Overview of Virtual In-Path Deployment
In a virtual in-path deployment, the SteelHead is virtually in the path between clients and servers. Traffic moves in and out of the same WAN interface, and the LAN interface is not used. This deployment differs from a physical in-path deployment in that a packet redirection mechanism directs packets to SteelHeads that are not in the physical path of the client or server.
Figure 10‑1. Virtual In-Path Deployment on the Server-Side of the Network
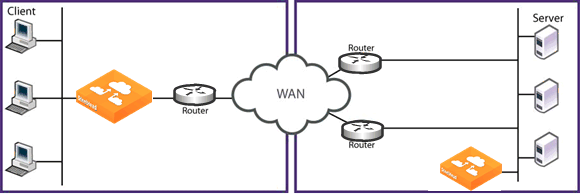
Redirection mechanisms include:
Layer-4 switch - You enable Layer-4 switch (or server load balancer) support when you have multiple SteelHeads in your network to manage large bandwidth requirements. Hybrid - A hybrid deployment is a deployment in which the SteelHead is deployed either in a physical or virtual in-path mode, and has out-of-path mode enabled. A hybrid deployment is useful in which the SteelHead must be referenced from remote sites as an out-of-path device (for example, to bypass intermediary SteelHeads). PBR - PBR enables you to redirect traffic to a SteelHead that is configured as a virtual in-path device. PBR allows you to define policies that override routing behavior. For example, instead of routing a packet based on routing table information, it is routed based on the policy applied to the router. You define policies to redirect traffic to the SteelHead and policies to avoid loop-back. WCCP - WCCP was originally implemented on Cisco routers, multilayer switches, and Web caches to redirect HTTP requests to local Web caches (Version 1). Version 2, which is supported on SteelHeads, can redirect any type of connection from multiple routers to multiple Web caches. For example, if you have multiple routers or if there is no in-path place for the SteelHead, you can place the SteelHead in a virtual in-path mode through the router so that they work together. Interceptor appliance - The SteelHead Interceptor is a load balancer specifically used to distribute optimized traffic to a local cluster of SteelHeads. The SteelHead Interceptor is SteelHead-aware, and so offers several benefits over other clustering techniques like WCCP and PBR. The SteelHead Interceptor is dedicated to redirecting packets for optimized connections to SteelHeads, but does not perform optimization itself. As a result, you can use the SteelHead Interceptor in extremely demanding network environments with extremely high throughput requirements. For information about the SteelHead Interceptor, see the SteelHead Interceptor Deployment Guide and the SteelHead Interceptor User’s Guide.For networks that contain firewalls or tunnels (VPN, GRE, IPSec transport mode) between SteelHeads and require manual tuning of the MTU values, see
MTU Sizing.


