About Riverbed Cloud Services
Public, private, and hybrid cloud environments all face the same performance limitations of today’s applications and networks. To maximize the flexibility and savings of the public cloud, you must first overcome the same latency and bandwidth constraints that challenge distributed IT infrastructure environments.
Riverbed cloud services help transform the cloud into an extension of the data center. Cloud Accelerator virtual appliances accelerate the migration of data and applications to the cloud, while speeding access to that data from anywhere. Compatibility with industry leading cloud environments eliminates vendor lock-in.
As you migrate services to the cloud, and later broaden your application and data footprint there, Cloud Accelerator virtual appliances ensure you will meet application performance service level agreements (SLAs), regardless of network latency and enterprise bandwidth limitations, to ensure seamless public-cloud integration through features like:
• transparent cloud interception.
• a flexible cloud pricing model.
• portal-based management.
• elastic sizing and cloning.
• interoperability with Cloud Accelerator virtual appliances, SteelHead physical appliances,
and Client Accelerator.
About Riverbed Cloud Services system components
This section provides an overview of the Riverbed cloud services system and its components.
Figure: Riverbed cloud services shows an overview of Riverbed cloud services.
Riverbed cloud services
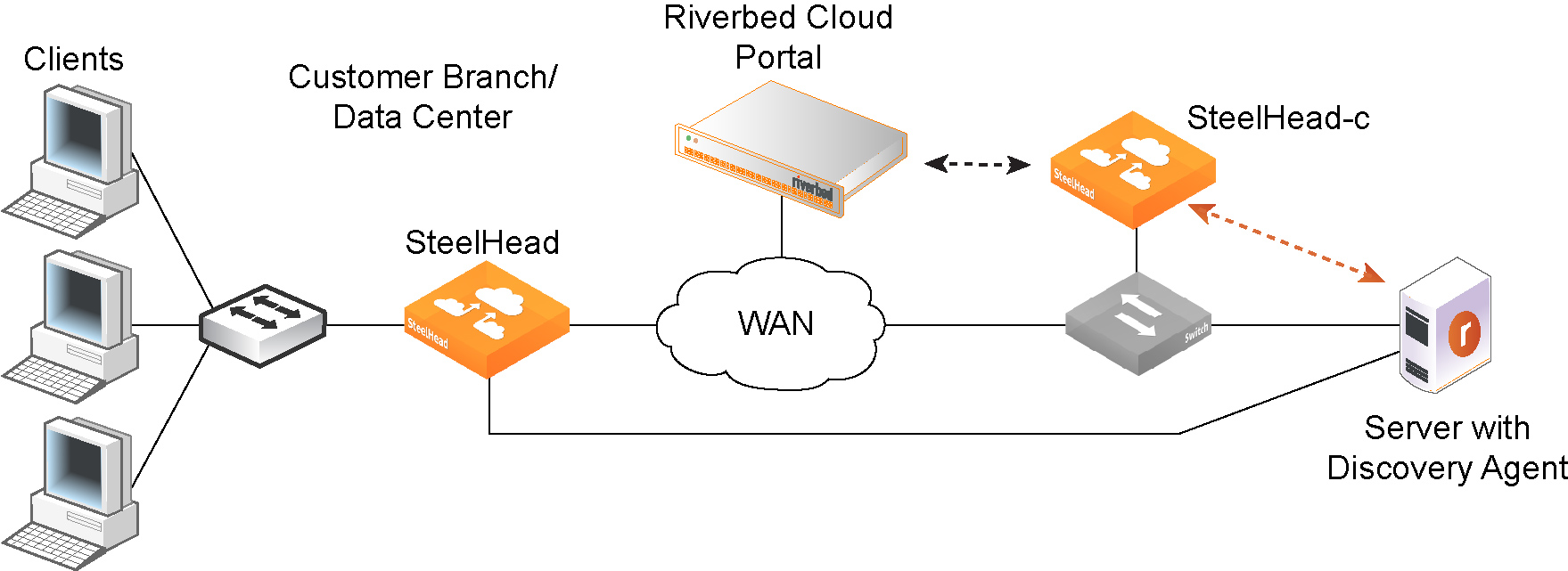
The Riverbed cloud services system consists of these components:
• Cloud Portal—A web portal hosted and managed by Riverbed. The Cloud Portal manages licensing, deployment, and discovery of your Cloud Accelerator virtual appliances. For details, see
About the Cloud Portal. • Cloud Accelerator—Software form factor of SteelHead that is purpose-built for compatibility with a variety of IaaS vendors.
• Discovery Agent—Software that can be installed in the cloud where your optimized applications are hosted. The Discovery Agent assists client-side SteelHead appliances in locating peer Cloud Accelerator virtual appliances on the server side. It also provides failure detection and load balancing. For details, see
About the Discovery Agent. The Cloud Portal uses elastic scaling technology. As a result, the portal is not always served from a static IP address. Ensure that all appliances that you want to communicate with the Cloud Portal are configured to use DNS and hostnames for the portal.
About Supported deployments
This section illustrates the client-server deployments that Riverbed cloud services support.
Figure: Servers in the cloud behind a Cloud Accelerator in a NATed environment shows a deployment in which the server-side servers are behind a Cloud Accelerator in a network address translated (NATed) environment.
Servers in the cloud behind a Cloud Accelerator in a NATed environment
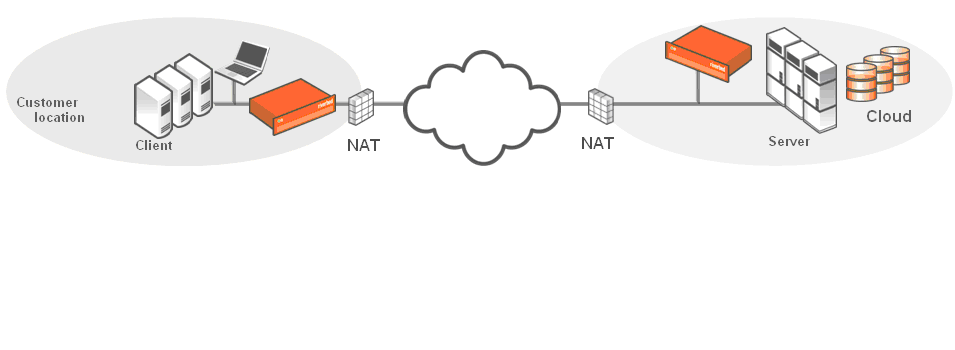
Figure: Servers in the cloud behind a Cloud Accelerator shows a deployment in which the servers in the cloud are behind a Cloud Accelerator. In this case, the network does not have NAT: for example, when you use an Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (VPC).
Servers in the cloud behind a Cloud Accelerator
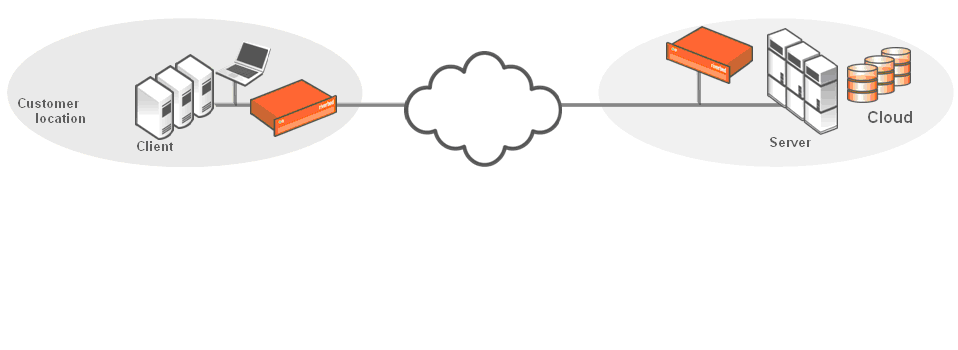
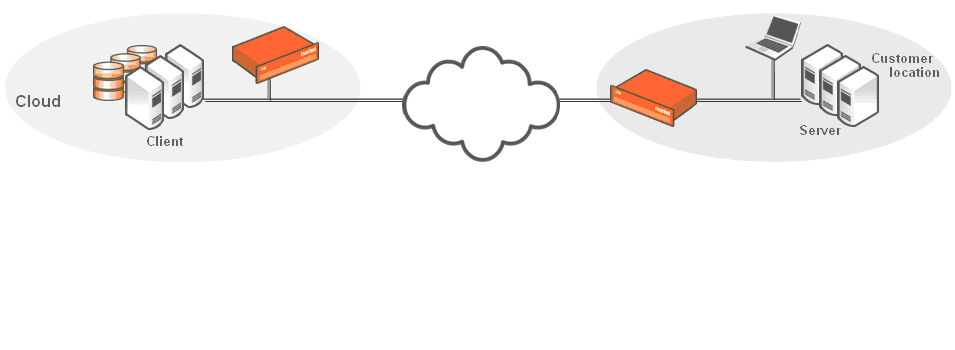
Figure: Clients in the cloud behind a Cloud Accelerator shows a deployment in which the clients in the cloud are behind a Cloud Accelerator. In this case, the network does not have NAT: for example, when you use an Amazon VPC. In this deployment, you must use a Discovery Agent in the network.
Riverbed cloud services do not support clients in the cloud in a NATed environment.
Clients in the cloud behind a Cloud Accelerator
About Cloud Accelerator models and required resources
For complete model specifications, go to the
SteelHead Family Specification Sheet.
Each Cloud Accelerator instance requires at least two virtual disks. One disk stores the Cloud Accelerator configuration and management resources (this disk is automatically deployed when you create the virtual appliance); the other disk serves as the data store (you must manually add this disk). In AWS, virtual disk drives are referred to as Elastic Block Stores (EBS). Hard disk drives (HDDs), also known as magnetic drives, can be used for most models, but solid-state drives (SSDs) can provide higher performance.
We recommend SSD drives for models CCX-SUB-PERF-TIER3 and greater.
About System limitations and dependencies
Cloud Accelerator images can be installed on AWS, VMware ESX/ESXi, and Microsoft Azure. The Cloud Portal supports licensing and simple management for Cloud Accelerator virtual appliances on all virtual machine platforms.
All Cloud Accelerator virtual appliances, including virtual appliances intended for AWS China or AWS GovCloud regions, must be manually deployed. However, Cloud Accelerator virtual appliances can be automatically licensed through the Cloud Portal providing they have web access to the portal.
Hybrid networking features such as path selection and secure transport are not supported. Also, SCPS licenses are not supported.
Limitations on AWS
This section describes the deployment and feature options that the Cloud Accelerator for AWS does not support.
Deployment limitations
• Automatic peering—The Cloud Accelerator does not use automatic peering. When you run a server in the cloud, you deploy the Cloud Accelerator to be the furthest SteelHead in the network, because
the Discovery Agent on the server is configured to use the Cloud Accelerator automatically. When you run a client in the cloud, and there are multiple SteelHeads in the path to the server, the
Cloud Accelerator is selected for optimization first. You can enable automatic peering on the remote SteelHeads to make the Cloud Accelerator peer with the furthest SteelHead in the network.
• Simplified routing—The Cloud Accelerator for AWS is not deployed in-path, but rather in its unique
out-of-path method using one interface. Simplified routing does not apply.
• WCCP/PBR/L4—The Cloud Accelerator for AWS uses a unique redirection mechanism that enables deployments in any cloud environment. The Cloud Accelerator also supports WCCP/PBR/L4 redirection when made available by the cloud provider. Amazon EC2 does not support these traditional redirection mechanisms.
• Connection forwarding—The Cloud Accelerator uses a unique out-of-path method; connection forwarding does not apply.
Feature limitations
• RSP—The Cloud Accelerator for AWS is a virtual SteelHead deployed into the AWS virtualization environment. You need not run virtualization on top of virtualized software.
• PFS—It is easier and simpler for you to run a separate file server instance in the cloud and not use the SteelHead for Proxy File Service (PFS).
• WAN visibility mode—The Cloud Accelerator currently supports only correct addressing. It does not support full transparency and port transparency.
• CIFS prepopulation—CIFS prepopulation is not supported on the Cloud Accelerator for AWS because it requires the Riverbed Copy Utility (RCU) to run on a different interface. Prepopulation also requires a switch to make the traffic loop back through the SteelHead, which is not possible in the cloud. If you want prepopulation, you can install the RCU or a similar tool on a machine in the cloud. You would most likely configure prepopulation on the remote SteelHead instead of the Cloud Accelerator.
Limitations on VMware ESX/ESXi
This section describes the deployment and feature options that the ESX Cloud Accelerator does not support.
Deployment limitations
• Automatic peering—ESX Cloud Accelerator virtual appliances deployed with Web Cache Communication Protocol (WCCP) or Policy-Based Routing (PBR) support automatic peering. ESX Cloud Accelerator virtual appliances deployed with the Discovery Agent do not support automatic peering.
• Simplified routing—ESX Cloud Accelerator virtual appliances deployed in-path with the Discovery Agent support simplified routing. ESX Cloud Accelerator virtual appliances deployed with WCCP or PBR do not support simplified routing.
Feature limitations
• RSP—RSP enables virtualization in physical SteelHead appliances. Cloud Accelerator is a virtual SteelHead appliance running on a virtual machine. Additional layers of virtualization are not needed.
• PFS—It is easier to run a separate file server instance in the cloud and not use the Cloud Accelerator for Proxy File Service (PFS).
• WAN visibility mode—ESX Cloud Accelerator virtual appliances deployed with WCCP or PBR support WAN visibility mode. When deployed with the Discovery Agent, however, WAN visibility mode is not supported.
• CIFS prepopulation—ESX Cloud Accelerator virtual appliances deployed with WCCP or PBR support CIFS prepopulation. When deployed with the Discovery Agent, however, CIFS prepopulation is not supported.
Reduced data store feature
This feature is only supported on ESX-based Cloud Accelerator virtual appliances.
In Cloud Accelerator versions before 1.2, you must allocate a data store volume of exactly 440 GB for the virtual appliance; otherwise, the Cloud Accelerator does not function correctly.
The reduced data store support feature in Cloud Accelerator 1.2 first checks if 440 GB of disk space is allocated for the data store. If less than 440 GB of disk space has been provisioned, the Cloud Accelerator software creates a 30-GB data store. This allows you to create Cloud Accelerator that require less disk space but still provide WAN optimization. The optimization performance is impacted when you do not use a 440-GB disk for the data store. Performance depends on the size of your working data set.
The Cloud Accelerator uses either 440 GB or 30 GB. If you allocate a disk space that is less than 440 GB, but later than 30 GB (such as 250 GB), the Cloud Accelerator uses only 30 GB; it disregards 220 GB. If you allocate less than 30 GB, the Cloud Accelerator does not function correctly.
After you create a disk, if you resize it to 440 GB, the Cloud Accelerator still uses only 30 GB. To increase the data store size to 440 GB, you must delete the original disk and create a new 440 GB disk. Doing this reverts the data store to a “cold” state; performance improves as the SteelHead executes subsequent data transfers over the WAN.
Limitations on Microsoft Azure
These limitations apply to the Cloud Accelerator for Azure:
• Multiple NICs, PBR, and WCCP are not supported.
About Licensing Cloud Accelerator virtual appliances
Licenses for Cloud Accelerator virtual appliances are stored on the Cloud Portal. Each license is associated with a one-time token unique to it. Applying a one-time token to a Cloud Accelerator enables the virtual appliance to contact the portal and to associate the token’s license with the Cloud Accelerator. To obtain a one-time token, you must have an account on the Cloud Portal. Typically, Riverbed will establish a user account on the portal for you after you purchase a cloud product, and Riverbed will send you an email with details and login information about your account. After your account is established, you can log in and view your purchased licenses. Select a license to view details about it, including the one-time token associated with it.
For virtual appliances that cannot be provisioned through the portal, the token must manually be applied to the appliance.
To obtain a one-time token
1. Log in to the Cloud Portal.
2. Select the Cloud Appliances tab and select Licenses to display the Licenses page.
3. Select the serial number of an unprovisioned license to display the License Details page.
4. Copy the one-time token displayed on the License Details page.
To apply the token using the portal
1. Open another browser window and navigate to the appliance’s management console.
2. Navigate to this console page:
– If you are licensing a Cloud Accelerator running RiOS 8.6.x or earlier, choose Configure > Maintenance > Licenses.
– If you are licensing a Cloud Accelerator running RiOS 9.0.x or later, choose Administration > Maintenance: Licenses.
3. Under the Cloud Licensing section, paste the one-time token into the One-time Token field.
4. Click Initialize License Client.
To apply the token using the command-line interface
1. Log in to the appliance’s command-line interface as admin.
The default password is password. If you specified administrator credentials at the time you created the virtual appliance instance, use those credentials.
2. Enable configuration mode:
enable
configure terminal
3. Enter this command:
license client init <one-time-token>
4. Verify that the license is applied:
show licenses
Upgrading and downgrading Cloud Accelerator models
To upgrade a Cloud Accelerator virtual appliance to a model that does not require a higher-capacity virtual machine, simply purchase a license for the new Cloud Accelerator model. Downgrading a Cloud Accelerator model is as simple as downgrading the license to that of a lower-end model. The Cloud Accelerator detects any change in the license associated with it when it communicates with the Cloud Portal.
To upgrade a Cloud Accelerator virtual appliance to a model that requires a higher-capacity virtual machine:
1. Purchase a license for the new Cloud Accelerator model.
2. Deprovision the original Cloud Accelerator virtual appliance and its underlying virtual machine.
3. Provision a new virtual machine that meets the requirements of the new Cloud Accelerator model.
4. Obtain the image for the new Cloud Accelerator model and install it on the virtual machine.
Downgrading a Cloud Accelerator model is as simple as downgrading the license to that of a lower-end model.
Upgrading and downgrading Cloud Accelerator RiOS software
You can upgrade and downgrade the operating system software on your Cloud Accelerator for AWS virtual appliances through the Cloud Portal by performing the task described in this section.
You can upgrade and downgrade the operating system software on your Cloud Accelerator virtual appliances hosted on other cloud platforms in the same manner as physical SteelHead appliances by using the Software Upgrade page in an appliance’s management console. For details, see the
SteelHead User Guide and
To upgrade a Cloud Accelerator for Azure or ESX/ESXi to RiOS 9.2 or later.
To upgrade or downgrade RiOS software on Cloud Accelerator for AWS
1. Log in to the portal and select the Cloud Appliances tab.
2. If your user account is associated with multiple companies, select the company that contains the appliance you want to upgrade.
3. Select Appliances.
4. Select the name of the appliance you want to upgrade or downgrade.
5. Select the Summary tab.
6. Stop the appliance.
7. Select a version from the Version drop-down list.
8. Click Update Details.
The Cloud Accelerator IP addresses will change. Ensure that you update any rules or configurations that depend on it such as fixed-target rules on on-premise SteelHeads that peer your Cloud Accelerator, on-premise firewall configurations, or security group configurations.
To upgrade a Cloud Accelerator for Azure or ESX/ESXi to RiOS 9.2 or later
With RiOS 9.2 and later, Cloud Accelerator images use a partition layout for the data store disk that is different from the layout of Cloud Accelerator images using previous versions of RiOS.
Because of this change, upgrading through the virtual appliance’s console or the CLI will not work. For Azure and ESX/ESXi environments, you must first create Cloud Accelerator running RiOS 9.2 or later and then manually transfer the license, configuration file, and data store disk from a pre-RiOS 9.2 or later Cloud Accelerator to the RiOS 9.2 or later Cloud Accelerator.
Upgrading any Cloud Accelerator model on Azure to RiOS 9.5 clears the Cloud Accelerator data store.
If you are using Cloud Accelerator, ensure that you reconfigure the Discovery Agent to use the primary IP address of the new RiOS 9.2 or later Cloud Accelerator and that you restart the Discovery Agent.
1. Create a new Cloud Accelerator running RiOS 9.2 or later. Do not create a new data store disk for it.
2. Deactivate the license for the pre-RiOS 9.2 Cloud Accelerator on the Cloud Portal and on the virtual appliance itself.
3. Remove the data store disk from the pre-RiOS 9.2 Cloud Accelerator using the procedure for your platform.
Azure:
– In the Azure portal, select the Virtual Machines tab.
– Select the virtual machine that is hosting the virtual appliance
– Click Detach Disk.
– Select the data store disk and click OK. Remember the name of the data store disk.
ESX:
– Log in to vSphere or the host for the virtual machine hosting the virtual appliance.
– Find the virtual machine hosting the virtual appliance and power the virtual machine off.
– Choose Edit Settings > Hard Disk options and delete the data store disk.
– Power on the virtual machine.
4. Attach the disk from
Step 3 to the RiOS 9.2 or later Cloud Accelerator that you created in
Step 1.
Azure:
– In the Azure portal, select the Virtual Machines tab.
– Select the virtual machine that is hosting the new virtual appliance.
– Click Attach, and then click Attach Disk.
– Select the data store disk from
Step 3 from the Available Disks menu and click
OK.
ESX:
– Log in to vSphere or the host for the virtual machine hosting the new virtual appliance.
– Select the virtual machine hosting the new virtual appliance
– Navigate to Edit Settings > New Device and select Existing Hard Disk.
– Click
Add, and navigate to the data store disk from
Step 3 (.vmdk file), and click
Add.
– If the virtual machine is not running, power it on.
5. Copy the configuration file from the pre-RiOS 9.2 Cloud Accelerator to the RiOS 9.2 or later Cloud Accelerator that you created in
Step 1. If you have SteelCentral Controller for SteelHead, you can use it to copy the configuration file to the new RiOS 9.2 or later Cloud Accelerator. See the
SteelCentral Controller for SteelHead User Guide.
If you do not have SteelCentral Controller for SteelHead, use this procedure to copy the configuration file to the new RiOS 9.2 or later Cloud Accelerator.
– Connect to the command-line interface (CLI) for the pre-RiOS 9.2 Cloud Accelerator. See the Riverbed Command-Line Interface Reference Manual.
– Use the scp command to copy the configuration to a location that is accessible to both the pre-RiOS 9.2 Cloud Accelerator and the RiOS 9.2 or later Cloud Accelerator.
sh (config)# configuration upload <config-file-name> <destination ftp/http/scp server>
– Connect to the CLI for the RiOS 9.2 or later Cloud Accelerator and use the fetch command to copy the configuration file from the upload location to the RiOS 9.2 or later Cloud Accelerator.
sh (config)# configuration fetch <ftp/http/scp server>/<config-file-name>
– On the RiOS 9.2 or later Cloud Accelerator, show configurations. The list includes the new configuration file.
sh (config)# show configuration files
initial.bak 2016/03/29 20:30:34
<config-file-name> 2016/03/29 22:22:48
initial (active) 2016/03/29 20:37:58
– Apply the configuration.
sh (config)# configuration switch-to <config-file-name>
6. Activate the license from
Step 2 on the RiOS 9.2 or later Cloud Accelerator.
7. Log in to the console for the RiOS 9.2 or later Cloud Accelerator and ensure that the status for the virtual appliance is healthy.
8. Delete the old instance of the virtual appliance.





