About NFS settings
NFS settings are under Optimization > Protocols: NFS.
NFS settings
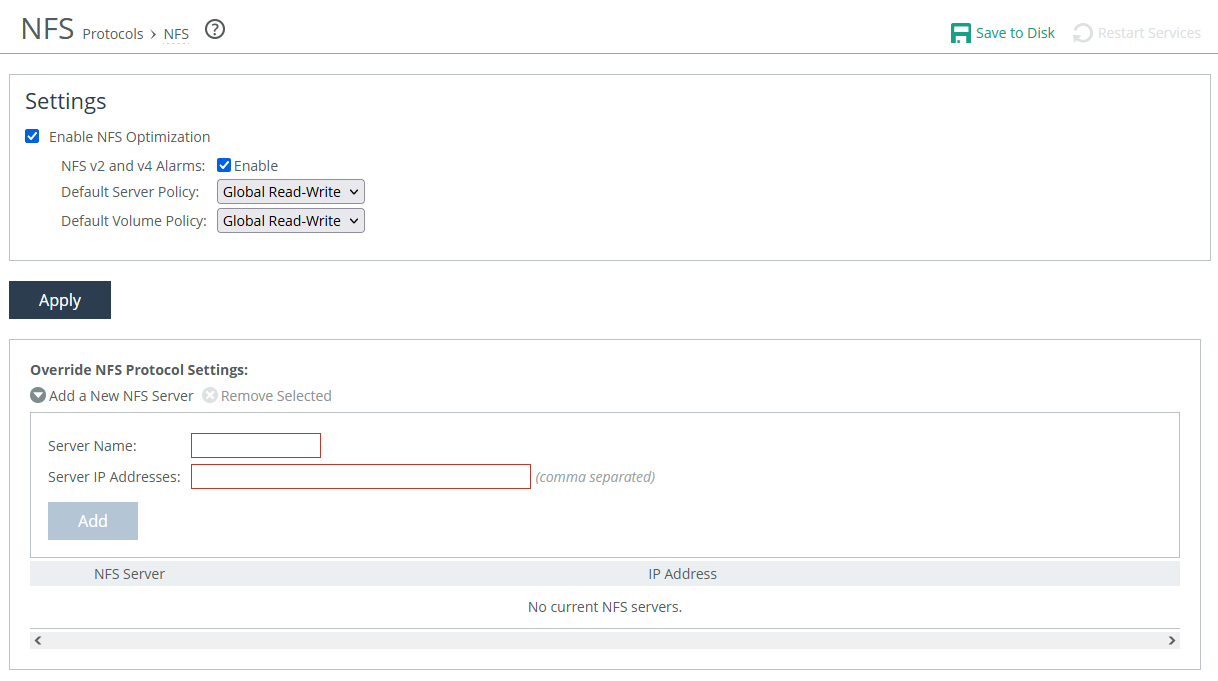
Enable NFS Optimization provides latency optimization for NFS in high latency environments. Enabled by default.
NFS v2 and v4 Alarms enables an alarm that triggers when the appliance detects NFSv2 and NFSv4 traffic. The triggered alarm changes the appliance’s health status to Needs Attention until you reset the alarm. The option to reset the alarm appears only after it has been triggered.
Default Server Policy and Default Volume Policy specifies policies used to configure connections to servers or volumes that don’t already have one.
• Custom specifies a custom policy.
• Global Read-Write provides data consistency rather than performance. All of the data can be accessed from any client, including LAN-based NFS clients (which don’t go through SteelHeads) and clients using other file protocols such as CIFS. This option severely restricts the optimization that can be applied without introducing consistency problems. Default.
• Read-only specifies that clients can read data from NFS servers or volumes but can’t make changes.
Server and volume overrides
Add specific servers to the override table, and then edit their settings to create server and volume-specific configurations that override the default settings. The appliance uses the global settings or all other NFS servers and volumes.
Server Name specifies a display label for the server.
Server IP Addresses specifies the IP addresses of the server, separated by commas. If you have configured IP aliasing (multiple IP addresses) for an NFS server, specify all of the server IP addresses.
Default Server Policy and Default Volume Policy are the same as for the global settings.
Default Volume enables the default volume configuration for the server.
Volume override settings appear after you add a server. For convenience while configuring volume-specific settings, an uneditable list of volumes available on the selected NFS server also appears.
FSID specifies the volume File System ID. An FSID is a number NFS uses to distinguish mount points on the same physical file system. Because two mount points on the same physical file system have the same FSID, more than one volume can have the same FSID.
Policy specifies the policy used for the volume. Options are functionally the same as those in the global settings.
Root Squash turns off acceleration for the root user on NFS clients. When the root user accesses an NFS share, its ID is squashed (mapped) to another user (most commonly “nobody”) on the server. Root squash improves security because it prevents clients from giving themselves access to the server file system.
Permission Cache enables the permission cache, where the SteelHead stores file read data and uses it to respond to client requests. For example, if a user downloads data and another user tries to access that data, the appliance ensures that the second user has permission to read the data before releasing it.
Default Volume enables the default volume configuration for this server.


