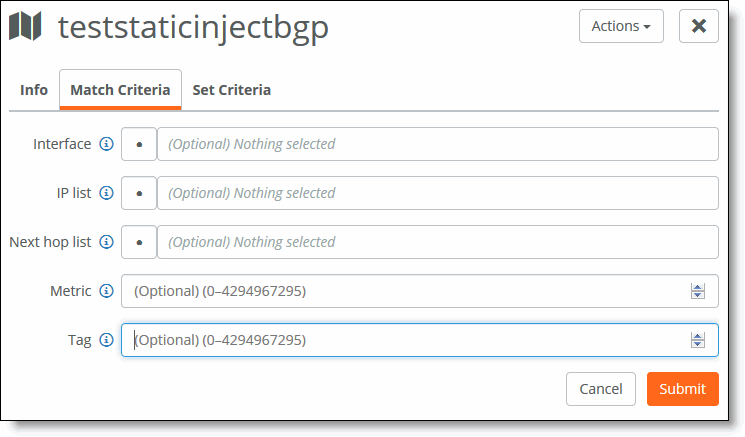
7. Fill out the fields for the Match Criteria and Set Criteria using this table. The criteria differ according to the use case you have chosen.
Use case | Match criteria | Set criteria |
Route injection in OSPF | •Interface- Optionally, select the interface. When the interface matches the next-hop interface of the route, the route qualifies for redistribution by the router. •IP list - Optionally, select an IP list. When a routes prefix address matches a prefix in the list, then that route is qualified for distribution. •Next hop list - Optionally, select the next-hop prefix. When the next-hop address matches the selected address, the route qualifies for distribution by the router. •Metric - Optionally, enter a value from 0 to 4294967295. When a metric value in a route matches this value, the route qualifies for distribution by the router. •Tag - Optionally, enter a value from 0 to 4294967295. When a tag in a route matches this value, the route qualifies for distribution by the router. | No set criteria required. |
Default route origination in OSPF | •Metric - Optionally, enter a value from 0 to 4294967295. When a metric value in a route matches this value, the route qualifies for distribution by the router. •Tag - Optionally, enter a value from 0 to 4294967295. When a tag in a route matches this value, the route qualifies for distribution by the router. | •Tag - Optionally, enter a value from 0 to 4294967295. When a tag in a route matches this value, the route qualifies for distribution by the router. |
Static and connected route injection in BGP | •Interface - Optionally, click the search selector and select the interface. When the interface matches the next-hop interface of the route, the route qualifies for redistribution by the router. •IP list - Optionally, select the IPv4 prefix list. •Next hop list - Optionally, select the next-hop prefix. When the next-hop address matches the selected address, the route qualifies for distribution by the router. •Metric - Optionally, enter a value from 0 to 4294967295. When a metric value in a route matches this value, the route qualifies for distribution by the router. •Tag - Optionally, enter a value from 0 to 4294967295. When a tag in a route matches this value, the route qualifies for distribution by the router. | •AS path - Click On to set the AS path for the route. Specify the AS string as space separated list from 1 to 4294967295. •Tag - If On, then the value is prepended with the AS path of the BGP route. •IP next hop - If On, then updates the IP next-hop address of the routes. Enter the IP address to be used as the next hop. •Self address - If On, under Self address, click On to use the self address as the next-hop address. •Metric - Optionally, enter a value from 0 to 4294967295. When a metric value in a route matches this value, the route qualifies for distribution by the router. •Community - In addition to the keywords below, you can also configure numbers in the range from 1 to 65535 and numbers in AA:NN format where the range for AA and NN is 1 to 65535. –internet –local-AS –no-export –no-advertise •Additive - The specified community string is added to the route’s community string. |
OSPF route injection in BGP | •Interface - Optionally, select the interface. When the interface matches the next-hop interface of the route, the route qualifies for redistribution by the router. •IP list - Optionally, select the IPv4 prefix list. •Next hop list - Optionally, select the next-hop prefix. When the next-hop address matches the selected address, the route qualifies for distribution by the router. •Metric - Optionally, enter a value from 0 to 4294967295. When a metric value in a route matches this value, the route qualifies for distribution by the router. •Metric type - When the type matches the value specified, then that route is qualified to be distributed: –Type 1 - This type includes the external cost to the destination as well as the cost (metric) to reach the AS boundary router. –Type 2 - This type uses only the external cost to the destination and ignores the cost (metric) to reach the AS boundary router. •Tag - Optionally, enter a value from 0 to 4294967295. When a tag in a route matches this value, the route qualifies for distribution by the router. | •AS path - Click On to set the AS path for the route. Specify the AS string as space separated list from 1 to 4294967295. •Tag - If On, then the value is prepended with the AS path of the BGP route. •IP next hop - If On, then updates the IP next-hop address of the routes. Enter the IP address to be used as the next hop. •Self address - If On, under Self address, click On to use the self address as the next-hop address. •Metric - Optionally, enter a value from 0 to 4294967295. When a metric value in a route matches this value, the route qualifies for distribution by the router. •Community - In addition to the keywords below, you can also configure numbers in the range from 1 to 65535 and numbers in AA:NN format where the range for AA and NN is 1 to 65535. –internet –local-AS –no-export –no-advertise •Additive - The specified community string is added to the route’s community string. |
Policies at the BGP neighbor level | •Community - Optionally, select the community list. A BGP route is permitted if it belongs to the specified community string. •Next hop list - Optionally, select the next-hop prefix. When the next-hop address matches the selected address, the route qualifies for distribution by the router. •Metric - Optionally, enter a value from 0 to 4294967295. When a metric value in a route matches this value, the route qualifies for distribution by the router. •Tag - Optionally, enter a value from 0 to 4294967295. When a tag in a route matches this value, the route qualifies for distribution by the router. | •AS path - Click On to set the AS path for the route. Specify the AS string as space separated list from 1 to 4294967295. •Tag - If On, then the value is prepended with the AS path of the BGP route. •IP next hop - If On, then updates the IP next-hop address of the routes. Enter the IP address to be used as the next hop. •Self address - If On, under Self address, click On to use the self address as the next-hop address. •Metric - Optionally, enter a value from 0 to 4294967295. When a metric value in a route matches this value, the route qualifies for distribution by the router. •Local-preference - Optionally, enter the value from 0 to 4294967295 to set the value to the received routes. If the iBGP speaker receives multiple routes to the same destination, then the route with the highest value is preferred. •Tag - Optionally, enter a value from 0 to 4294967295. When a tag in a route matches this value, the route qualifies for distribution by the router. •Community - In addition to the keywords below, you can also configure numbers in the range from 1 to 65535 and numbers in AA:NN format where the range for AA and NN is 1 to 65535. –internet –local-AS –no-export –no-advertise •Additive - The specified community string is added to the route’s community string. |
Default route origination in BGP for a neighbor | •Metric - Optionally, enter a value from 0 to 4294967295. When a metric value in a route matches this value, the route qualifies for distribution by the router. •Tag - Optionally, enter a value from 0 to 4294967295. When a tag in a route matches this value, the route qualifies for distribution by the router. | •AS path - Click On to set the AS path for the route. Specify the AS string as space separated list from 1 to 4294967295. •Tag - If On, then the value is prepended with the AS path of the BGP route. •IP next hop - If On, then updates the IP next-hop address of the routes. Enter the IP address to be used as the next hop. •Self address - If On, under Self address, click On to use the self address as the next-hop address. •Metric - Optionally, enter a value from 0 to 4294967295. When a metric value in a route matches this value, the route qualifies for distribution by the router. •Tag - Optionally, enter a value from 0 to 4294967295. When a tag in a route matches this value, the route qualifies for distribution by the router. •Community - Specify the community list to be set for this route: –internet –local-AS –no-export –no-advertise •Additive - The specified community string is added to the route’s community string. |
8. Click Submit.











