Installing SteelHead SD
This chapter describes how to install and perform the initial configuration of the SteelHead SD appliance. It includes these sections:
This chapter doesn’t provide detailed information about configuring and managing SD-WAN or WAN optimization features. For detailed information, see the SteelConnect Manager User Guide, SteelHead SD User Guide, and the SteelHead User Guide.
Overview
You use SteelConnect Manager (SCM) to install, configure, and manage the SteelHead SD appliances in your SD-WAN network. SteelConnect uses a zero-touch provisioning (ZTP) to install and manage your appliances, enabling you to configure and visualize the appliances in your network before you install and connect the hardware.
Defining an organization
SCM uses these terms to describe the network:
•Organization - A company representing an end customer. You can assign administrative rights to individual administrator accounts per organization. You can also manage appliances and licensing per organization.
•Site - A physical location of one or more office buildings, a hosting center, or a cloud location that make up the organization. A site houses a SteelConnect gateway and uses a permanent DNS alias. Every site requires a local network zone and at least one internet uplink. The zone is automatically created when you create a site.
•Zone - Zones are at the center of an SD-WAN network. A zone is equivalent to a Layer 2 IP segment within a site. Zones define subnets and VLANs on gateways. Every site has at least one zone and can have multiple zones. When you create a site, SteelConnect automatically adds a default zone.
SCM is delivered with a default organization and site. You add your company name and basic information for your organization or change and customize this information later. For details about defining an organization, network, sites, zones, and uplinks, see the SteelConnect Manager User Guide.
To log in to SCM
•Using the SCM URL emailed to you, log in to SCM using the default username (admin) and the default password (pppp).
After a successful log in, you're greeted by the dashboard.
SCM dashboard
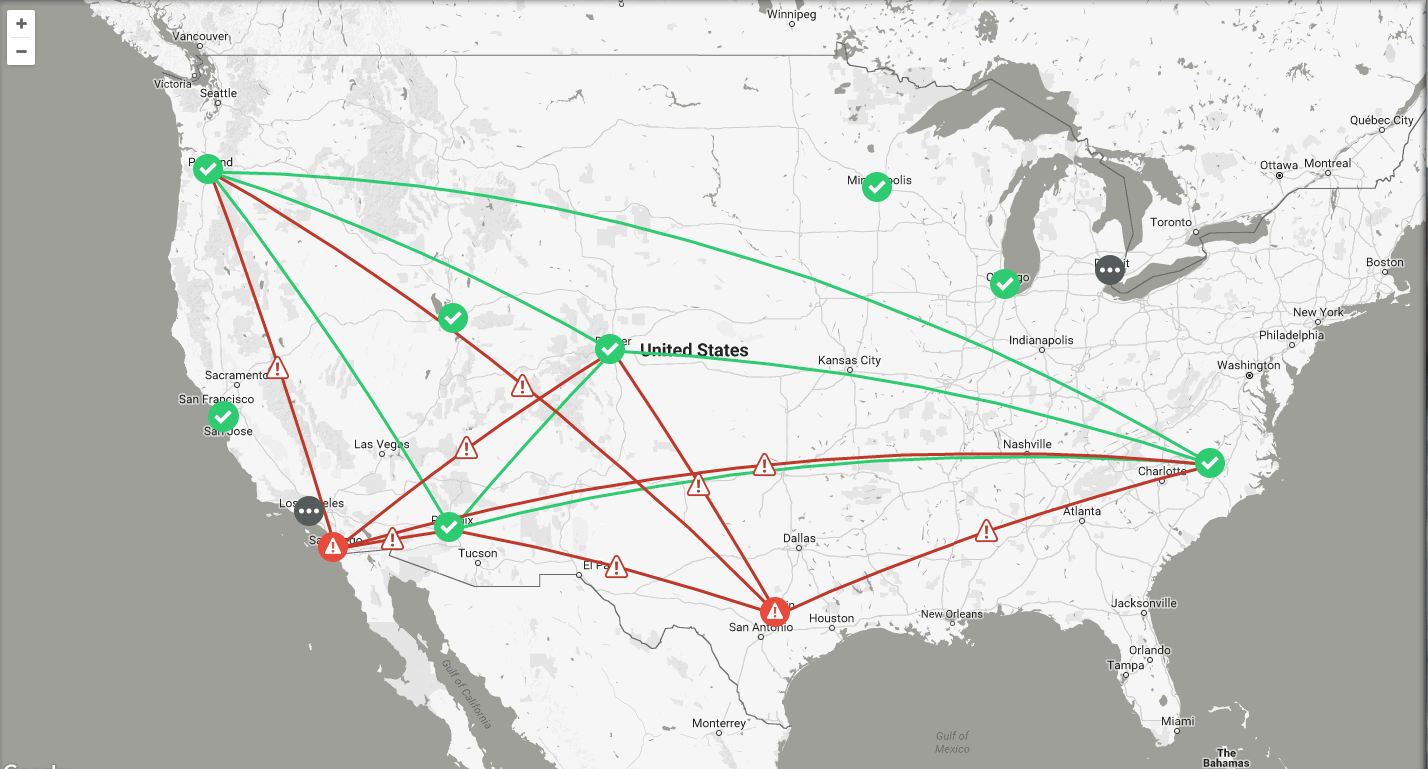
The dashboard map updates dynamically to keep an accurate visual overview of your network. You can always refer to the dashboard map as you define your topology to make sure the deployment is accurate.
To change the default name and location of the organization
1. Choose Organization to display the default organization settings.
2. Change the organization name.
3. Click Submit.
4. Under location, type the company headquarters physical address.
5. Click Submit.
Adding sites
The next task is to create one or more sites. If you have a lot of sites you can also do a bulk import. For detailed information creating sites and bulk imports, see “Creating Sites” in the SteelConnect Manager User Guide.
All internet connections, or uplinks, are automatically created when you set up your sites. By default, all uplinks use DHCP; however, SteelConnect also supports static IPs and PPPoE with authentication. For details, see “Creating uplinks” in the SteelConnect Manager User Guide.
To add sites
1. Choose Network Design > Sites.
2. Click New Site to expand the page.
3. Add a site tag: for example, headquarters.
4. Add the site’s location: for example, San Francisco.
5. Type the site’s address, country, and time zone.
6. Click Submit.
7. Repeat the steps for the remaining sites in your network topology.
A zone is automatically created when you create a site. You can modify a zone now or wait until you have completed the installation process. For details, see the SteelConnect Manager User Guide.
Changing the default zone in a site
Zones are at the center of an SD-WAN network. A zone is equivalent to a Layer 2 IP segment within a site. Zones define subnets and VLANs on gateways.
Every site has at least one zone and can have multiple zones. When you create a site, SteelConnect automatically adds a default zone.
Zones can cross sites. For example, for a business application that involves a call center that requires peer-to-peer networking, you can stretch a single zone across multiple sites, providing users all over the globe with one universal security policy applied to the same IP zone.
You can add zones to any sites or any organization. A zone belongs to a site, but it can also belong to multiple sites. A site is a location like an office building, a hosting center, or a cloud location. Every site has at least one internet uplink and one local network zone.
To change the default zone
1. Choose Network Design > Zones.
2. Select a zone, click Settings, and update the zone name.
3. Select the IP tab, and change the IP address to match your LAN subnet on the SteelHead.
4. Click Submit.
By default, all sites are configured with an internet uplink and a AutoVPN uplink which automatically creates secure tunnels over internet links to create a secure overlay network.
You can add additional zones to a site, if necessary. For details on configuring zones, see “Designing a Network,” in the SteelConnect Manager User Guide.
Adding shadow appliances
SCM stores all configurations, including your existing and future network plans. This means you can either add an appliance when you physically have it or you can preplan and configure an appliance by adding a shadow appliance and later drop the physical appliance into the topology with no further configuration.
To add shadow appliances
1. Choose Appliances > Overview.
2. Click Add appliances and select Create Shadow Appliance.
3. Select 570-SD, 770-SD, or 3070-SD from the model drop-down list.
4. Select the site where you want to deploy the shadow appliance from the site drop-down list.
5. Click Submit.
6. Repeat these steps for each of your appliances.
After adding the virtual gateways, SCM automatically connects them using AutoVPN to create secure VPN tunnels. Later, you’ll register the gateways to transform them from shadow appliances to physical appliances.
7. Choose Network Design > Uplinks to see that SCM has automatically assigned uplinks to the new gateways.
Before deploying the hardware, you can configure other SteelConnect features now or wait until later. For details about configuring SteelConnect features, see the SteelConnect Manager User Guide.
Next, you register the physical appliances to transform them from shadow appliances into physical appliances using the SteelConnect gateway serial number.
Registering appliances
The SteelConnect serial number is in the email from Riverbed that you received when your sales order was confirmed. It is also available on the appliance label. The SteelConnect gateway serial number always begins with the prefix XN. Find that serial number and MAC address on the appliance and write them down.
The SteelHead SD 3070-SD label is located on top of the appliance. The SteelHead SD 570-SD, 770-SD labels are located on the side of the appliance.
SteelConnect serial number and MAC address
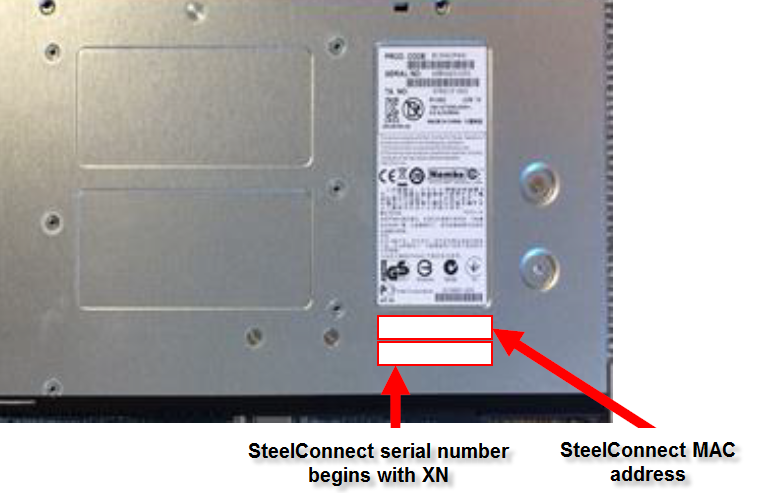

Make sure you register your appliances using the SteelConnect serial number starting with XN. If you don’t, SCM won’t autodetect the appliances when you register them.
To register a hardware appliance
1. Choose Appliances > Overview to view the shadow appliances you just created.
Example of a shadow appliance

2. Select the shadow appliance to expand the page.
3. Choose Actions > Register hardware.
Registering appliances

4. Type the SteelConnect serial number. Make sure you use the SteelConnect gateway serial number that begins with XN.
5. Click Submit.
6. Repeat the steps to register the remaining appliances.
The provisioning server hands off the appliance when it connects into the particular organization and site. It gives the appliance its configuration, brings it online, performs all firmware upgrades, and realizes your design on the appliance in the real world.
Configuring the primary and LAN ports in SCM
The next task is to configure the ports for the SteelHead SD appliance.
You set the LAN port mode to single-zone uplink for the SteelHead WAN optimization service. By default, the LAN port is disabled on SteelHead SD appliances unless it is explicitly enabled. If you don't enable the LAN port, SteelConnect won’t see either the SteelHead WAN optimization service or the clients on the LAN side of the network.
You set the primary port mode to SteelHead Primary for the SteelHead SD appliance.
To configure the primary and LAN ports
1. Choose Appliances > Ports.
2. Select the site with the SteelHead SD appliance from the drop-down list. The ports for the appliance are displayed.
3. Select the primary port to expand the page.
Configuring the primary port
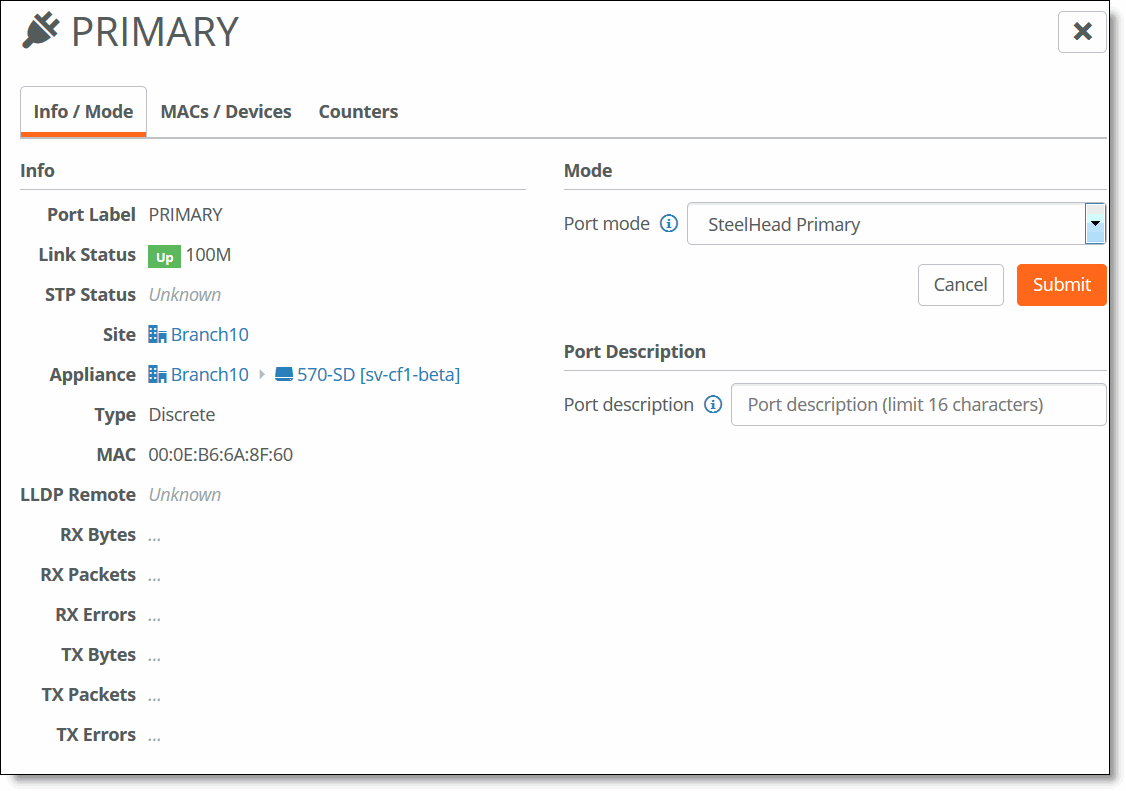
4. Select SteelHead Primary for the Port mode.
5. Optionally, provide a description of the port.
6. Click Submit.
7. Select the LAN port for the SteelHead SD appliance. The Info/Mode tab is displayed.
Configuring the LAN port
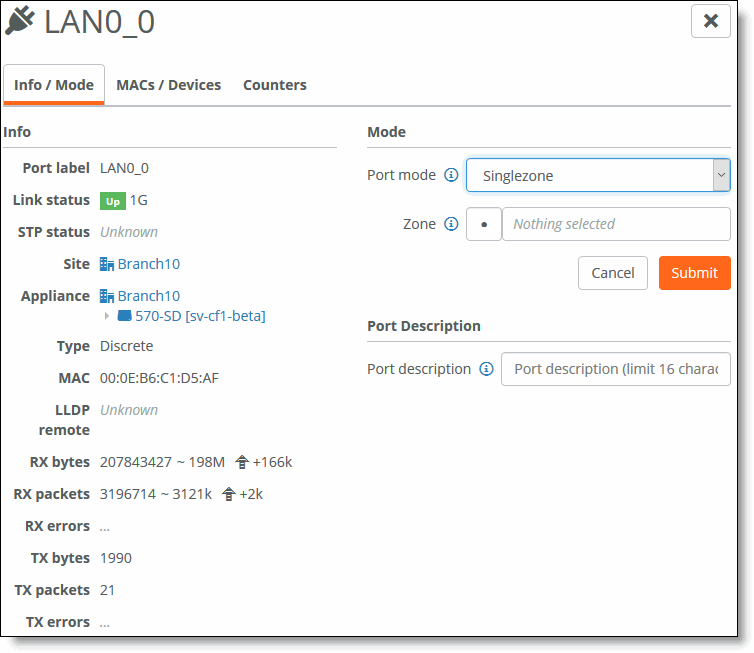
8. Select Singlezone for the Port mode.
9. Select the zone from the drop-down list.
10. Optionally, specify a patch label.
11. Click Submit.
You can continue configuring your LAN ports and WAN uplinks or you can do this later. For detailed information about configuring multizone LAN trunk ports, see the SteelHead SD User Guide. For detailed information on WAN uplinks, see the SteelConnect Manager User Guide.
Next, you configure an IP address for the in-path interface (inpath0_0). The default gateway for that IP address will be the default gateway of the zone you select.
Assigning the in-path IP address and default gateway in SCM
A single in-path interface address is assigned in SCM for the SteelHead SD appliance. You choose an IP address for the LAN zone in which the SteelHead SD is installed. You will use this IP address to configure the in-path interface on the virtual SteelHead appliance.
If the LAN port attached to the SteelHead SD appliance is in a VLAN trunk, the virtual SteelHead appliance must be given an IP address from one of the zones that is part of the trunk, and the virtual SteelHead in-path IP address must also be configured with the corresponding VLAN ID.
To assign the in-path IP address and default gateway in SCM
1. In SCM, choose Network Design > Zones.
2. Select the zone with the SteelHead SD appliance to expand the pane. The IP tab is displayed.
3. Under IPv4 Network, specify the LAN zone subnet. Write down this IP address. You will use this address when you configure the inpath0_0 interface for WAN optimization on the virtual SteelHead instance.
Obtaining the IP address for the in-path interface
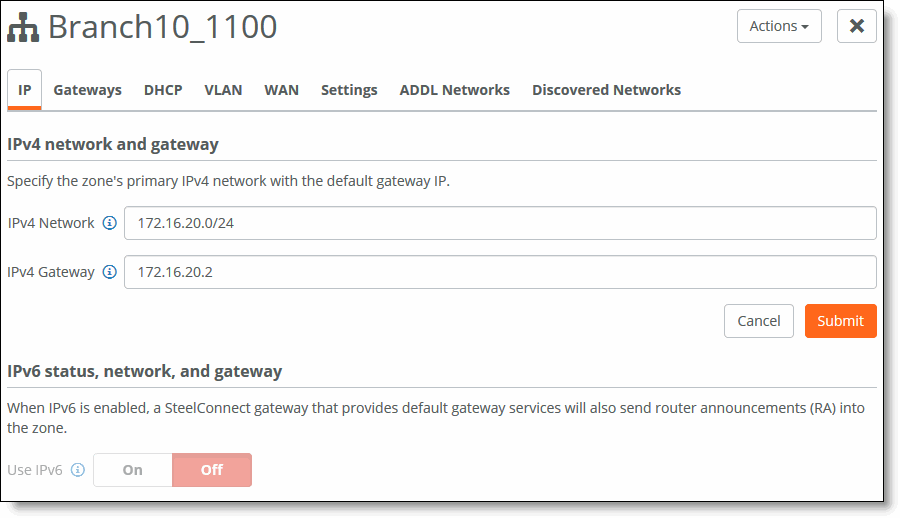
If the network IP address is 172.16.20.0/24, you can assign any IP address from 172.16.20.1 to 172.16.20.254 for the SteelHead in-path interface.
4. Under IPv4 Gateway, specify the default gateway. Write down this IP address. You will use this address when you configure the default gateway for WAN optimization on the virtual SteelHead appliance.
Configuring SteelConnect to act as DHCP server
For SteelConnect to act as a DHCP server, you configure the SteelHead LAN and primary ports to connect to the same switch so that the SteelConnect gateway acts as the DHCP server. This configuration provides the primary IP address of the virtual SteelHead and reports it in SCM.
As the virtual SteelHead instance boots within SteelHead SD, it’s primary interface tires to obtain the primary IP address via DHCP. We highly recommend that the SteelHead SD primary port is attached to a network where a DHCP service is available. There are two ways to connect to a DHCP server:
–Through the switch - Connect the LAN port and primary port to the switch port and configure in the same VLAN.
–Back-Back - Connect the LAN port directly to the primary port.
To configure SteelConnect to act as a DHCP server
1. When you cable the appliance, make sure you connect the LAN port and primary port to the same switch.
2. Choose Networks Design > Zones.
3. Select the zone with the SteelHead SD appliance to expand the page.
4. Select the Gateways tab.
5. Under Default Gateway configuration, click Manual.
6. Under Gateway assignments, click Edit. (You can also add a new assignment if necessary.)
Editing the gateway to act as the DHCP server
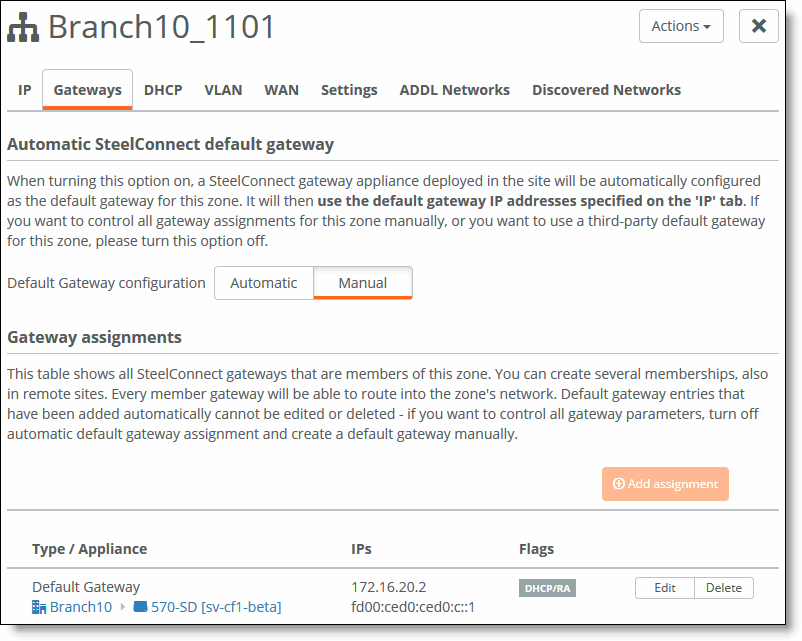
7. Make sure the DHCP/RA Server is on. (It will be green.)
8. Click Submit.
DHCP/RA Server setting to On
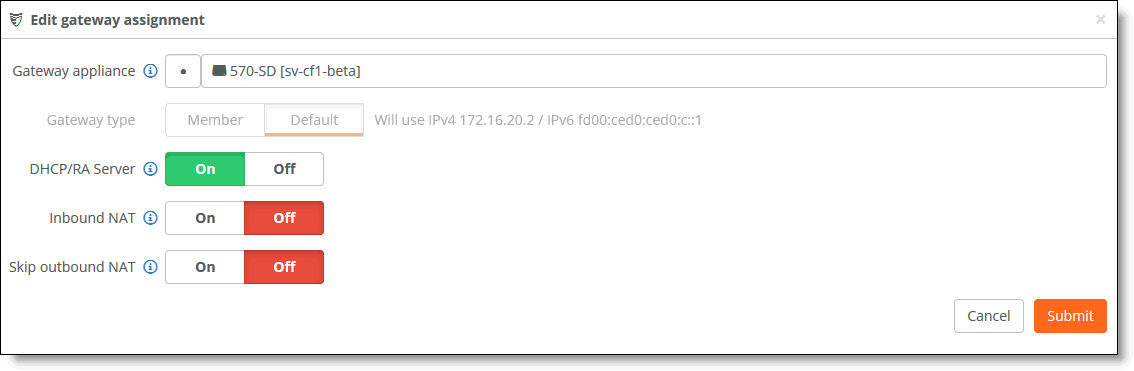
9. Choose Appliances > Ports to associate the LAN port to the appropriate Zone.
10. Select the site with the SteelHead SD appliance from the drop-down list.
11. Select the LAN port you want to associate.
Associating the LAN port to a zone
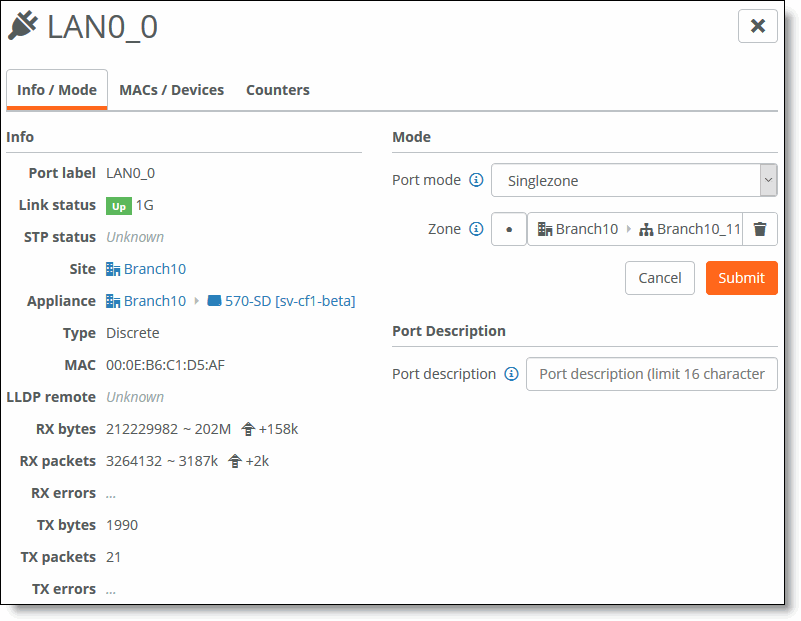
12. Select the zone from the Zone drop-down list.
13. Click Submit.
Cabling the appliance
In SteelHead SD, both the WAN and LAN ports are connected through the service virtual machine (VM).
The key task is to connect at least one WAN port to an uplink from a service provider that provides a path to the internet:
•On the SteelHead SD 570-SD or 770-SD appliances, use a straight-through cable to connect either the WAN0_0 or WAN0_1 ports to a WAN router with an internet uplink or an MPLS uplink for back-hauled internet traffic.
•On the SteelHead SD 3070-SD appliance, use a straight-through cable to connect either the WAN3_0 or WAN3_1 port to a WAN router. Internet reachability can be via a local breakout or via a data center over MPLS—whichever you prefer.
WAN ports require an IP address as they represent the uplink configuration. The SteelHead in-path interface must have an IP address and VLAN ID—this can be in any SteelConnect zone.
After powering on the appliances, each appliance will download the latest SteelConnect firmware if necessary, and reboot. After the appliances are updated with the latest firmware, SteelConnect will automatically start building a secure overlay of VPN tunnels.
We recommend you cable the primary port to a DHCP reachable port on the switch.
Port definitions
Port | Description |
Primary | The primary port is the management interface that enables you to connect to the SteelHead Management Console. Preferably the primary port connects to a DHCP reachable port on a switch. In a deployments where data store synchronization is used between two adjacent SteelHead appliances, the primary interface must be used for the data synchronization of traffic. |
AUX | The AUX port can be used as an additional WAN uplink on SteelHead SD. The AUX port is also the dedicated port for SteelHead SD HA deployments. The AUX port is not available for data store synchronization between two adjacent SteelHead appliances, the primary interface must be used for the synchronization traffic. |
WANX_X | WAN ports function as uplinks for internet service providers that connect to the internet. Connect the WAN port to a WAN router using a straight-through cable. For SteelHead SD 570-SD and 770-SD appliances, the default internet access port is WAN0_0 or WAN0_1. For SteelHead SD 3070-SD appliances, the default internet access port is WAN3_0 or WAN3_1. |
LANX_X | Connect the LAN port to the LAN switch using a straight-through cable. For SteelHead SD 570-SD and 770-SD appliances, the default port is LAN0_0 and LAN0_1. For SteelHead SD 3070-SD appliances, the default port is LAN3_0 or LAN3_1. |
Console | Connects you to the controller virtual machine (CVM) using a serial cable. CVM is the runtime management platform that connects you to the hypervisor via SSH. Typically, you should be able to troubleshoot and modify network issues using SCM. |
Cabling the SteelHead SD appliance
This section describes how to cable a SteelHead SD appliance.
For detailed information on how to cable the SteelConnect SDI-2030 gateway, see the SteelConnect Gateway Hardware Installation Guide (SDI-2030, SDI-5030).
To cable the SteelHead SD
1. Plug the straight-through cable into the primary port on the SteelHead SD appliance. We recommend that this is a DHCP port that connects to a DHCP server.
Connecting the primary port to the LAN switch
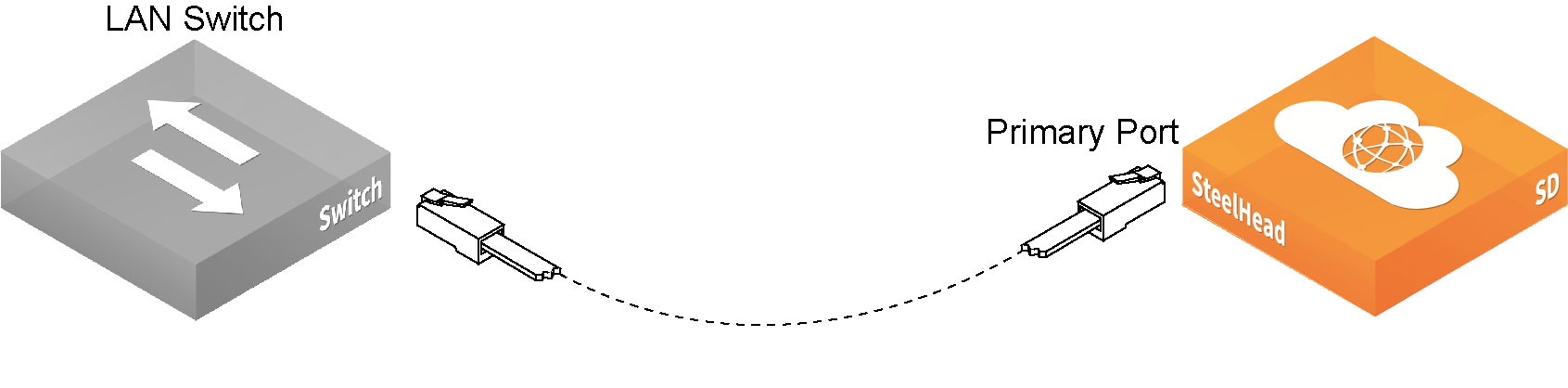
2. Plug the straight-through cable into at least one LAN port (LAN0_0, LAN0_1, and so on) to the LAN port on the switch.
Connecting the LAN switch to the LAN port
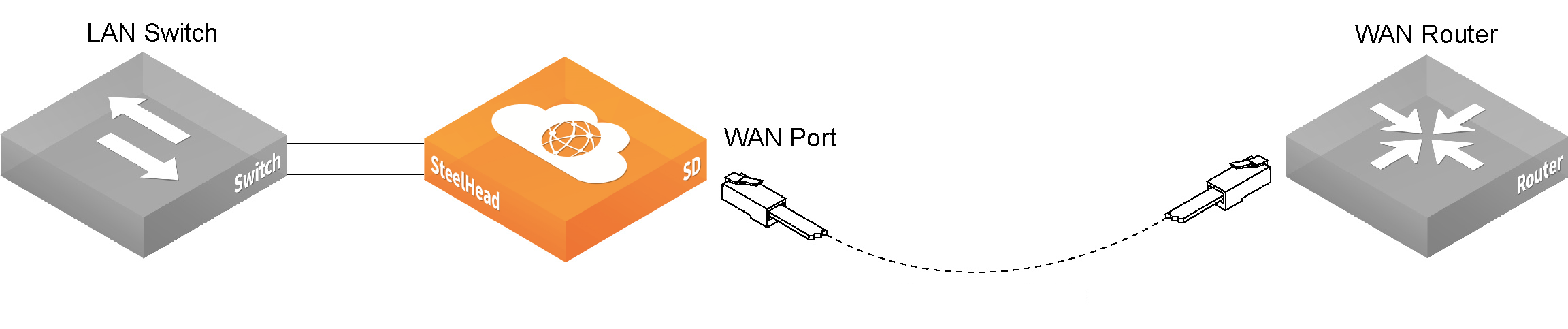
3. Connect at least one WAN port to an uplink from a service provider. For example, on a SteelHead SD 570-SD or 770-SD appliance, use a straight-through cable to connect the WAN0_0 or WAN0_1 port to a WAN router. On a SteelHead SD 3070-SD appliance, connect either the WAN3_0 or WAN3_1 port to a WAN router. Internet reachability can be via a local break-out or via a data center over MPLS.
Connecting the WAN port to the WAN router
Enabling WAN optimization in SCM
You enable WAN optimization in SCM in the Appliances page under the Services tab. You also specify the virtual SteelHead appliance in-path IP address. The in-path IP address must be within the LAN zone subnet that you have defined.
The WAN optimization service is disabled by default. When disabled, the WAN optimization service will not participate in any WAN optimization functionality. If disabled, any configuration related to WAN optimization service on this appliance will not be applied.
Only zones that are attached to a physical port can be used to configure the SteelHead SD IP address. Choose Appliances > Port to attach a zone to a port.
To enable WAN optimization
1. Choose Appliances > Overview.
2. Select the SteelHead SD appliance to expand the page.
3. Select the Services tab.
Enabling WAN optimization in the SCM
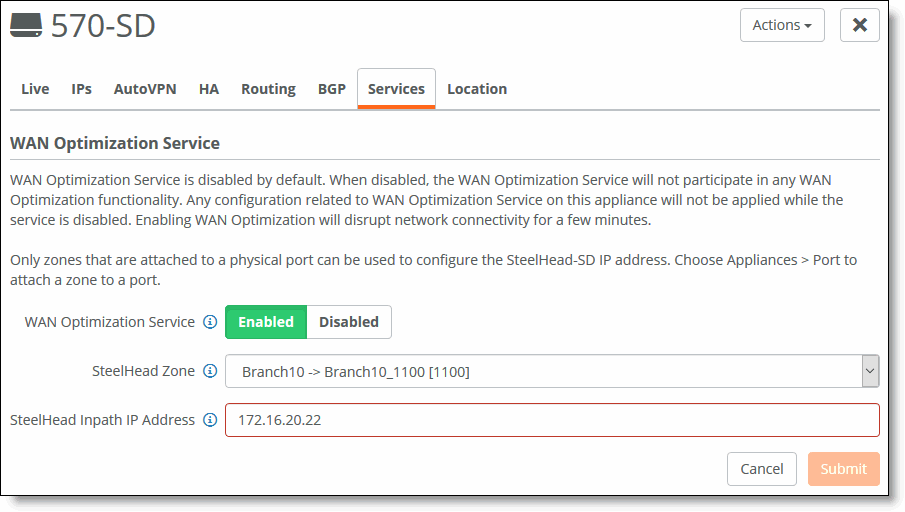
4. Under WAN Optimization Service, fill out these required session attributes:
•WAN Optimization Service - Click Enabled to enable the WAN optimization service for the selected SteelHead SD appliance. When disabled, the WAN optimization service will not participate in any WAN optimization functionality. If disabled, any configuration related to WAN optimization service on this appliance will not be applied.
•SteelHead Inpath IP - Specify the SteelHead in-path IP address. The IP address must be within the LAN zone subnet. This value tells SCM what in-path IP address you are using for the virtual SteelHead instance.
•SteelHead Zone - Select the zone to which this SteelHead SD appliance belongs. Only zones that are attached to a physical port can be used to configure the SteelHead SD IP address. Choose Appliances > Port to attach a zone to a port.
5. Click Submit.
After the WAN optimization service has been enabled within the SCM, the SteelHead SD triggers the orchestration and provisioning of the virtual SteelHead instance. This action will cause a momentary interruption to operations within SteelConnect because it is reconfigured with the SteelHead LAN and WAN interfaces.
Identifying the primary IP address of the SteelHead
You use the primary IP address of the SteelHead to connect to the virtual SteelHead instance. You can identify the primary IP address of the SteelHead in one of the following ways:
•When SteelConnect acts as the DHCP server - You can set the SteelConnect virtual gateway to act as a DHCP server and identify the primary IP address for the SteelHead in SCM. To view the SteelHead primary IP address in SCM, choose Appliances > Overview and select the SteelHead SD appliance. The primary IP address is listed under the IPs tab. For details on configuring SteelConnect to act as a DHCP server, see Configuring SteelConnect to act as DHCP server. •When the SCC is used to manage SteelHeads - If you are using the SCC to manage the WAN optimization service, you can obtain the primary IP address for each appliance in your network. SCC automatically registers all SteelHeads it detects in your network and provides the primary IP address for each in the Appliances page. For details on connecting to SCC, see the SteelCentral Controller for SteelHead User Guide.
•When an external server acts as the DHCP server - You can obtain the MAC address from the appliance and search for the primary IP address on the DHCP server console. You can find the MAC address on the appliance label (see SteelConnect serial number and MAC address) or you can view it in SCM. To view the MAC address in SCM, choose Ports and select the primary port for the appliance. The MAC address is listed under the Info-Mode tab. After you have discovered the primary IP address that has been leased to the virtual SteelHead instance, you simply log in to the management console user interface and complete the configuration of the virtual SteelHead instance.
Enabling WAN optimization on the virtual SteelHead instance
To enable WAN optimization for SteelHead SD, you must configure the inpath0_0 interface and default gateway for each appliance in your network using the SCC or the SteelHead Management Console.
Configuring the in-path interface and default gateway
These instructions describe how to configure the in-path interface and default gateway using the SteelHead Management Console.
Tip: In the SCC, choose Manage: Appliances > Appliance Pages > In-Path Interfaces to modify the inpath0_0 interface and default gateway. You can push the policy to the selected appliance.
To configure the in-path interface and the default gateway in the virtual SteelHead
1. Using the Primary IP address you obtained from SCM, SCC, or the DHCP server, enter it in the location box of your web browser using HTTPS. The sign in page for the SteelHead Management Console is displayed.
2. Specify the default user login (admin) and password (password).
3. Click Sign In to display the Dashboard.
4. Choose Networks > Networking: In-Path Interfaces.
In-Path Interfaces page
5. Select the interface to expand the page.
Configuring the in-path interface
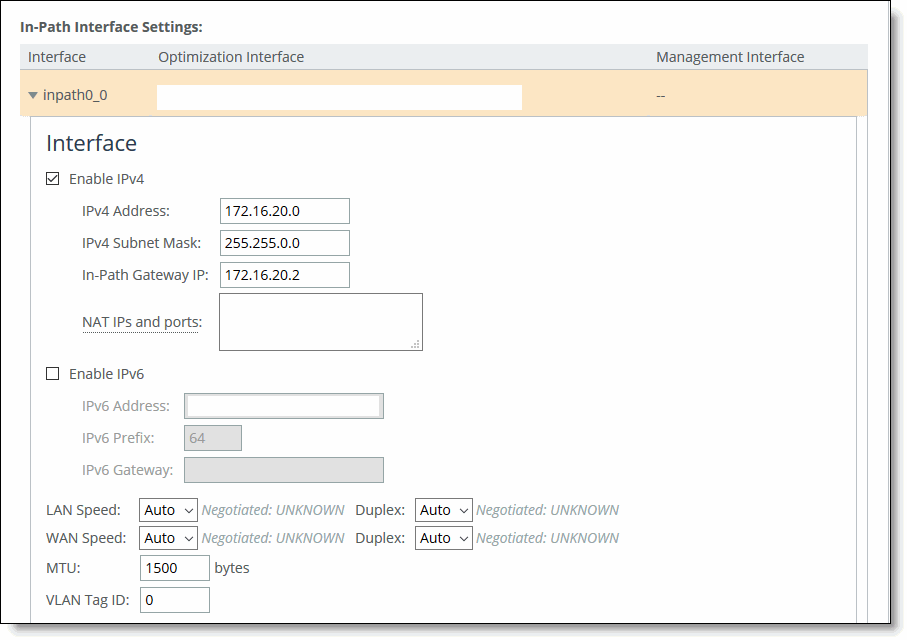
7. Type the subnet mask address. The subnet mask on the in-path must match the subnet mask on the zone (typically /24, but it can be whatever you specified in the zone settings).
9. Click Apply.
10. You can refine your in-path WAN optimization settings using the SteelHead Management Console. For details, see the SteelHead User Guide.
Next steps
Connect to SCM and finish configuring the SD-WAN features for SteelHead SD. For details, see the SteelHead SD User Guide and SteelConnect Manager User Guide.
Troubleshooting
This section contains some basic troubleshooting procedures.
Can’t generate config error
Typically, this error occurs when assignments are missing for the appliance in SteelConnect. For example in SCM, make sure the uplinks are assigned and the ports are enabled for the appliance.
License server errors
If there is an error connecting to the license server or the license server returns an HTTP error status, make sure you have connectivity to the internet. If you have internet connectivity and automatic licensing continues to fail, go to the Riverbed Licensing Portal at https://licensing.riverbed.com/ and follow the instructions for retrieving your licenses.
The certificate from license server doesn’t match the private key
If an error is displayed stating that there is no valid certificate. This means that the appliance entitlement certificate is out of date and the certificate on the license server needs to be validated. Contact Riverbed Support at https://support.riverbed.com.
Firmware upgrade error
If you have multiple site level DNS addresses configured at the site level, the firmware download might fail on SteelHead SD appliances. We recommend that you have only one DNS IP address defined when you configure a site in SCM. A single-site level DNS configuration resolves both SCM and the upgrade image hostname. If you encounter this error, make these configuration changes in SCM and retry firmware upgrade. If the upgrade continues to fail, contact Riverbed Support at https://support.riverbed.com.

















