Overview of Virtual Edge
This chapter provides an overview of SteelFusion Edge (virtual edition), including an overview of the hardware platform and hardware and software dependencies. It includes these sections:
SteelFusion overview
SteelFusion is a converged infrastructure solution, encompassing all branch services such as server, storage, networking, and WAN optimization. SteelFusion is a dual-ended system that comprises two logical components: SteelFusion Edge and SteelFusion Core.
SteelFusion Core is a physical or virtual appliance in the data center that mounts all logical unit numbers (LUNs) that need to be made available to applications and servers at the branch from the centralized storage array. Core appliances communicate across the WAN with the SteelFusion Edge appliances at the branch.
SteelFusion Edge is a physical or virtual appliance that is located at the branch. The Edge appliance provides a virtualized environment that hosts the branch application servers. The Edge appliance also provides RiOS WAN optimization (depending on your order) and BlockStream-enabled storage.
SteelFusion delivers local user performance to applications and data, while enabling the centralization of these applications and data, instant recovery, and lower total operating costs. You can access applications that run locally in your branch while the data is maintained and protected in your data center. Decoupling computation from its underlying storage allows your applications to run in a stateless mode, which reduces your branch footprint and centralizes management of your branch services.
Figure: Typical SteelFusion deployment shows a typical SteelFusion deployment.
Figure: Typical SteelFusion deployment
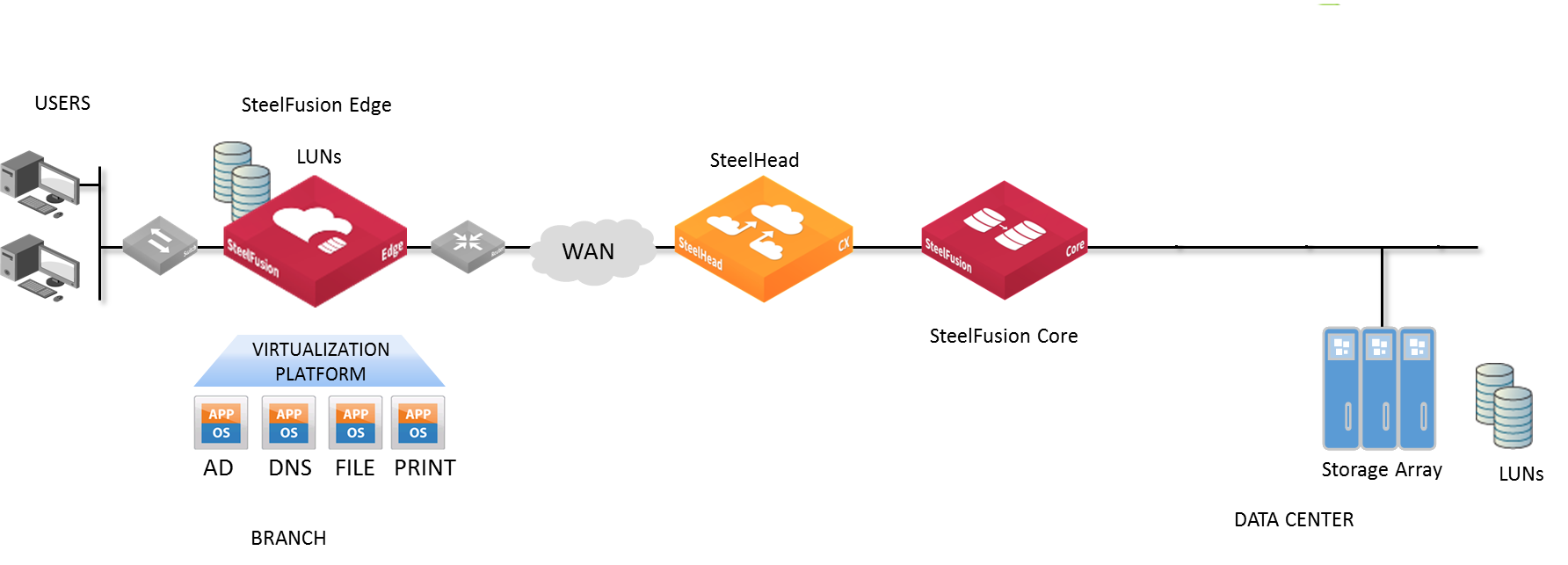
For more information about SteelFusion and how it works, see the SteelFusion Edge User Guide and the SteelFusion Design Guide.
Virtual SteelFusion Edge overview
Virtual Edge is a virtual storage appliance that acts as a branch storage tier to the storage in your data center, while also providing the flexibility of virtualization. It acts as a Virtual Storage Provider to the underlying Hyper-V hypervisor, running on the host hardware by presenting storage through iSCSI.
Virtual Edge enables consolidation while providing most of the functionality of the physical SteelFusion Edge, with the following exceptions:
• Virtual Services Platform (VSP) or Riverbed Services Platform (RSP)
• Hardware reports such as the Disk Status report
• Hardware-based alerts and notifications such as a RAID alarm
A typical Virtual Edge deployment consists of a single Hyper-V host on a Windows Server 2016 (Standard Edition or Data Center Edition Version 1607) with a single Virtual Edge VM along with other compute VMs.
All storage-related features available with SteelFusion are available on the Edge appliance. You manage the storage and networking components using the SteelFusion Management Console, and you use Hyper-V Manager to interact with the hosted VMs.
Virtual Edge provides BlockStream iSCSI storage for the hypervisor datastores. You can format and use the LUNs provided by BlockStream iSCSI storage through Hyper-V.
Note: Virtualization and hypervisor features are not available on Virtual Edge.
Networking interfaces
The Edge hardware platform includes:
• Management interfaces - Management network ports for RiOS are provided using the primary (PRI) and auxiliary (AUX) interfaces.
• SteelHead bypass interfaces - SteelHead bypass ports are provided through a preinstalled NIC (LANX_Y, WANX_Y).
• Storage interfaces - Storage ports for external iSCSI connections for SteelFusion are provided via the storage ports (DATA0, DATA1).
This table summarizes the required network interfaces that connect the Edge appliance to your network.
Port | Description |
PRI
(Primary) | The primary port connects the Edge appliance to a LAN switch. This interface enables you to connect to the Edge Management Console and the SteelFusion Edge CLI. This interface can also be used to connect the SteelFusion Core through the RiOS node, in-path interface. The primary and auxiliary ports cannot share the same network subnet. |
AUX
(Auxiliary) | The auxiliary port provides an additional management interface to a secondary network such as a management VLAN. You can connect a computer directly to the appliance with a crossover cable. |
LAN 1_0
LAN 0_0 | This port connects the LAN port of the Edge appliance to the LAN switch using a straight-through cable. The Edge appliance uses one or more in-path interfaces to provide Ethernet network connectivity for optimized traffic. Each in-path interface comprises two physical ports: the LAN port and the WAN port. Use the LAN port to connect the Edge appliance to the internal network of the branch office. If the Edge appliance is deployed between two switches, both the LAN and WAN ports must be connected with straight-through cables. |
WAN 1_0
WAN 0_0 | This port connects the WAN port of the Edge appliance to the WAN router using a crossover cable. The WAN port is the second of two ports that compose the in-path interface. The WAN port is used to connect the Edge appliance toward WAN-facing devices such as a router, firewall, or other equipment located at the WAN boundary. |
DATA0, DATA1 | These ports provide additional iSCSI interfaces for storage traffic to external servers when used by the RiOS node. The ports are connected to a LAN switch using a straight-through cable. |
Figure: Typical SteelFusion Edge port connections shows typical branch office connections for the Edge
appliance.
Figure: Typical SteelFusion Edge port connections
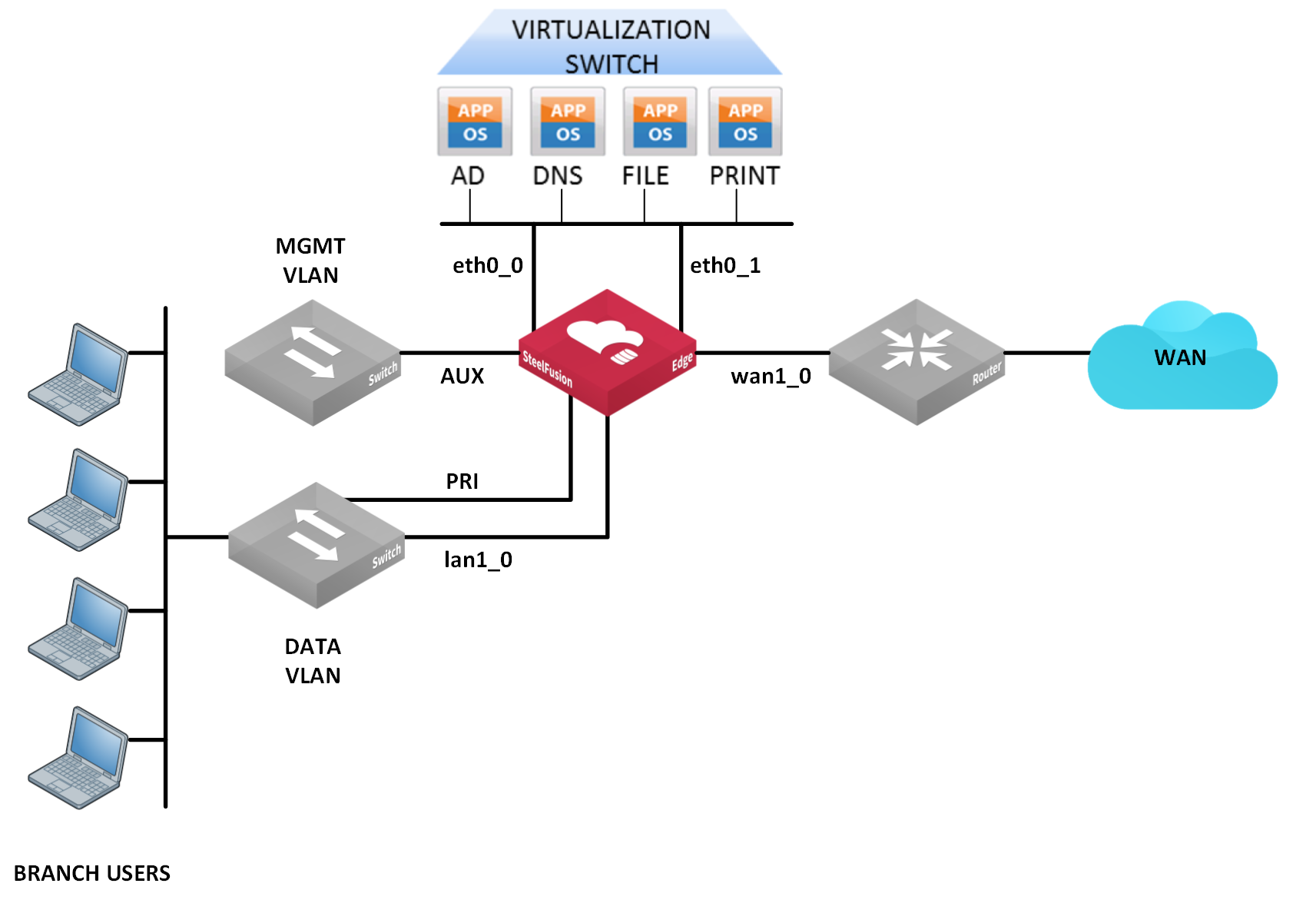
Understanding hypervisor modes
In SteelFusion 6.0, you can connect the physical Core appliance (SFCR3500) to the new Hyper-V Edge appliances (VSFH1100 and VSFH1200). The hypervisor mode on the Core must match the hypervisor mode on the Edges at your branch offices.
About hypervisor modes
Based on the appliance model, the hypervisor mode is automatically set on the Edge during installation. For the Virtual Edges deployed on Hyper-V, the hypervisor mode is set to Hyper-V. For the Virtual Edges deployed on ESXi, the hypervisor mode is set to ESXi. For the physical Edges that are preloaded with ESXi, the hypervisor mode is set to ESXi.
On the Core, ESXi mode is the default hypervisor mode. The Core and Edge appliances operate either in ESXi or Hyper‑V hypervisor mode. You can connect an Edge and a Core only if they operate in the same hypervisor mode, regardless of the licenses installed on them. A Core or an Edge cannot operate in both the ESXi and Hyper-V modes at the same time.
Note: A Core or an Edge operating in Hyper-V hypervisor mode supports only the block (iSCSI) mode. The file (NFS) mode is not applicable for Hyper-V deployments.
Upgrade and downgrade
In releases prior to SteelFusion 6.0, ESXi is the only operational hypervisor mode. If you upgrade to SteelFusion 6.0 from prior releases, the Core and Edge will boot up in ESXi mode after successful upgrade.
You cannot downgrade from SteelFusion 6.0 to prior releases if your Core and Edge are operating in Hyper-V hypervisor mode. If you downgrade your Core and Edge operating in ESXi hypervisor mode from SteelFusion 6.0 to prior releases, the hypervisor modes will not be applicable after downgrade.
High availability and replication
If you configure high availability (HA) in your SteelFusion deployments, the HA peers must operate in the same hypervisor mode for successful HA implementation. If you configure SteelFusion replication (FusionSync), the primary and secondary Cores must operate in the same hypervisor mode for successful data replication.
Viewing hypervisor mode
You can view the hypervisor mode specified in the banner above the menus in the Core and Edge UI. On the Virtual Edge management console, you can also choose Help to display the Help page. You can view the hypervisor mode displayed as Appliance Mode in the Appliance Details pane of the Help page.
Figure: Banner and Help page - hypervisor mode shows the hypervisor mode displayed in the banner and Help page.
Figure: Banner and Help page - hypervisor mode
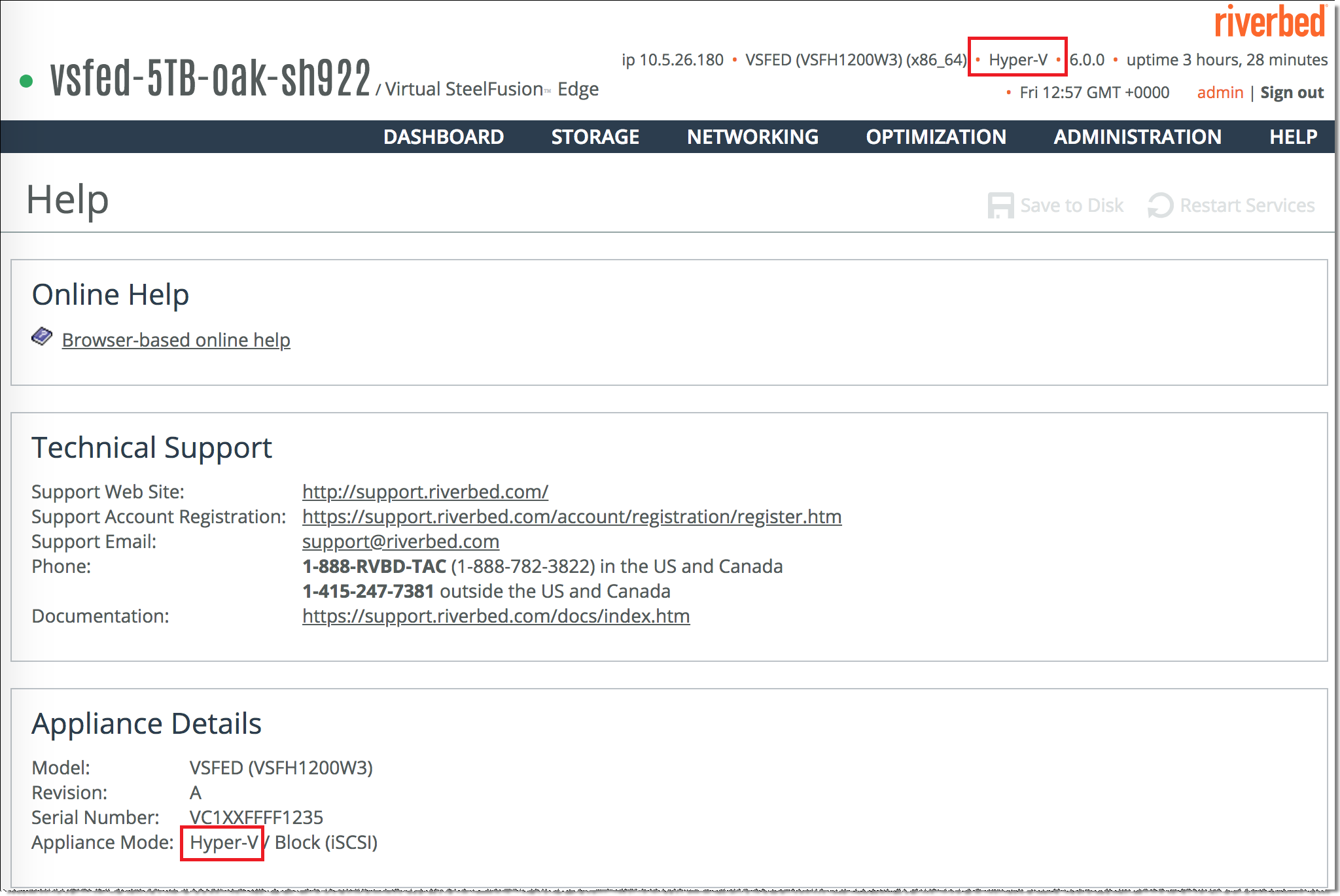
For information about changing the hypervisor mode on a physical Core, see the SteelFusion Core User Guide.
Product dependencies and compatibility
This section describes the product dependencies for Virtual Edge.
Hardware and software dependencies
For a RiOS, Storage Edge, SteelFusion Core, and hypervisor release matrix, go to the Riverbed Knowledge Base article at
https://supportkb.riverbed.com/support/index?page=content&id=S:S27472.
Riverbed component | Hardware and software requirements |
SteelFusion Edge Management Console | Any computer that supports a web browser with a color image display. The Management Console has been tested with Mozilla Firefox Extended Support Release 31.0, Google Chrome, and Microsoft Internet Explorer 9.0. JavaScript and cookies must be enabled in your web browser. |
BlockStream, SteelFusion Core Management Console | Version 6.0 (in Hyper-V hypervisor mode). Note: The hypervisor mode on the Core must match the hypervisor mode on the Edges at your branch offices. For more information about hypervisor modes, see Understanding hypervisor modes. |
SteelHead, SteelHead Management Console | RiOS 9.8.0a |
SteelCentral Controller for SteelHead (SCC) | Version 9.8.0 |
Firewall requirements
We recommend that you deploy the Edge appliance behind your firewall. Ports 7800 and 7810 must be open.
SNMP-based management compatibility
The Edge appliance supports a proprietary Riverbed MIB accessible through SNMP. SNMPv1 (RFCs 1155, 1157, 1212, and 1215), SNMPv2c (RFCs 1901, 2578, 2579, 2580, 3416, 3417, and 3418), and SNMPv3 are supported, although some MIB items might be accessible only through SNMPv3 and SNMPv2.
SNMP support allows the Edge to be integrated into network management systems such as Hewlett-Packard OpenView Network Node Manager, BMC Patrol, and other SNMP-based network management tools.
Ethernet network compatibility
For details on Ethernet network compatibility, see the hardware manufacturer’s documentation. If your appliance has a Riverbed bypass card, see the SteelFusion Edge Hardware and Maintenance Guide for details about the bypass card’s Ethernet network.
Limitations
These limitations are applicable for the Virtual Edge on Hyper-V deployments:
• Microsoft Failover Cluster and Cluster Shared Volumes (CSV) are not supported.
• Prefetch optimization of snapshot trees (VHDX with more than one child snapshot) is not supported.
• Prefetch optimization is not supported for differencing disks on Hyper-V.
• Prefetch optimization is supported only for Windows Server 2016 and Windows 2012 R2 guest VMs with NTFS volumes.
• ESXi Edges (SFED or Virtual Edge on ESXi) are not supported.
• Storage provisioned by Edge should be mapped to Windows servers only (ESXi is not supported).
• Hardware iSCSI adapters are not supported with Hyper-V as iSCSI initiators. Microsoft software iSCSI initiator is qualified for Virtual Edge deployments on Hyper-V.
• Virtual Edge VM snapshot, Live Migration, and System Center Virtual Machine Manager (SCVMM) are not supported.




