Figure 7‑3. Policies - In-Path Rules page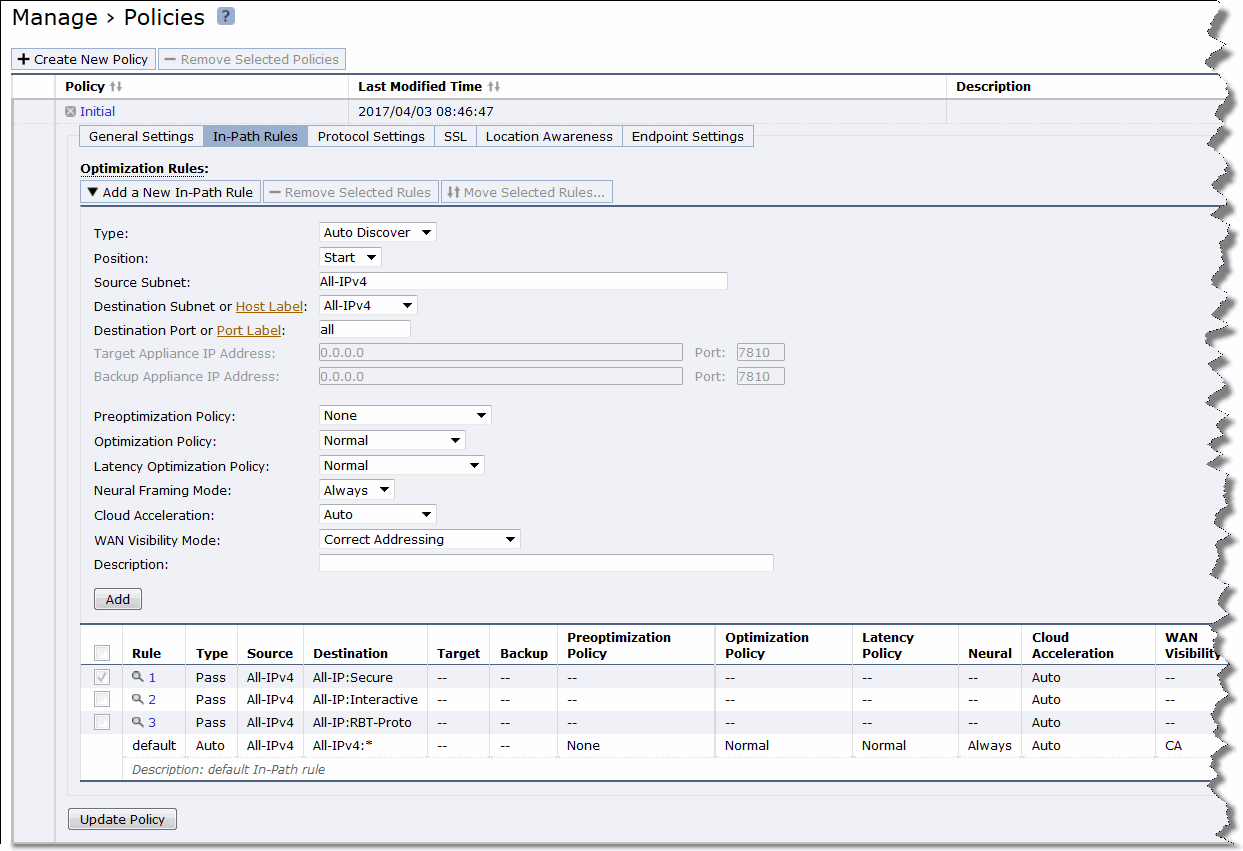


Control | Description |
Add a New In-Path Rule | Displays the controls for adding a new rule. |
Type | Select one of these rule types from the drop-down list: • Auto-Discover - Autodiscover is the process by which the Client Accelerator automatically intercepts and optimizes traffic on all IP addresses and ports. By default, autodiscover is applied to all IP addresses and ports that are not secure, interactive, or default Riverbed ports. Defining in-path rules modifies this default setting. For details, see the SteelHead User Guide. • Fixed-Target - Fixed-target rules specify that a Client Accelerator always goes to a specific SteelHead first. Fixed-target rules can be used if the SteelHead is located out-of-path, or for troubleshooting purposes. In addition to the settings available for autodiscovery rules, you also must set a target SteelHead. You can also specify a backup SteelHead. – Target Appliance IP Address - Enter the IP address and port number for your target SteelHead. – Backup Appliance IP Address - Enter the IP address and port number for your backup SteelHead. • Pass-Through - Pass-through rules identify traffic that is passed through the network unoptimized. You define pass-through rules to exclude subnets from optimization. Traffic is also passed through when the SteelHead is in bypass mode. Traffic may be passed through by the Client Accelerator because of pass through rule, because the connection was established before the Client Accelerator was put in place or before the service was enabled. • Discard - Drops the SYN packets silently. The Client Accelerator filters out traffic that matches the discard rules. This process is similar to how routers and firewalls drop disallowed packets: the connection-initiating application has no knowledge of the fact that its packets were dropped until the connection times out. • Deny - Drops the SYN packets, sends a message back to its source, and resets the TCP connection being attempted. Using an active reset process rather than a silent discard allows the connection initiator to know that its connection is disallowed. |
Position | Select Start, End, or a rule number from the drop-down list. The Client Accelerator evaluates rules in numerical order starting with rule 1. If the conditions set in the rule match, the rule is applied and the system moves on to the next packet. If the conditions set in the rule don’t match, the system consults the next rule. For example, if the conditions of rule 1 don’t match, rule 2 is consulted. If rule 2 matches the conditions, it is applied, and no further rules are consulted. The default rule, Auto-Discover, which optimizes all remaining traffic that has not been selected by another rule, can’t be removed and is always listed last. |
Source Subnet | Choose one of these options: • Specify the subnet IP address and netmask for the source network. Use this format for an individual subnet IP address and netmask: xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx/xx(IPv4) You can also specify 0.0.0.0/0 as the wildcard for all traffic. • IPv4 Traffic - Specifies all IPv4 traffic subnets. |
Destination Subnet or Host Label | Subnet - Specify the subnet IP address and netmask for the destination network: • All IPv4 - Maps to 0.0.0.0/0. • IPv4 - Prompts you for a specific IPv4 address. Use this format for an individual subnet IP address and netmask: xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx/xx • Host Label - Choose a destination host label to selectively optimize connections to specific services. A host label includes a fully qualified domain name (hostname) and/or a list of subnets. Host labels replace the destination. When you select a host label, RiOS ignores any destination IP address specified within the in-path rule. • The Management Console dims the host label selection when there aren’t any host labels.Click Host Label to choose Administration > Networking: Host Labels page for reference. • SaaS Application - Defines an in-path rule for SaaS optimization through SteelConnect Manager. When you choose SaaS Application, you also need to specify an application (such as SharePoint for Business) or an application bundle (such as Microsoft Office 365). Only applications and application bundles set up for SaaS acceleration on SAM appear in the list. For detailed information on SaaS Accelerator, see
Managing SaaS Accelerator and the SaaS Accelerator Manager User Guide. |
Destination Port or Port Label | Specify the destination port number, port label, or All. Click Port Label to choose Administration > Networking > Port Labels page for reference. |
Target Appliance IP Address | Specify the target appliance address for a fixed-target rule. Port - Specify the target port number for a fixed-target rule. |
Backup Appliance IP Address | Specify the backup appliance address for a fixed-target rule. Port - Specify the backup destination port number for a fixed-target rule. |
Preoptimization Policy | Select a traffic type from the drop-down list: • None - If the Oracle Forms, SSL, or Oracle Forms-over-SSL preoptimization policy is enabled and you want to disable it for a port, select None. This is the default setting. Port 443 always uses a preoptimization policy of SSL even if an in-path rule on the client-side SteelHead sets the preoptimization policy to None. To disable the SSL preoptimization for traffic to port 443, you can either: – disable the SSL optimization on the client-side or server-side SteelHead. —or— – modify the peering rule on the server-side SteelHead by setting the SSL Capability control to No Check. • Oracle Forms - Enables preoptimization processing for Oracle Forms. This policy is not compatible with IPv6. • Oracle Forms over SSL - Enables preoptimization processing for both the Oracle Forms and SSL encrypted traffic through SSL secure ports on the client-side SteelHead. You must also set the Latency Optimization Policy to HTTP. This policy is not compatible with IPv6. If the server is running over a standard secure port—for example, port 443—the Oracle Forms over SSL in-path rule needs to be before the default secure port pass-through rule in the in-path rule list. • SSL - Enables preoptimization processing for SSL encrypted traffic through SSL secure ports on the client-side SteelHead. |
Optimization Policy | Optionally, if the rule type is Auto-Discover or Fixed Target, you can configure these types of data reduction policies: • Normal - Performs LZ compression and SDR. • SDR-Only - Performs SDR; doesn’t perform LZ compression. • Compression-Only - Performs LZ compression; doesn’t perform SDR. • None - Doesn’t perform SDR or LZ compression. |
Latency Optimization Policy | Select one of these policies from the drop-down list: • Normal - Performs all latency optimizations (HTTP is activated for ports 80 and 8080). This is the default setting. • HTTP - Activates HTTP optimization on connections matching this rule. • Outlook Anywhere - Enables Outlook Anywhere latency optimization. Outlook Anywhere is a feature of Microsoft Exchange Server 2003, 2007, and 2010 that allows Microsoft Office Outlook 2003, 2007, and 2010 clients to connect to their Exchange servers over the internet using the Microsoft RPC tunneling protocol. For details about Outlook Anywhere, see the SteelHead User Guide. • Citrix - Activates Citrix-over-SSL optimization on connections matching this rule. This policy is not compatible with IPv6. Add an in-path rule to the server-side SteelHead that specifies the Citrix Access Gateway IP address, select this latency optimization policy on the server-side SteelHeads, and set the preoptimization policy to SSL. The server-side SteelHeads must be running RiOS 7.0 or later. The preoptimization policy must be set to SSL. SSL must be enabled on the Citrix Access Gateway. On the server-side SteelHead, enable SSL and install the SSL server certificate for the Citrix Access Gateway. The server-side SteelHeads establish an SSL channel between themselves to secure the optimized Independent Computing Architecture (ICA) traffic. End users log in to the Access Gateway through a browser (HTTPS) and access applications through the web interface. Clicking an application icon starts the Online Plug-in, which establishes an SSL connection to the Access Gateway. The ICA connection is tunneled through the SSL connection. The SteelHead decrypts the SSL connection from the user device, applies ICA latency optimization, and reencrypts the traffic over the internet. The server-side SteelHead decrypts the optimized ICA traffic and re-encrypts the ICA traffic into the original SSL connection destined to the Access Gateway. • Exchange Autodetect - Automatically detects MAPI transport protocols (Autodiscover, Outlook Anywhere, and MAPI over HTTP) and HTTP traffic. For MAPI transport protocol optimization, enable SSL and install the SSL server certificate for the Exchange Server on the server-side SteelHead. To activate MAPI over HTTP bandwidth and latency optimization, you must also choose Manage > Services: Policies and select the Protocol Settings tab, click the MAPI tab, and click the Enable MAPI over HTTP optimization on the server-side SteelHead. The server-side SteelHeads must be running RiOS 9.2 for MAPI over HTTP latency optimization. • None - Don’t activate latency optimization on connections matching this rule. For Oracle Forms-over-SSL encrypted traffic, you must set the Latency Optimization Policy to HTTP. Setting the Latency Optimization Policy to None excludes all latency optimizations, such as HTTP, MAPI, and SMB. |
Neural Framing Mode | Optionally, if you have selected Auto-Discover or Fixed Target, you can select a neural framing mode for the in-path rule. Neural framing enables the system to select the optimal packet framing boundaries for Scalable Data Referencing (SDR). Neural framing creates a set of heuristics to intelligently determine the optimal moment to flush TCP buffers. The system continuously evaluates these heuristics and uses the optimal heuristic to maximize the amount of buffered data transmitted in each flush, while minimizing the amount of idle time that the data sits in the buffer. You can specify these neural framing settings: • Never - Don’t use the Nagle algorithm. The Nagle algorithm is a means of improving the efficiency of TCP/IP networks by reducing the number of packets that need to be sent over the network. It works by combining a number of small outgoing messages and sending them all at once. All the data is immediately encoded without waiting for timers to fire or application buffers to fill past a specified threshold. Neural heuristics are computed in this mode but are not used. In general, this setting works well with time-sensitive and chatty or real-time traffic. • Always - Use the Nagle algorithm. This is the default setting. All data is passed to the codec which attempts to coalesce consume calls (if needed) to achieve better fingerprinting. A timer (6 ms) backs up the codec and causes leftover data to be consumed. Neural heuristics are computed in this mode but are not used. For different types of traffic, one algorithm might be better than others. The considerations include: latency added to the connection, compression, and SDR performance. To configure neural framing for an FTP data channel, define an in-path rule with the destination port 20 and set its data reduction policy. To configure neural framing for a MAPI data channel, define an in-path rule with the destination port 7830 and set its data reduction policy. |
Cloud Acceleration | After you subscribe to a SaaS platform and enable it, ensure that cloud acceleration is ready and enabled. When cloud acceleration is enabled, connections to the subscribed SaaS platform are optimized by the SteelHead SaaS. You don’t need to add an in-path rule unless you want to optimize specific users and exclude others. Select one of these choices from the drop-down list: • Auto - If the in-path rule matches, the connection is optimized by the SteelHead SaaS connection. • Pass Through - If the in-path rule matches, the connection is not optimized by the SteelHead SaaS, but it follows the other rule parameters so that the connection might be optimized by this SteelHead with other SteelHeads in the network, or it might be passed through. Domain labels and cloud acceleration are mutually exclusive. When using a domain label, the Management Console dims this control and sets it to Pass Through. You can set cloud acceleration to Auto when domain label is set to n/a. Using host labels is not recommended for SteelHead SaaS traffic. This applies to the legacy cloud acceleration service and not the SaaS Accelerator. |
WAN Visibility Mode | Enables WAN visibility, which pertains to how packets traversing the WAN are addressed. WAN visibility mode is configurable for Auto-Discover and Fixed-Target rules. To configure WAN Visibility for Fixed-Target rules, you must use CLI commands. For details on WAN Visibility CLI commands, see the Riverbed Command-Line Interface Reference Manual. You configure WAN visibility on the client-side Client Accelerator (where the connection is initiated). The server-side SteelHead must also support WAN visibility. Select one of these modes from the drop-down list: • Correct Addressing - Turns WAN visibility off. Correct addressing uses SteelHead IP addresses and port numbers in the TCP/IP packet header fields for optimized traffic in both directions across the WAN. This is the default setting. • Port Transparency - Port address transparency preserves your server port numbers in the TCP/IP header fields for optimized traffic in both directions across the WAN. Traffic is optimized while the server port number in the TCP/IP header field appears to be unchanged. Routers and network monitoring devices deployed in the WAN segment between the communicating SteelHeads can view these preserved fields. Use port transparency if you want to manage and enforce policies that are based on destination ports. If your WAN router is following traffic classification rules written in terms of client and network addresses, port transparency enables your routers to use existing rules to classify the traffic without any changes. Port transparency enables network analyzers deployed within the WAN (between the SteelHeads) to monitor network activity and to capture statistics for reporting by inspecting traffic according to its original TCP port number. Port transparency does not require dedicated port configurations on your Client Accelerators. Port transparency only provides server port visibility. It does not provide server IP address visibility. For the Client Accelerator, the client IP address and port numbers are preserved. • Full Transparency - Full address transparency preserves your client and server IP addresses and port numbers in the TCP/IP header fields for optimized traffic in both directions across the WAN. It also preserves VLAN tags. Traffic is optimized while these TCP/IP header fields appear to be unchanged. Routers and network monitoring devices deployed in the WAN segment between the communicating SteelHeads can view these preserved fields. If both port transparency and full address transparency are acceptable solutions, port transparency is preferable. Port transparency avoids potential networking risks that are inherent to enabling full address transparency. For details, see the SteelHead Deployment Guide. However, if you must see your client or server IP addresses across the WAN, full transparency is your only configuration option. |
WAN Visibility Mode (continued) | Enabling full address transparency requires symmetrical traffic flows between the client and server. If any asymmetry exists on the network, enabling full address transparency might yield unexpected results, up to and including loss of connectivity. For details, see the SteelHead Deployment Guide. RiOS includes an option for using Full Transparency with a stateful firewall. A stateful firewall examines packet headers, stores information, and then validates subsequent packets against this information. If your system uses a stateful firewall, this option is available: • Full Transparency with Reset - Enables full address and port transparency and also sends a forward reset between receiving the probe response and sending the transparent inner channel SYN. This option ensures the firewall does not block inner transparent connections because of information stored in the probe connection. The forward reset is necessary because the probe connection and inner connection use the same IP addresses and ports and both map to the same firewall connection. The reset clears the probe connection created by the SteelHead and allows for the full transparent inner connection to traverse the firewall. Notes: • For details on configuring WAN visibility and its implications, see the SteelHead Deployment Guide. • To turn full transparency on globally by default, create an in-path auto-discover rule, select Full, and place it above the default in-path rule and after the Secure, Interactive, and RBT-Proto rules. • You can configure a SteelHead for WAN visibility even if the server-side SteelHead does not support it, but the connection is not transparent. • You can enable full transparency for servers in a specific IP address range and you can enable port transparency on a specific server. For details, see the SteelHead Deployment Guide. • The Top Talkers report displays statistics on the most active, heaviest users of WAN bandwidth, providing some WAN visibility without enabling a WAN Visibility Mode. |
Description | Describe the rule to facilitate administration. |
Add | Adds the rule to the list. The Management Console redisplays the In-Path Rules table and applies your modifications to the running configuration, which is stored in memory. |
Remove Selected Rules | Select the check box next to the name and click Remove Selected Rules. |
Move Selected Rules | Moves the selected rules. Click the arrow next to the desired rule position; the rule moves to the new position. |
Edit Rule | Select an existing rule number from the table and expand it. Make required changes and click Edit Rule to update an existing rule. |
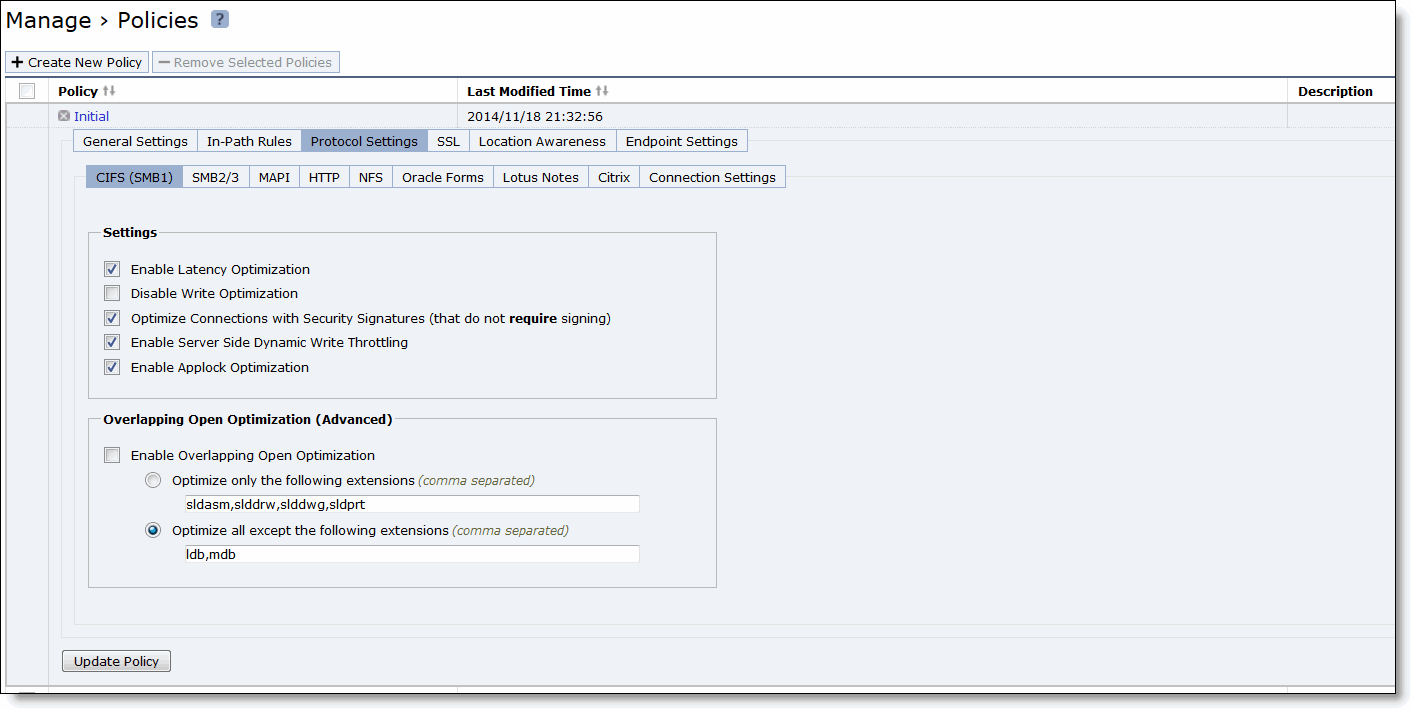
Control | Description |
Enable Latency Optimization | CIFS SMB1 optimization performs latency and SDR optimizations on SMB1 traffic. Without this feature, the Client Accelerator performs only SDR optimization without improving CIFS latency. Latency optimization is enabled by default. Typically, you disable latency optimization to troubleshoot problems with the system. To disable CIFS optimization, it must also be disabled on the server-side SteelHead. |
Disable Write Optimization | Select this option to disable write optimization. Disable write optimization only if you have applications that assume and require write-through in the network. If you disable write optimization, the Client Accelerator still provides optimization for CIFS reads and for other protocols, but you might experience a slight decrease in overall optimization. Most applications operate safely with write optimization because CIFS allows you to explicitly specify write-through on each write operation. However, if you have an application that does not support explicit write-through operations, you must disable it on the Client Accelerator. If you don’t disable write-through, the Client Accelerator acknowledges writes before they are fully committed to disk, to speed up write operation. The Client Accelerator does not acknowledge the file close until the file is safely written. |
Optimize Connections with Security Signatures (that don’t require signing) | Prevents Windows SMB signing. This is the default setting. The Secure-CIFS feature enables you to automatically disable Windows SMB signing. SMB signing prevents the appliance from applying full optimization on CIFS connections and significantly reduces the performance gain from a Client Accelerator deployment. Because many enterprises already take additional security precautions (such as firewalls, internal-only reachable servers, and so forth), SMB signing adds little additional security, at a significant performance cost (even without Riverbed optimization). Before you enable Secure-CIFS, consider these factors: • If the client machine has Required signing, enabling Secure-CIFS prevents the client from connecting to the server. • If the server-side machine has Required signing, the client and server connect but you can’t perform full latency optimization with the appliance. Domain controllers default to Required. For details about SMB signing and the performance cost associated with it, see the SteelHead User Guide. |
Enable Server Side Dynamic Write Throttling | Enables the CIFS dynamic throttling mechanism, which replaces the current static buffer scheme. If you enable CIFS dynamic throttling, it is activated only when there are suboptimal conditions on the server side causing a backlog of writes messages; it does not have a negative effect under normal network conditions. |
Enable Applock Optimization | Enables CIFS latency optimizations to improve read and write performance for Microsoft Word (.doc) and Excel (.xls) documents when multiple users have the file open. This setting is enabled by default in RiOS 6.0 and later. This feature enhances the Enable Overlapping Open Optimization feature by identifying and obtaining locks on read write access at the application level. The overlapping open optimization feature handles locks at the file level. Applock Optimization is a client-side setting only. To enable this feature on Client Accelerator endpoints, select Applock Optimization on the Client Accelerator policy assigned to the clients. |
Enable Overlapping Open Optimization | Overlapping Open Optimization is disabled by default. To prevent any compromise to data integrity, the appliance optimizes only data to which exclusive access is available (in other words, when locks are granted). When an oplock is not available, the Client Accelerator does not perform application-level latency optimizations but still performs SDR and compression on the data, as well as TCP optimizations. Enabling this feature on applications that perform multiple opens of the same file to complete an operation results in a performance improvement (for example, CAD applications). If a remote user opens a file that is optimized using the overlapping open feature and a second user opens the same file, the second user might receive an error if the file fails to go through a Client Accelerator, or if it does not go through a SteelHead (for example, certain applications that are sent over the LAN). If this error occurs, disable overlapping opens for those applications. |
Optimize only these extensions | Specify a list of extensions you want to optimize using overlapping opens. |
Optimize all except these extensions | Specify a list of extensions you don’t want to optimize using overlapping opens. |
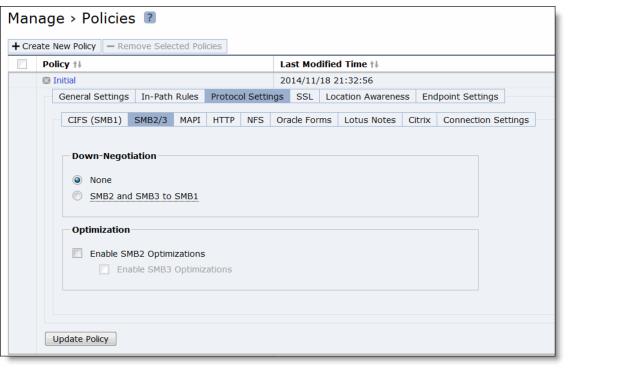
Control | Description |
Down-Negotiation | Select this option so that connections that can be successfully down-negotiated will be optimized according to the settings in the CIFS (SMB1) section. If down-negotiation is enabled, select one of these options: • None - Don’t down-negotiate connections. No connections can be down negotiated. • SMB2 and SMB3 to SMB1 - Down-negotiate SMB2, SMB3, or SMB3.1.1 connections to SMB1. |
Enable SMB2 Optimization | Performs SMB2 optimization in addition to the existing bandwidth optimization features. These optimizations include cross-connection caching, read-ahead, write-behind, and batch prediction among several other techniques to ensure low-latency transfers. The Client Accelerator maintains the data integrity, and the client always receives data directly from the servers. By default, SMB2 optimization is enabled. • Enable SMB3 Optimization - Select this option to enable SMB3 (or SMB3.1.1) optimization. You must enable (or disable) SMB2, SMB3, or SMB3 1.1 (if applicable) optimization on both the Client Accelerator and server-side SteelHead. After enabling SMB2, SMB3, or SMB3.1.1 optimization, you must restart the optimization service. |
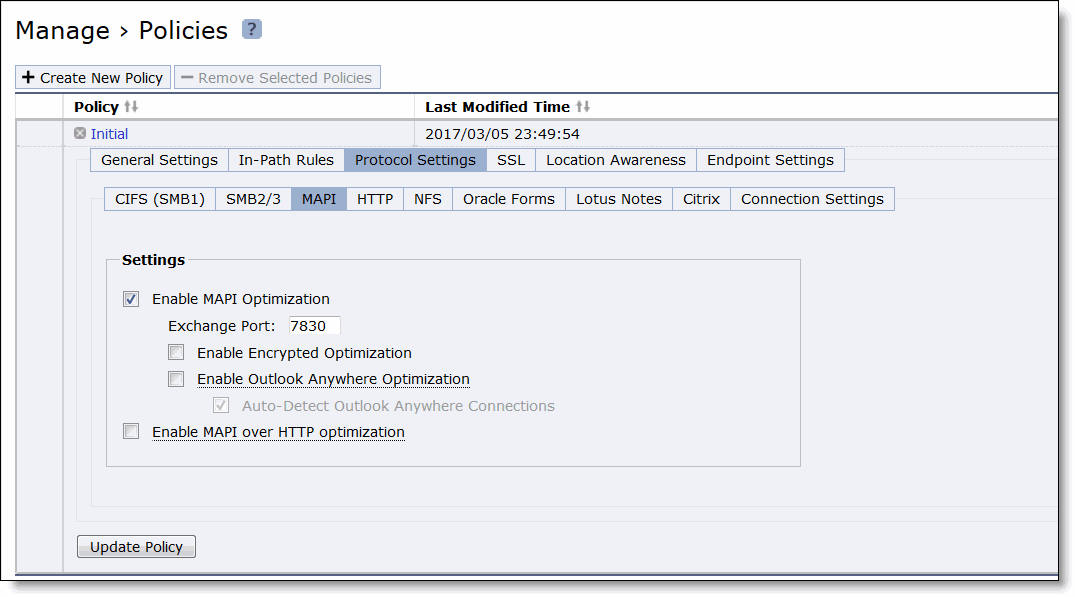
Control | Description |
Enable MAPI Optimization | MAPI optimization is enabled by default. Only clear this check box if you want to disable MAPI optimization. Only disable MAPI if you’re experiencing an issue with Outlook traffic. |
Exchange Port | Specify the MAPI Exchange port. The default value is 7830. |
Enable Encrypted Optimization | Select this option to enable encrypted optimization. |
Enable Outlook Anywhere Optimization | Enables Outlook Anywhere latency optimization. Outlook Anywhere is a feature of Microsoft Exchange Server 2003, 2007, and 2010 that allows Microsoft Office Outlook 2003, 2007, and 2010 clients to connect to their Exchange servers over the internet using the Microsoft RPC tunneling protocol. Outlook Anywhere allows for a VPN-less connection as the MAPI RPC protocol is tunneled over HTTP or HTTPS. RPC over HTTP can transport regular or encrypted MAPI. If you use encrypted MAPI, the server-side SteelHead must be a member of the Windows domain. By default, this feature is disabled. To use this feature, you must also enable HTTP Optimization on the Client Accelerator and server-side SteelHeads (HTTP optimization is enabled by default). If you’re using Outlook Anywhere over HTTPS, you must enable SSL and the IIS certificate must be installed on the server-side SteelHead: • When using HTTP, Outlook can only use NTLM proxy authentication. • When using HTTPS, Outlook can use NTLM or Basic proxy authentication. • When using encrypted MAPI with HTTP or HTTPS, you must enable and configure encrypted MAPI in addition to this feature. Outlook Anywhere optimized connections can’t start MAPI prepopulation. After you apply your settings, you can verify that the connections appear in the Endpoint report as a MAPI-OA or an eMAPI-OA (encrypted MAPI) application. The Outlook Anywhere connection entries appear in the system log with an RPCH prefix. Outlook Anywhere can create twice as many connections on the SteelHead as regular MAPI (depending on the versions of the Outlook client and Exchange server). This effect results in the SteelHead entering admission control twice as fast with Outlook Anywhere as with regular MAPI. For details and troubleshooting information, see the SteelHead Deployment Guide. For details about enabling Outlook Anywhere, see http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/bb123513(EXCHG.80).aspx |
Auto-Detect Outlook Anywhere Connections | Automatically detects the RPC over HTTPS protocol used by Outlook Anywhere. This feature is dimmed and unavailable until you enable Outlook Anywhere optimization. By default, these options are enabled. You can enable automatic detection of RPC over HTTPS using this option or you can set in-path rules. Autodetect is best for simple Client Accelerator configurations and when the IIS server is also handling websites. If the IIS server is only used as RPC Proxy, and for configurations with asymmetric routing, connection forwarding or Interceptor installations, add in-path rules that identify the RPC Proxy server IP addresses and select the Outlook Anywhere latency optimization policy. After adding the in-path rule, disable the auto-detect option. |
Enable MAPI over HTTP optimization | Optimizes MAPI-over-HTTP traffic. MAPI over HTTP is a transport mechanism that provides faster connections between Outlook and Exchange. |
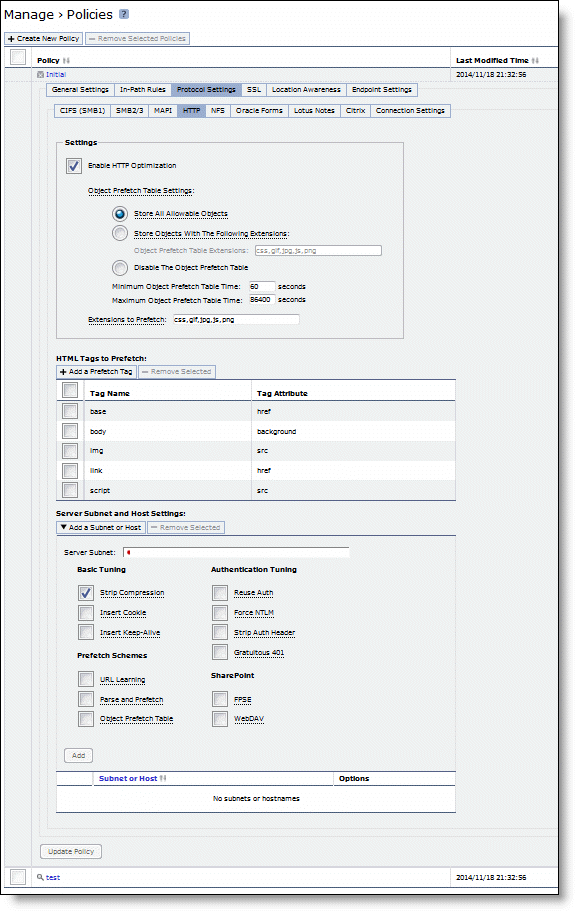
Control | Description |
Enable HTTP Optimization | Enable this feature to prefetch and store objects embedded in web pages to improve HTTP traffic performance. By default, HTTP optimization is disabled. |
Store All Allowable Objects | Examines the control header to determine which objects to store. When enabled, the Client Accelerator does not limit the objects to those listed in Extensions to prefetch but rather prefetches all objects that the control header indicates are storable. This option is useful to store web objects encoded into names without an object extension: for example, SharePoint objects. By default, Store All Allowable Objects is enabled. |
Store Objects With The Following Extensions: Object Prefetch Table Extensions | Specify object extensions to prefetch and store in the local object prefetch table. Separate extensions with a comma. By default, the SteelHead prefetches .jpg, .gif, .js, .png, and .css object extensions. |
Disable the Object Prefetch Table | Stores nothing. |
Minimum Object Prefetch Table Time | Sets the minimum number of seconds the objects are stored in the local object prefetch table. The default is 60 seconds. This setting specifies the minimum lifetime of the stored object. During this lifetime, any qualified If-Modified-Since (IMS) request from the client receives an HTTP 304 response, indicating that the resource for the requested object has not changed since stored. |
Maximum Object Prefetch Table Time | Sets the maximum number of seconds the objects are stored in the local object prefetch table. The default is 86,400 seconds (24 hours). This setting specifies the maximum lifetime of the stored object. During this lifetime, any qualified If-Modified-Since (IMS) request from the client receives an HTTP 304 response, indicating that the resource for the requested object has not changed since stored. |
Extensions to Prefetch | Specifies object extensions to prefetch, separated by commas. By default the SteelHead prefetches .jpg, .gif, .js, .png, and .css object extensions. |
HTML Tags to Prefetch | Selects which HTML tags to prefetch. By default, these tags are prefetched: base/href, body/background, img/src, link/href, and script/src. |
Add a Prefetch Tag | Configures a new prefetch tag with these controls: • Tag Name - Specifies the tag name. • Attribute - Specifies the tag attribute. These tags are for the Parse and Prefetch feature only and don’t affect other prefetch types, such as object extensions. |
Server Subnet and Host Settings | Under Server Subnet and Host Settings, you can enable URL Learning, Parse and Prefetch, and Object Prefetch Table in any combination for any server subnet. You can also enable authorization optimization to tune a particular subnet dynamically with no service restart required. The default settings are URL Learning for all traffic with automatic configuration disabled. The default setting applies when HTTP optimization is enabled, regardless of whether there is an entry in the Subnet list. In the case of overlapping subnets, specific list entries override any default settings. Suppose the majority of your web servers have dynamic content applications but you also have several static content application servers. You could configure your entire server subnet to disable URL Learning and enable Parse and Prefetch and Object Prefetch Table, optimizing HTTP for the majority of your web servers. Next, you could configure your static content servers to use URL Learning only, disabling Parse and Prefetch and Object Prefetch Table. |
Add a Subnet or Host | Displays the controls for adding a server subnet or host. The server must support keepalive. |
Server Subnet | Specify an IP address and mask pattern for the server subnet on which to set up the HTTP optimization scheme. Use this format: xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx/xx |
Basic Tuning | • Strip Compression - Removes the accept-encoding lines from the HTTP compression header. An accept-encoding directive compresses content rather than using raw HTML. Enabling this option improves the performance of the Client Accelerator data reduction algorithms. By default, strip compression is enabled. • Insert Cookie - Adds a cookie to HTTP applications that don’t already have one. HTTP applications frequently use cookies to keep track of sessions. The Client Accelerator uses cookies to distinguish one user session from another. If an HTTP application does not use cookies, the Client Accelerator inserts one so that it can track requests from the same client. By default, this setting is not selected. • Insert Keep Alive - Uses the same TCP connection to send and receive multiple HTTP requests and responses, as opposed to opening a new one for every single request and response. Select this option when using the URL Learning or Parse and Prefetch features with HTTP 1.0 or HTTP 1.1 applications using the Connection Close method. By default, this setting is not selected. |
Prefetch Schemes | • URL Learning - Enables URL Learning, which learns associations between a base URL request and a follow-on request. Stores information about which URLs have been requested and which URLs have generated a 200 OK response from the server. This option fetches the URLs embedded in style sheets or any JavaScript associated with the base page and located on the same host as the base URL. URL Learning works best with nondynamic content that does not contain session-specific information. URL Learning is enabled by default. Your system must support cookies and persistent connections to benefit from URL Learning. If your system has cookies turned off and depends on URL rewriting for HTTP state management, or is using HTTP 1.0 (with no keepalives), you can force the use of cookies using the Add Cookie option and force the use of persistent connections using the Insert Keep Alive option. • Parse and Prefetch - Enables Parse and Prefetch, which parses the base HTML page received from the server and prefetches any embedded objects to the Client Accelerator. This option complements URL Learning by handling dynamically generated pages and URLs that include state information. When the browser requests an embedded object, the Client Accelerator serves the request from the prefetched results, eliminating the round-trip delay to the server. The prefetched objects contained in the base HTML page can be images, style sheets, or any Java scripts associated with the base page and located on the same host as the base URL. Parse and Prefetch requires cookies. If the application does not use cookies, you can insert one using the Insert Cookie option. • Object Prefetch Table - Enables the Object Prefetch Table, which stores HTTP object prefetches from HTTP GET requests for cascading style sheets, static images, and Java scripts in the Object Prefetch Table. When the browser performs If-Modified-Since (IMS) checks for stored content or sends regular HTTP requests, the Client Accelerator responds to these IMS checks and HTTP requests, cutting back on round trips across the WAN. |
Authentication Tuning | • Reuse Auth - Allows an unauthenticated connection to serve prefetched objects, as long as the connection belongs to a session whose base connection is already authenticated. This option is most effective when the web server is configured to use per-connection NTLM or Kerberos authentication. • Force NTLM - In the case of negotiated Kerberos and NTLM authentication, forces NTLM. Kerberos is less efficient over the WAN because the client must contact the Domain Controller to answer the server authentication challenge and tends to be employed on a per-request basis. We recommend enabling Strip Auth Header along with this option. • Strip Auth Header - Removes all credentials from the request on an already authenticated connection. This option works around Internet Explorer behavior that reauthorizes connections that have previously been authorized. This option is most effective when the web server is configured to use per-connection NTLM authentication. If the web server is configured to use per-request NTLM authentication, enabling this option might cause authentication failure. • Gratuitous 401 - Prevents a WAN round trip by issuing the first 401 containing the realm choices from the Client Accelerator. We recommend enabling Strip Auth Header along with this option. This option is most effective when the web server is configured to use per-connection NTLM authentication or per-request Kerberos authentication. If the web server is configured to use per-connection Kerberos authentication, enabling this option might cause additional delay. |
SharePoint | • FPSE (FrontPage Server Extensions) - FPSE is an application-level protocol used by SharePoint. FPSE allows a website to be presented as a file share. FPSE initiates its communication with the server by requesting well-defined URLs for further communication and determining the version of the server. • WebDAV (Web-based Distributed Authoring and Versioning) - WebDAV is a set of extensions to the HTTP/1.1 protocol that allows users to collaboratively edit and manage files on remote web servers. WebDAV is an IETF Proposed Standard (RFC 4918) that provides the ability to access the document management system as a network file system. |
Add | Adds the server subnet or host. |
Control | Description |
Enable Oracle Forms Optimization | Enables Oracle Forms optimization in native mode, also known as socket mode. Oracle Forms native mode optimization is enabled by default. Disable this option only to turn off Oracle Forms optimization; for example, if your network users don’t use Oracle applications. |
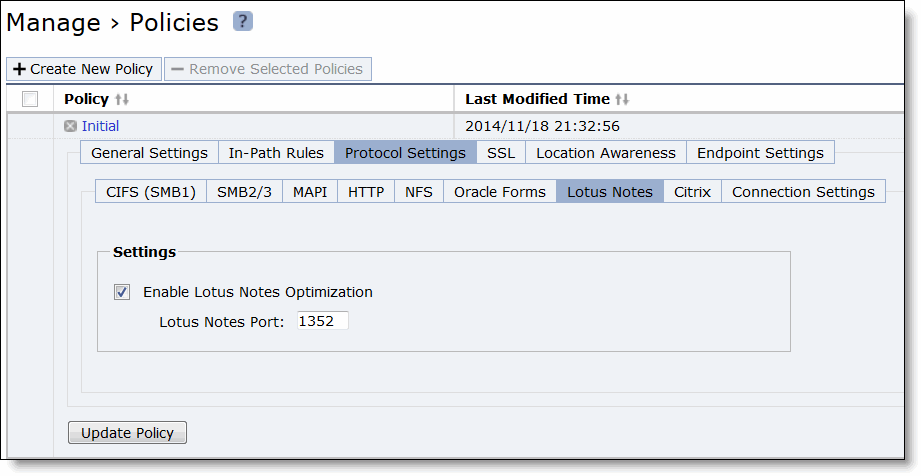
Control | Description |
Enable Lotus Notes Optimization | Enables latency and bandwidth optimization for Lotus Notes 6.0 and later traffic across the WAN. This feature accelerates email attachment transfers and server-to-server or client-to-server replications. Lotus Notes is only supported on Client Accelerator endpoints running on Windows PCs. |
Lotus Notes Port | Specify the Lotus Notes port for optimization. Typically, you don’t need to modify the default value of 1352. |
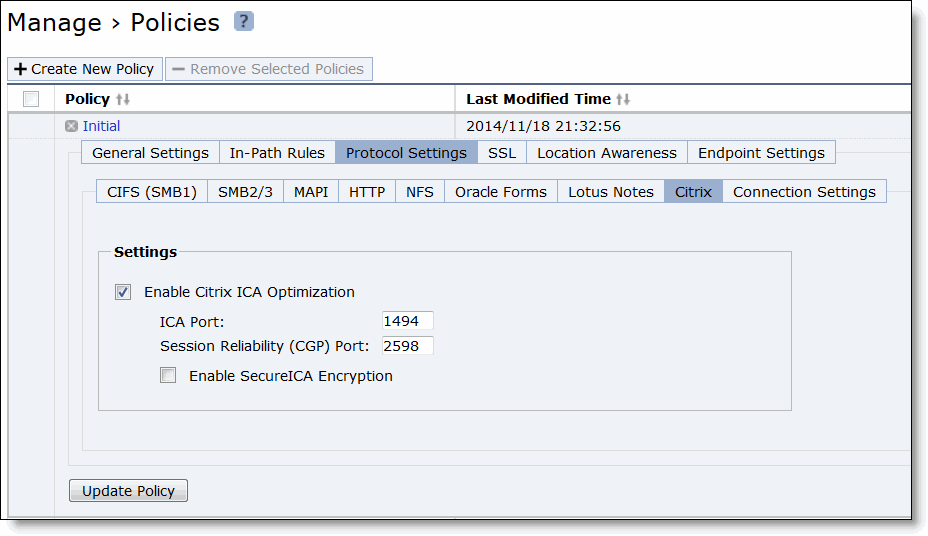
Control | Description |
Citrix | Optimizes the native Citrix traffic bandwidth. |
ICA Port | Specify the port on the Presentation Server for inbound traffic. The default port is 1494. |
Session Reliability (CGP) Port | Specify the port number for Common Gateway Protocol (CGP) connections. CGP uses the session reliability port to keep the session window open even if there is an interruption on the network connection to the server. By default, this setting is 2598. |
Enable SecureICA Encryption | Uses the RC5 algorithm to encrypt the ICA protocol, securing communication sent between a MetaFrame Presentation Server and a client. |
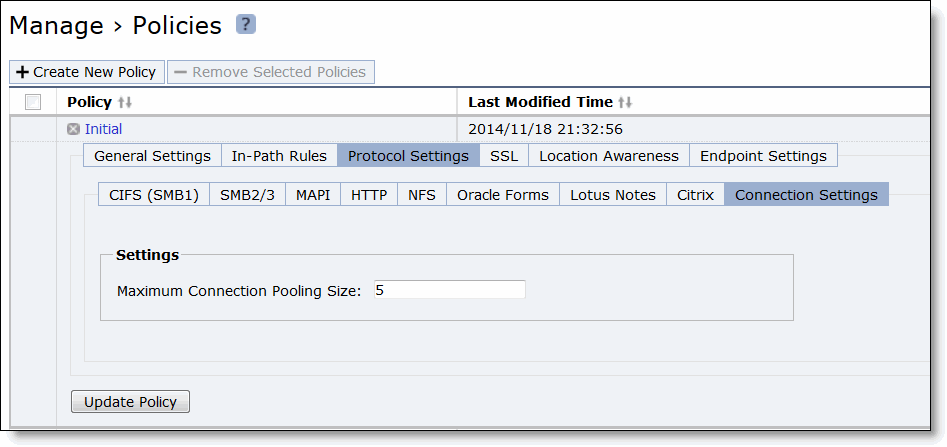
Control | Description |
Maximum Connection Pool Size | Specify the maximum number of TCP connections in a connection pool. Connection pooling enhances network performance by reusing active connections instead of creating a new connection for every request. Connection pooling is useful for protocols which create a large number of short-lived TCP connections, such as HTTP. To optimize such protocols, a connection pool manager maintains a pool of idle TCP connections, up to the maximum pool size. When a client requests a new connection to a previously visited server, the pool manager checks the pool for unused connections and returns one if available. Thus, the Client Accelerator and the SteelHead don’t have to wait for a three-way TCP handshake to finish across the WAN. If all connections currently in the pool are busy and the maximum pool size has not been reached, the new connection is created and added to the pool. When the pool reaches its maximum size, all new connection requests are queued until a connection in the pool becomes available or the connection attempt times out. The default value is 5. A value of 0 specifies no connection pool. |
Control | Description |
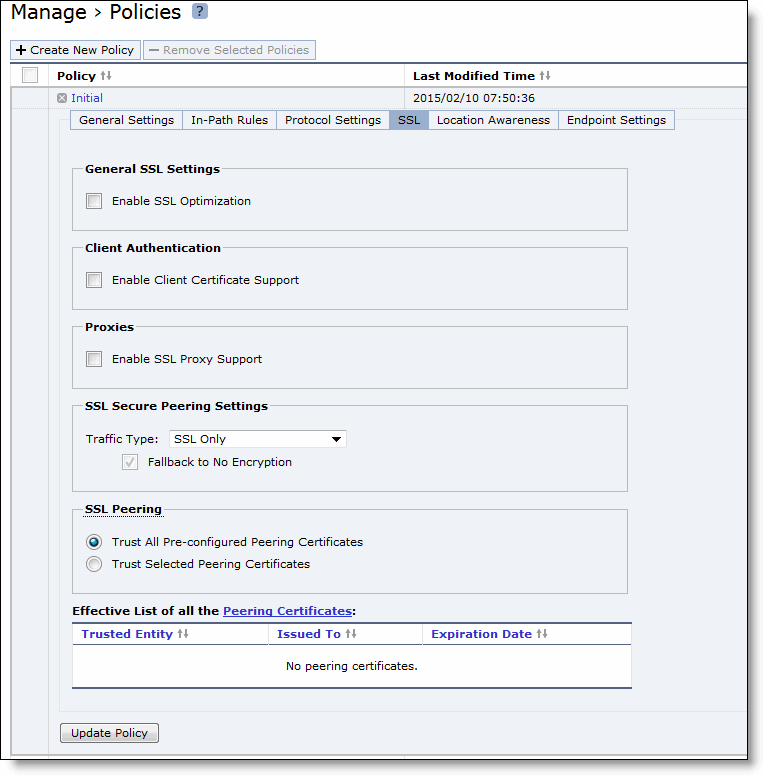
General SSL Settings | Enable SSL Optimization - Enables SSL optimization, which accelerates applications that use SSL to encrypt traffic. This option is disabled by default. You can choose to enable SSL optimization only on certain sessions (based on source and destination addresses, subnets, and ports), or on all SSL sessions, or on no SSL sessions at all. An SSL session that is not optimized simply passes through the Client Accelerator unmodified. To enable SNI support, you need to enable SSL optimization on the Client Accelerator and enable SNI on the SteelHead. For details, see
Basic steps for configuring SNI support. |
Client Authentication | Enable Client Certificate Support - Enables use of client-side SSL certificates to authenticate clients. |
Proxies | Enable SSL Proxy Support - Enables support for SSL proxy. |
SSL Secure Peering Settings Traffic Type | Traffic Type - Select one of these traffic types from the drop-down list: • SSL Only - The peer Client Accelerator and the server-side SteelHead authenticate each other and then encrypt and optimize all SSL traffic: for example, HTTPS traffic on port 443. This is the default setting. • SSL and Secure Protocols - The peer Client Accelerator and the server-side SteelHead authenticate each other and then encrypt and optimize all traffic traveling over these secure protocols: Citrix, SSL, SMB-signed, and encrypted MAPI. SMB-signing, MAPI encryption, or Secure ICA encryption must be enabled on both the Client Accelerator and server-side SteelHeads when securing SMB-signed traffic, encrypted MAPI traffic, or encrypted Citrix ICA traffic. Enabling this option requires an optimization service restart. • All - The peer Client Accelerator and the server-side SteelHead authenticate each other and then encrypt and optimize all traffic. Only the optimized traffic is secure; pass-through traffic is not. Enabling this option requires an optimization service restart. • Fallback to No Encryption - Specifies that the Client Accelerator optimizes but does not encrypt the connection when it is unable to negotiate a secure, encrypted inner channel connection with the peer. This is the default setting. Enabling this option requires an optimization service restart. We strongly recommend enabling this setting on both the Client Accelerator and the server-side SteelHeads, especially in mixed deployments. This option applies only to non-SSL traffic and is unavailable when you select SSL Only as the traffic type. Clear the check box to pass through connections that don’t have a secure encrypted inner channel connection with the peer. Use caution when disabling this setting, as doing so specifies that you strictly don’t want traffic optimized between nonsecure appliances. When this setting is disabled on the server-side SteelHead and All is selected as the traffic type, it will not optimize the connection when a secure channel is unavailable, and might drop it. |
SSL Peering | • Trust All Pre-configured Peering Certificates - Enables a trust relationship for all preconfigured Client Accelerator certificates listed in Effective List of all the Peering Certificates. • Trust Selected Peering Certificates - Enables a trust relationship only with selected peering certificates in the Selected Peering Certificates list. When you select this option, the Selected Peering Certificates options are displayed. |
Add Peering Certificate | Click to add a peering certificate from the drop-down list. |
Add | Adds the selected peering certificate to the Selected Peerings Certificates list. |
Remove Peering Certificate | Select the check box next to the name and click Remove Peering Certificate to remove the peering certificate. |
Control | Description |
Enable Latency-based location awareness | Click the check box only if you want to enable latency-based location awareness. Latency-based location awareness is disabled by default. |
Optimize over adapters specified above if latency to SteelHead is more than: ( ) ms | Specify the value of latency to the SteelHead (in milliseconds) above which optimization over the specified adapters occurs. |
Enable Branch Warming | Select the check box only if you want to enable branch warming. Branch warming is disabled by default. |
Adapters to Optimize: Add New Rule | Position - Select start, end, or a rule number from the drop-down list. The Client Accelerators evaluate rules in numerical order, starting with rule 1. If the conditions set in the rule match, then the rule is applied, and the system moves on to the next packet. If the conditions set in the rule don’t match, the system consults the next rule. For example, if the conditions of rule 1 don’t match, rule 2 is consulted. If rule 2 matches the conditions, it is applied, and no further rules are consulted. |
Adapter - Determines the adapter. Select the adapter from the drop-down list. You can also add a new adapter when you add a new rule. Select Other Adapter(s) from the drop-down list and enter the adapter name in the Other - Please specify field. | |
Optimize - Determines the optimization. Select one of these options from the drop-down list: • Yes - Enables optimization. • No - Disables optimization. | |
Add - Click Add to add the rule to the rules list. |
Control | Description |
Controller Options | Add a New Controller - Displays the controls for adding a new Client Accelerator to the list. |
Insert At - Select start, end, or a Client Accelerator number from the drop-down list. The default value is end. Specify the order in which endpoint clients connect with Client Accelerators. Client Accelerators connect according to the number you specify, starting with 1. If the system is unable to connect to 1 in the list, the system moves on to the next Client Accelerator in the list. For example, if the system is unable to connect to Client Accelerator 1, then Client Accelerator 2 is attempted. If Client Accelerator 2 is successful, no further Client Accelerators in the list are attempted. | |
Hostname/Port - Specify a fully qualified hostname or IP address and port for a Client Accelerator that the client connects to. You can specify more than one Client Accelerator. The default port value is 7870. | |
Use Random Ordering of Controllers when Connecting - Select the check box to disregard the Client Accelerator priority list and randomly connect to Client Accelerators in the group. The default setting is disabled. | |
Add - Adds a new Client Accelerator. | |
Remove Selected Controllers - To remove an entry, select the check box next to the entry and click Remove Selected Controllers. By default, a value for the local Client Accelerator is already in the list. In a clustered deployment, the entry should be removed and replaced with an explicit entry for the local Client Accelerator. |
Control | Description |
General Settings | Show Client in the System Tray - Select the check box to display the Client Accelerator in your client machine system tray. The default setting is enabled. When you enable Show Client in the System Tray, the endpoint user can override policy settings made by the system administrator. Even if a new policy is sent to the client, the settings in the client remain in effect until the endpoint user clicks Reset under Settings > Reset to Administrator policy. Allow User to Modify Optimization Settings - Select the check box to enable the Client Accelerator user to modify optimization settings. The default setting is enabled. |
Data Store Settings | Data Store Size - Select one of these options from the drop-down list. The minimum value is 256 MB. The default value is 10 GB. • 256 MB = 81 MB RAM • 512 MB = 81 MB RAM • 1 GB = 81 MB RAM • 2 GB = 100 MB RAM • 5 GB = 112 MB RAM • 10 GB = 161 MB RAM • 15 GB = 171 MB RAM • 20 GB = 228 MB RAM The amount of RAM used by the optimization service on the Client Accelerator is related to the Client Accelerator RiOS data store size that you select. If the Client Accelerator is visible on the client computer, the Data Store Size Auto setting for RiOS data store size means the client is using the size specified in the policy. Carefully consider the RiOS data store size for your Client Accelerator endpoints. Changing the size later requires emptying the RiOS data store, which temporarily slows performance. |
Log Settings | Maximum Log Size - Specify the maximum size for your log files to be stored on your client machine. The default value is 5000 KB. |
Windows-Only Settings | Disable TCP/IP Checksum Offloading (Requires client reboot) - For Windows only. Select the check box to disable TCP/IP checksum offloading. |