Citrix ICA Optimization
To consolidate operations, some organizations deploy desktop and application virtualization solutions such as Citrix XenDesktop and XenApp in the data center. Citrix uses a proprietary protocol called Independent Computing Architecture (ICA) to provide connectivity between its clients (called receivers) and its published applications and desktops.
This chapter includes the following sections:
Overview of Citrix ICA
RiOS 6.0 and later provide these optimizations:
• Classification and shaping of Citrix ICA traffic using Riverbed QoS to improve the end-user desktop experience
• Bandwidth reduction of compressed and encrypted Citrix ICA traffic using SteelHead Citrix optimization
RiOS 7.0 and later provide these optimizations:
• Latency optimization for client drive mapping in the Citrix ICA session
• Optimization of Citrix sessions over SSL using Citrix Access Gateway (CAG)
• SteelHead Citrix Optimization for multi-port ICA traffic
RiOS 7.0.4 and later provide traffic optimization for enhanced data reduction for small Citrix packets.
Citrix Version Support
RiOS 6.0 and later provide support for the following Citrix software components.
Citrix Receiver or ICA client versions:
• Online plug-in version 9.x
• Online plug-in version 10.x
• Online plug-in version 11.x
• Online plug-in version 12.x
• Online plug-in version13.x (Receiver version 3.x)
• Receiver for Windows version 4.x
Citrix XenDesktop:
• XenDesktop 4
• XenDesktop 5
• XenDesktop 5.5
• XenDesktop 5.6
• XenDesktop 7.x
Citrix XenApp:
• Presentation Server 4.5
• XenApp 5
• XenApp 6
• XenApp 6.5
• XenApp 7.x
In addition, RiOS supports encrypted and compressed Citrix ICA traffic optimization.
For information about configuring Citrix optimization, see the SteelHead Management Console User’s Guide, the Riverbed Command-Line Interface Reference Manual, and the white paper Optimizing Citrix ICA Traffic with RiOS 8.0 (June 2013).
Citrix ICA Traffic Optimization with SteelHeads
Citrix ICA traffic is usually transported on TCP port 1494. Citrix ICA traffic is transported on TCP port 2598 if Citrix session reliability is enabled. When you enable Citrix session reliability, the client tunnels its ICA traffic inside the Common Gateway Protocol (CGP) port 2598.
For more information about Citrix session reliability, go to
http://support.citrix.com/article/CTX104147.
To configure Citrix ICA traffic optimization with a SteelHead
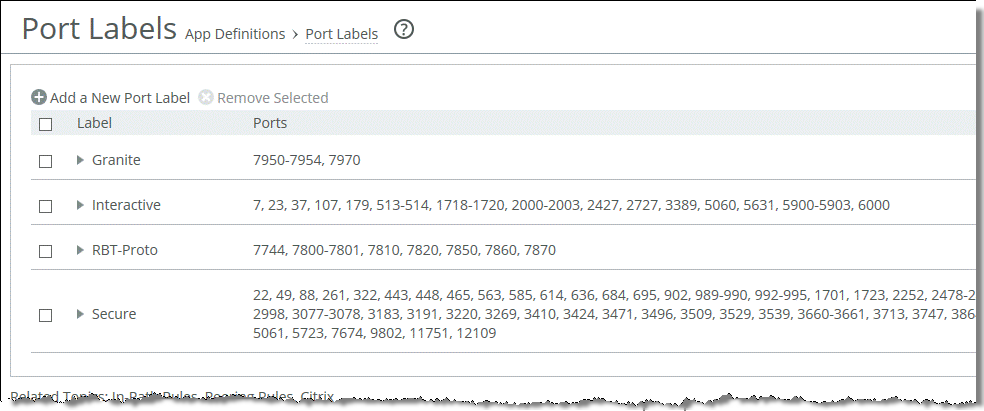
1. From the SteelHead Management Console, choose Networking > App Definitions: Port Labels and remove ports 1494 and 2598 from the Interactive port label.
Figure: Port Labels
2. Choose Optimization > Protocols: Citrix.
Figure: Citrix Optimization Settings
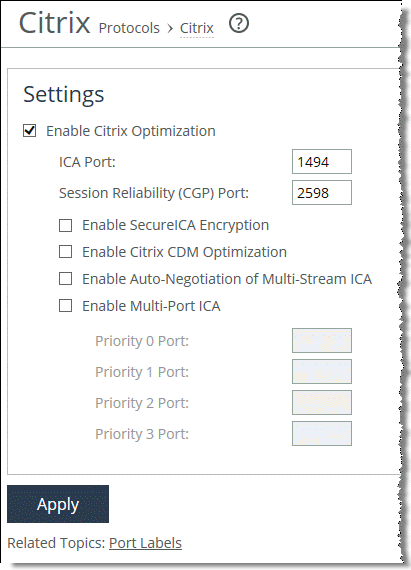
3. Select Enable Citrix Optimization.
4. Specify the ICA port and session reliability port.
5. Click Apply to apply the settings to the running configuration.
6. Restart the optimization service.
You must perform this configuration on both the client-side and server-side SteelHeads.
Citrix SecureICA Encryption
SecureICA is a Citrix ICA protocol feature that encrypts the session data transmitted between Citrix clients and servers. By default, all Citrix ICA sessions have SecureICA set to basic ICA protocol encryption. The basic ICA protocol encryption setting obfuscates data but does not provide industry standard encryption. Other settings are available to increase the level of encryption using the RC5 algorithm.
RiOS supports optimization of Citrix ICA sessions with SecureICA set to RC5 40-, 56-, and 128-bit encryption. By default, RiOS can optimize Citrix ICA traffic with SecureICA set to basic ICA protocol encryption. You must enable SecureICA encryption to allow RiOS to optimize ICA sessions with SecureICA encryption set to RC5 on both the client-side and the server-side SteelHeads.
To enable RiOS to optimize Citrix Sessions with SecureICA encryption set to RC5 SecureICA
1. From the SteelHead Management Console, choose Optimization > Protocols: Citrix.
2. Select Enable Citrix Optimization.
3. Specify the ICA port and session reliability port.
4. Select Enable SecureICA Encryption.
5. Click Apply to apply the settings to the running configuration.
6. Restart the optimization service.
You must perform this configuration on both the client-side and server-side SteelHeads.
Citrix Drive-Mapping Optimizations
Client drive mapping (CDM) is a Citrix ICA protocol feature that enables users to access their local drives (such as floppy disk drives, network drives, USB drives, CD-ROM drives, and hard disk drives) from within an ICA session. When you use CDM to access a mapped drive within an ICA session, the end-user desktop experience can be negatively affected by the underlying network performance.
RiOS 7.0 and later support CDM latency optimization. CDM latency optimization improves the end-user desktop experience when reading and writing files on a mapped drive in the following ways:
• Reading a file (client-to-server transfer) - The SteelHeads monitor the CDM virtual channel for files being read from the client drive. When the client-side SteelHead detects a chunk of file data being requested, it begins to read ahead and sends the file data in larger chunks to the server-side SteelHead. The server-side SteelHead buffers the file data until it is requested. This effectively eliminates many round trips across the WAN and improves the user desktop experience.
• Writing a file (server-to-client transfer) -The SteelHeads monitor the CDM virtual channel for files written to the client drive. Whenever the server sends file data to the client, the server-side SteelHead immediately sends an acknowledgment to the server so that the server continues to send file data quickly. Without this local acknowledgment, the server does not send any more data until it receives the acknowledgment from the client. This optimization eliminates round trips across the WAN, which improves the user desktop experience.
CDM latency optimization is available when both the client-side and server-side SteelHeads are running RiOS 7.0 or later. You cannot apply CDM latency optimization to Citrix sessions that use Citrix session reliability.
Note: File transfers greater than 1 GB do not perform as well as smaller file transfers.
To configure Citrix CDM latency optimization
1. Choose Optimization > Protocols: Citrix.
2. Select Enable Citrix Optimization.
Figure: Enable Citrix Optimization
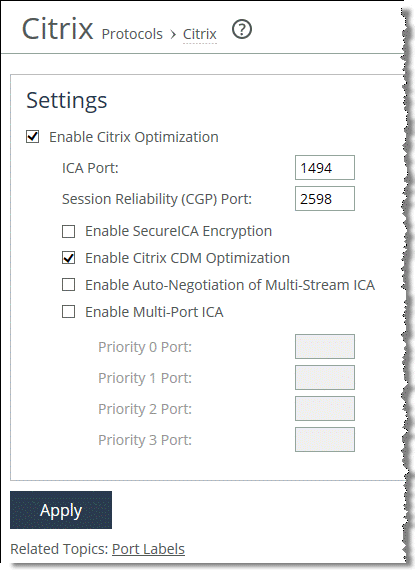
4. Click Apply to apply the settings to the running configuration.
5. Restart the optimization service.
To configure CDM with the CLI, use the following commands:
(config)# protocol citrix cdm enable
(config)# service restart
You must perform this configuration on both the client-side and server-side SteelHeads.
Citrix Multi-Stream ICA Traffic Optimization with SteelHeads
This section requires that you be familiar with the Citrix ICA protocol and how to configure your Citrix server. This section includes the following topics:
Citrix Virtual Channels and Traffic Priorities
The ICA traffic within a Citrix session comprises of many categories of traffic called virtual channels. A virtual channel provides a specific function of Citrix ICA remote computing architecture, such as print, CDM, audio and video. The ICA traffic within a Citrix session is also categorized by priority, in which virtual channels carrying real-time traffic, such as audio and video, are flagged with higher priority than virtual channels carrying bulk transfer traffic such as print and CDM. The ICA priority groups are as follows:
• Very High (priority 0)
• High (priority 1)
• Medium (priority 2)
• Low (priority 3)
For more information about Citrix ICA virtual channel, go to the Citrix Knowledge Base article CTX116890 at
http://support.citrix.com/article/CTX116890.
Single-Stream and Multi-Stream ICA
By default, a Citrix session uses a single TCP connection to carry traffic for all virtual channels and all priority groups. This is referred to as single-stream ICA.
XenApp 6.5 and XenDesktop 5.5 introduced a new feature, called multi-stream ICA, that enables use of multiple TCP connections to carry traffic for a Citrix session. Multi-stream ICA is available only when you enable Citrix session reliability. Multi-stream ICA carries traffic on port 2598 and three other user-configurable ports as defined in the multi-port Citrix computer policy. Each port represents an ICA priority group and enables you to apply true network-based QoS policies to the priority groups for the virtual channel traffic that they carry.
For more information about enhanced QoS with multi-stream ICA, go to
http://blogs.citrix.com/2011/08/25/enhanced-qos-via-multi-stream-ica/.
This table shows the association of Citrix ICA priority groups to the various ICA virtual channels for multi-stream ICA.
Value | Priority | Description |
0 | Very high | Audio |
1 | High | Thin Wire/DX command remoting, seamless, MSFT TS licensing; SmartCard redirection; control virtual channel; and end-user experience monitoring |
2 | Medium | MediaStream (Windows media and Flash), USB redirection, clipboard, and CDM |
3 | Low | Printing, client COM port mapping, LPT port mapping, and legacy OEM virtual channels |
You must use these software components to enable and optimize multi-stream and multi-port ICA:
• RiOS 7.0 or later
• Citrix XenApp 6.5 or later
• Citrix XenDesktop 5.5 or later
• Citrix Receiver 3.x (online plug-in 13.0) or later
In addition, you must enable Citrix session reliability. Citrix session reliability is enabled by default in XenApp 6.5 and XenDesktop 5.5.
For more information about Citrix session reliability, go to
http://support.citrix.com/article/CTX104147.
The following example shows how to configure multi-stream and multi-port ICA in XenApp 6.5.
To configure XenApp 6.5 multi-stream and multi-port ICA traffic optimization with a SteelHead
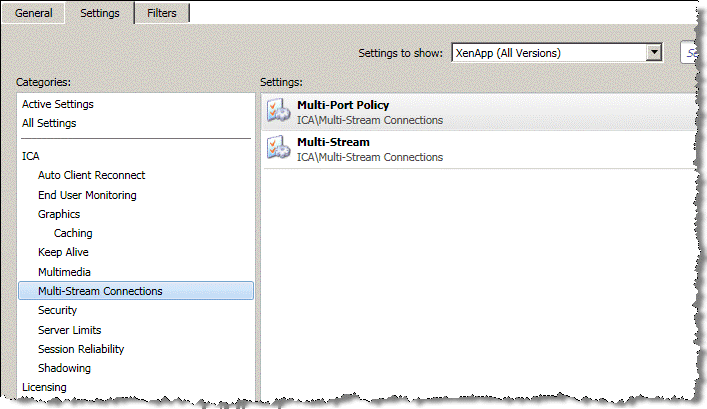
1. From the Citrix AppCenter or Windows Group Policy Editor, enable multi-stream ICA in the Citrix computer policy.
Figure: Citrix Computer Policy for Multi-Stream and Multi-Port ICA
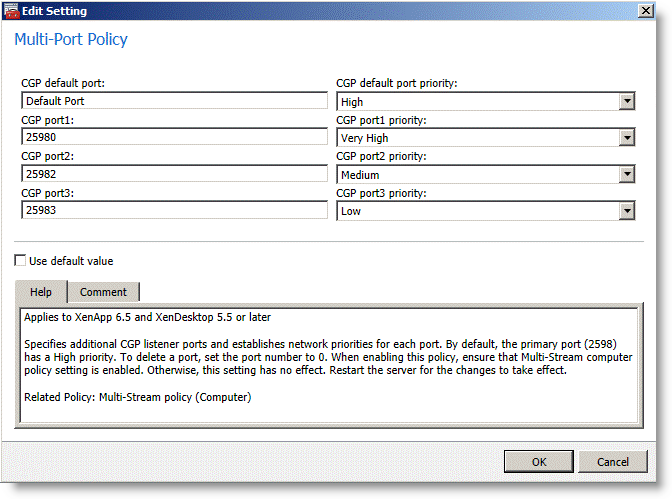
2. Configure the multi-port policy in the Citrix computer policy.
You cannot change the default port assigned to high priority. The default is mapped to the Citrix CGP port 2598 for session reliability.
Figure: Citrix Computer Policy for Multi-Port ICA
3. Enable multi-stream ICA in the Citrix user policy.
Figure: Citrix User Policy for Multi-Stream ICA
4. Restart the XenApp Server to apply the Citrix computer policy. Log in the user once more to apply the Citrix user policy.
5. From the SteelHead Management Console, choose Optimization > Protocols: Citrix and specify the ports according to what is configured in the multi-port policy.
Figure: Enable Multi-Port ICA
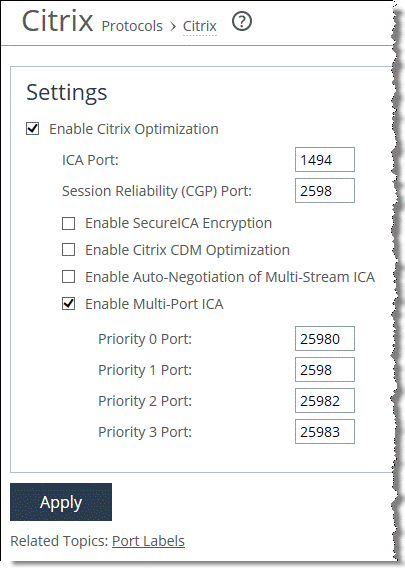
6. Click Apply to apply the settings to the running configuration.
7. Restart the optimization service.
You must repeat this configuration on both the client-side and the server-side SteelHead.
8. Log in to the XenApp server and launch a published application.
From the Current Connections page in the SteelHead Management Console, you see four unique TCP connections for the Citrix session, according to the TCP ports that you have configured in the multi-port policy.
Figure: Current Connections Report
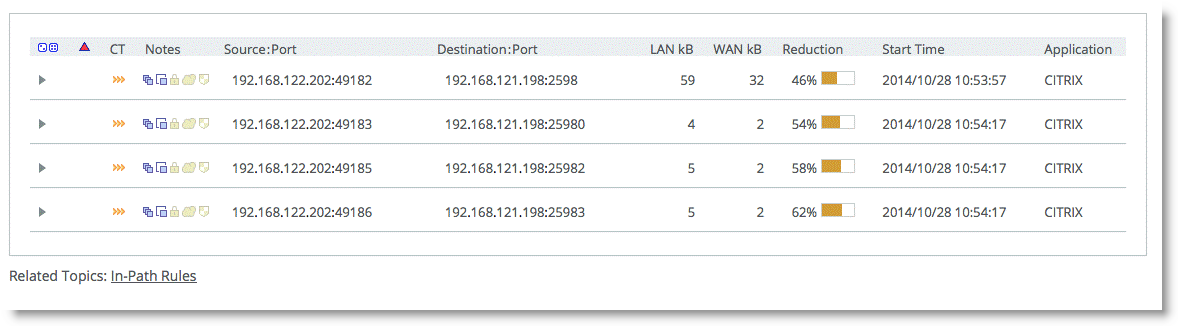
You do not need to change your current QoS configuration if you already have rules to prioritize Citrix ICA traffic on port 2598. However, you must configure additional QoS rules if you want to prioritize Citrix ICA traffic on the user-configurable ports that you have configured in the multi-port Citrix computer policy.
QoS Classification for Citrix Traffic
RiOS 6.0 and later enable you to classify Citrix traffic using QoS to prioritize the delivery of Citrix ICA traffic according to the ICA priority groups. QoS classification for Citrix traffic is beneficial in mixed-use environments in which Citrix users perform printing and use client drive-mapping features. Using QoS to classify Citrix traffic in a mixed-use environment improves the desktop computing experience for end users.
These RiOS QoS capabilities ensure optimal delivery of Citrix traffic over the network:
• Latency priority - Latency priority enables you to assign Citrix interactive traffic a higher priority than print or CDM traffic. A typical priority setting for interactive Citrix sessions, such as screen updates, is real-time or interactive. Remember that priority is relative to other classes in your QoS configuration.
• Bandwidth allocation for traffic shaping - When configuring QoS, you must allocate an appropriate amount of bandwidth for each QoS traffic class. The amount you specify is divided equally among all traffic flows with that class of traffic. Bandwidth allocation is important to ensure that a given traffic class has a minimum amount of bandwidth to perform on the network. While at the same time, the amount of bandwidth assigned to that traffic must not overrun the network and starve out other applications competing for network bandwidth.
For more information about configuring QoS, see the SteelHead Deployment Guide.
Note: RiOS 9.0 or later does not support Packet-Order Queue. Riverbed recommends that you use SFQ when you configure QoS for Citrix ICA traffic in RiOS 9.0 or later.
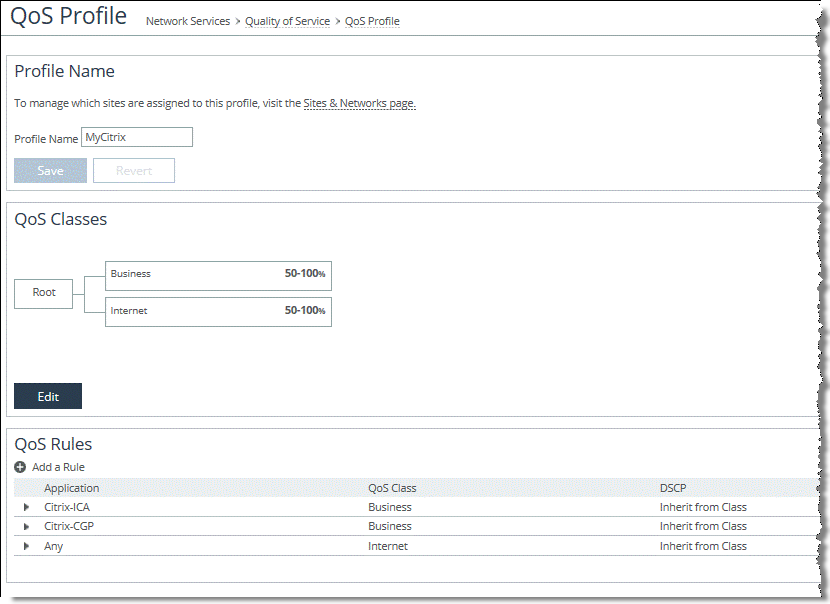
You can use the Riverbed Application Flow Engine (AFE) to classify Citrix ICA traffic. The AFE recognizes Citrix traffic on TCP port 1494 (Citrix-ICA) and port 2598 (Citrix-CGP). Use AFE to classify Citrix ICA traffic into a QoS class that is assigned with a higher priority than the QoS classes for other network traffic (
Figure: Classifying Citrix ICA Traffic with AFE).
Figure: Classifying Citrix ICA Traffic with AFE
To configure QoS for multi-stream and multi-port ICA traffic
Figure: Citrix Application Definition Using TCP Header Rules for Multi-Stream and Multi-Port ICA Traffic
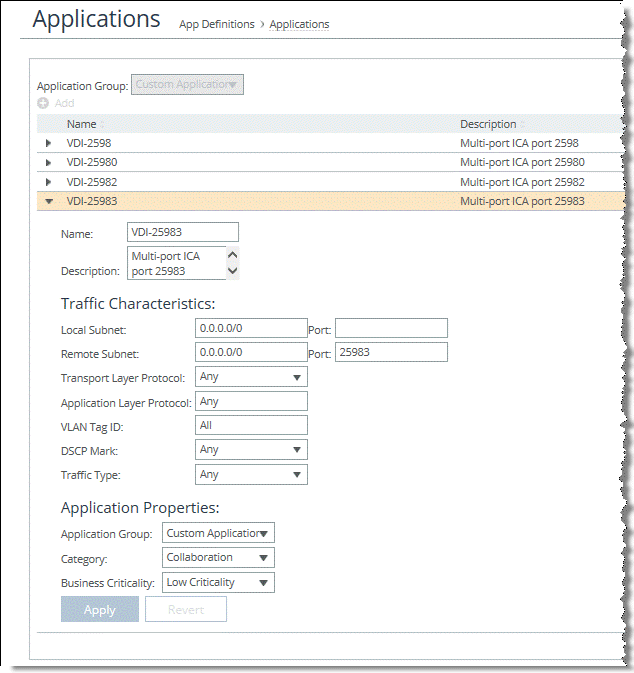
Figure: QoS Class Definition for Multi-Stream and Multi-Port ICA Traffic
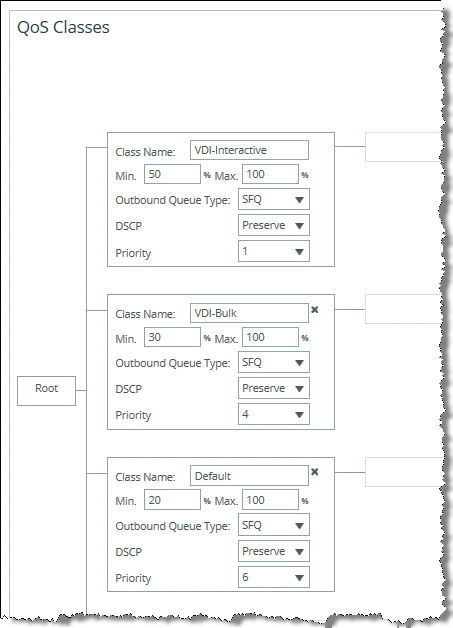
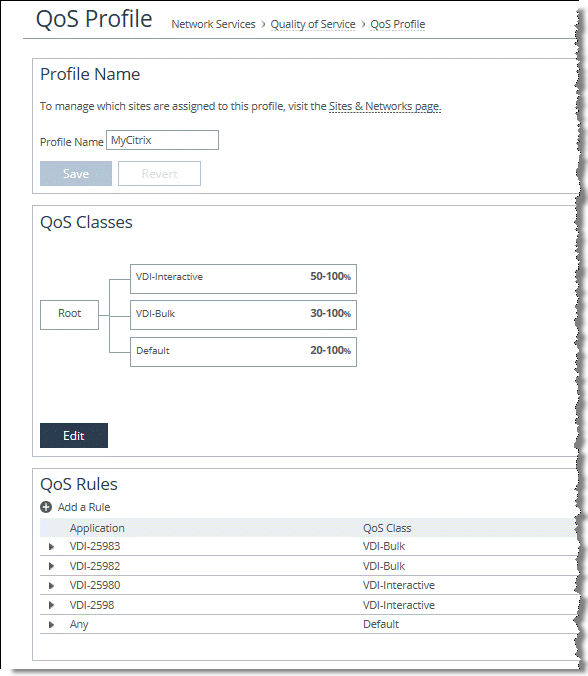
Figure: QoS Profile for Multi-Stream and Multi-Port ICA Traffic
Automatic Negotiation of Multi-Stream ICA Traffic for QoS Enforcement
RiOS 9.1 and later enable you to automatically configure and negotiate multi-stream ICA with the Citrix client from the client-side SteelHead and automatically use QoS to classify the negotiated multi-stream ICA traffic for QoS enforcement by the same client-side SteelHead. This configuration works with Citrix ICA traffic on both TCP port 1494 and 2598. This feature is independent of the Citrix computer policy for multi-stream and multi-port ICA on the Citrix server and the Citrix user policy for multi-stream ICA.
Note: Configure multi-stream ICA for network QoS enforcement of Citrix traffic from either the Citrix server using the Citrix multi-stream/multi-port computer and user policy or the client-side SteelHead using the SteelHead automatic negotiation of multi-stream ICA feature.
To enable RiOS to automatically negotiate multi-stream ICA on the client-side SteelHead
1. From the client-side SteelHead Management Console, choose Optimization > Protocols: Citrix.
You do not need to enable this setting on the server-side SteelHead.
Figure: Enable Auto-Negotiation for Multi-Stream ICA
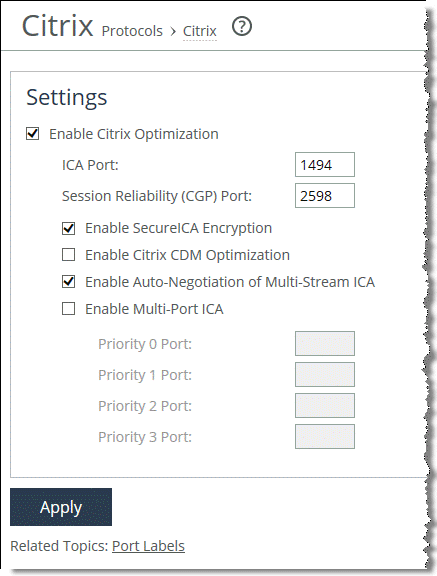
3. Click Apply to apply the settings to the running configuration.
You do not need to restart the service.
4. Restart the client connection from Citrix Receiver.
The client-side SteelHead automatically negotiates multi-stream ICA with the Citrix client after it receives a connection for a new Citrix session. If the negotiation is successful, the Citrix client initiates four TCP connections to the Citrix server. Each connection represents an ICA priority group. RiOS automatically classifies the ICA priority group into an equivalent predefined Citrix application (
Figure: Citrix Multi-Stream Application Definition).
Figure: Citrix Multi-Stream Application Definition

Thereafter, you can configure an appropriate QoS profile for Citrix ICA traffic. This feature is relevant only if you are going to use QoS for Citrix ICA traffic.
For more details on configuring QoS for multi-stream ICA traffic, see the section
QoS Classification for Citrix Traffic.
Note: Multi-stream ICA is supported on Citrix XenApp version 6.5, Citrix XenDesktop 5.5, and Receiver 3.0 or later (including online plug-in 13.0).
Reduction for Citrix Small Packet Real-Time Traffic
Riverbed recommends that you enable enhanced data reduction for real-time Citrix traffic that is sent in small packets, such as keystrokes, mouse clicks, and other Citrix packets that are less than 64 bytes.
Optimization for small Citrix packets is disabled by default.
To enable or disable Citrix optimization for small packets, use the following command:
[no] protocol citrix smallpkts enable
To check whether or not optimization for small Citrix packets is enabled, use the following command:
show protocol citrix smallpkts
You must perform this configuration on both the client-side and server-side SteelHeads.
Citrix ICA Optimization over SSL
Citrix Access Gateway (CAG) is an appliance that provides secure remote access to users of XenApp and XenDesktop over SSL VPN. CAG is also known as Access Gateway Enterprise Edition (AGEE) and Netscaler Gateway. CAG proxies the Citrix ICA traffic delivered from these applications and passes them securely over HTTPS or SSL to the end user.
Figure: Citrix ICA Client Communication Through a Citrix Access Gateway
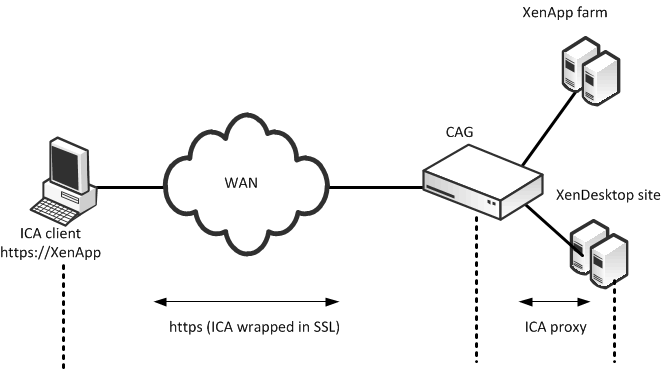
Figure: Citrix ICA Client Communication Through a Citrix Access Gateway shows a CAG deployment. The user reaches the login page by entering the XenApp or XenDesktop secure remote access URL (https://<CAG URL>) in a browser. This page is hosted on the CAG. The user enters their credentials for authentication.
Upon a successful authentication, a list of published applications and desktops is displayed. When the user accesses these applications and desktops, an ICA connection is launched from the user desktop to the XenApp and XenDesktop server. The CAG functions as a gateway to intercept and proxy the user ICA connection to the XenApp and XenDesktop servers on one end, while providing secure remote access over SSL VPN to the user on the other end.
RiOS 7.0 and later can optimize ICA traffic wrapped in SSL using an SSL preoptimization policy to the in-path rule. The in-path rule has several parameters that allow for the chaining of multiple optimization features.
Figure: SteelHead Deployment with CAG shows a SteelHead deployment with CAG.
Figure: SteelHead Deployment with CAG
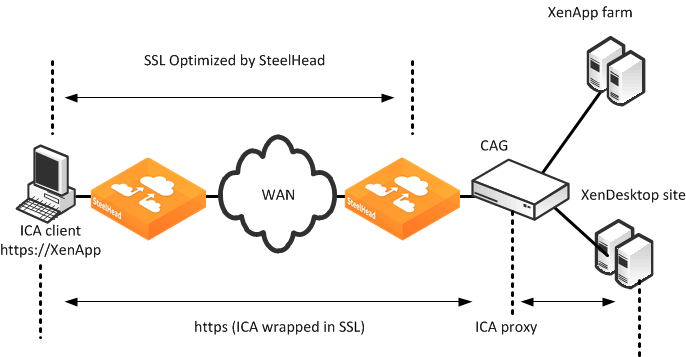
Figure: SteelHead In-Path Rule to Optimize Citrix ICA Traffic Through a CAG shows an in-path rule configuration to optimize Citrix ICA traffic wrapped in SSL.
Figure: SteelHead In-Path Rule to Optimize Citrix ICA Traffic Through a CAG
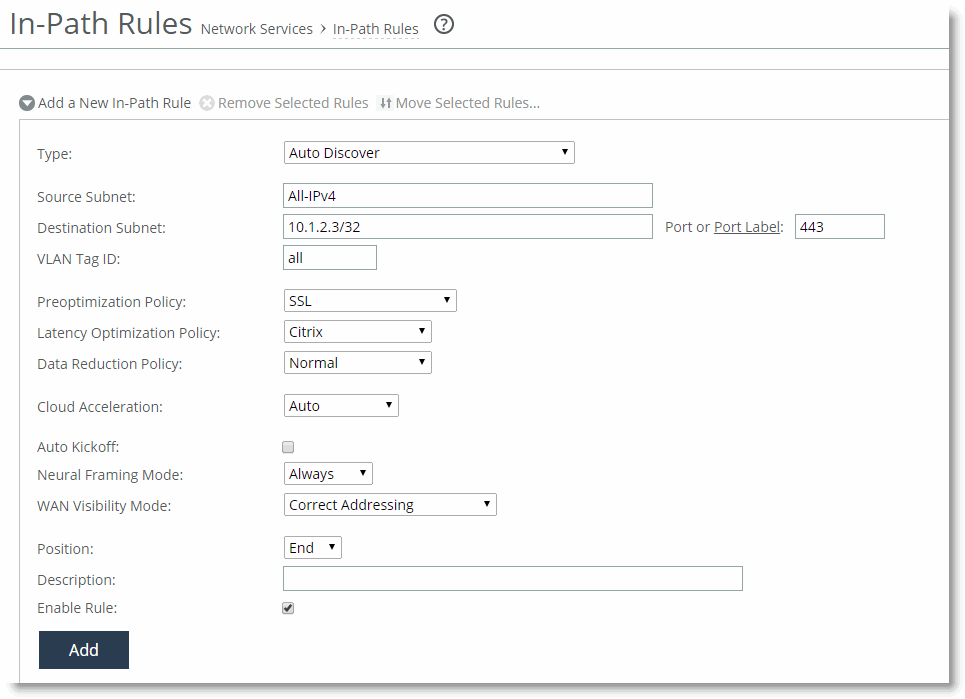
Citrix ICA traffic optimization with CAG has the following requirements:
• Both the client-side and server-side SteelHead must have RiOS 7.0 or later.
• The proxy certificate you use on the SteelHead must be a valid certificate.
You must import self-signed proxy certificates to the client trusted-root certificate authority certificate store. The Citrix client does not connect if you use an invalid certificate.


















