Alarm Status page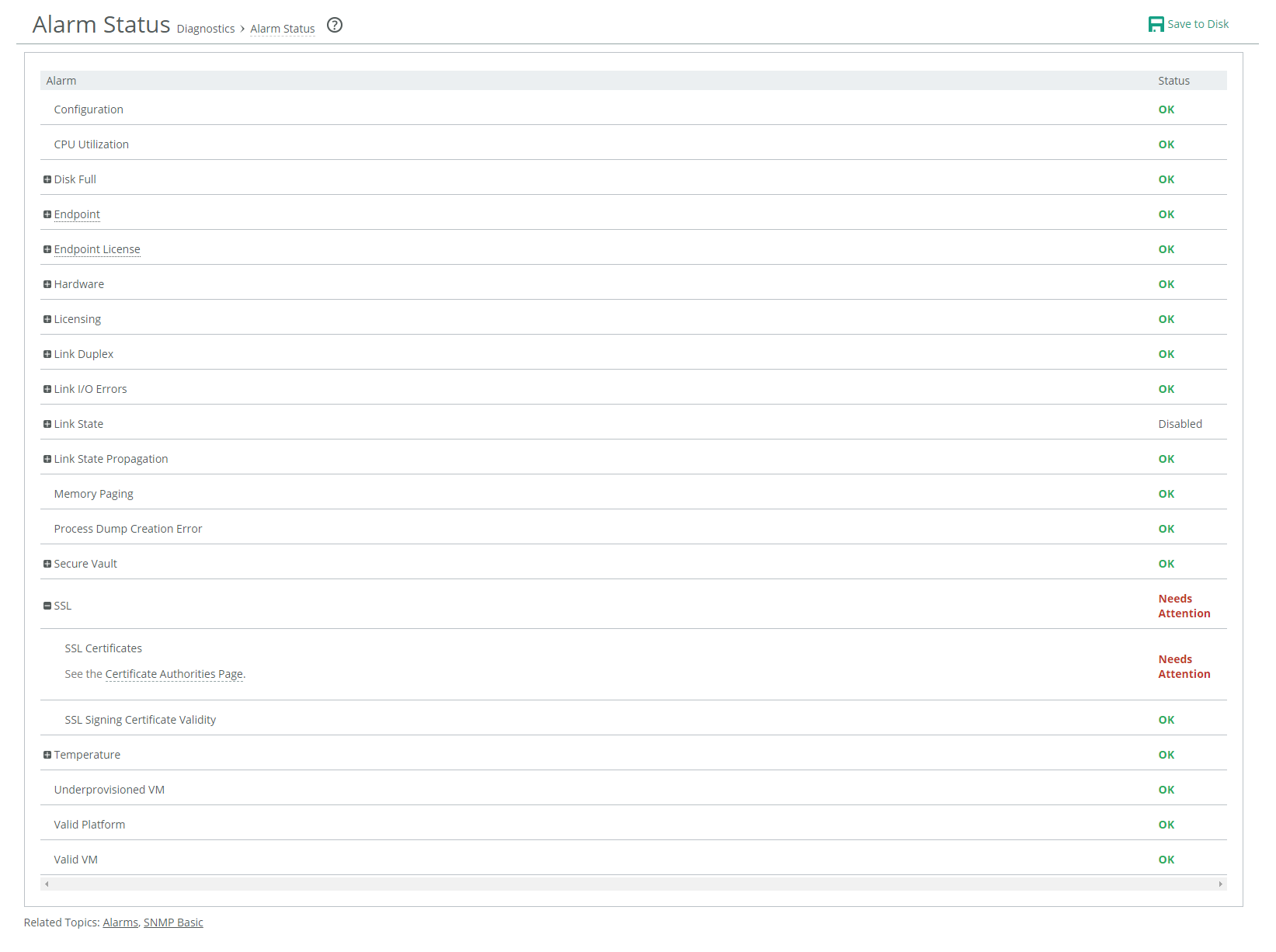

Alarm | State | Reason |
Configuration | Indicates whether a configuration error was detected. | |
CPU Utilization | Degraded | Indicates that the system has reached the CPU threshold for any of the CPUs in the controller. If the system has reached the CPU threshold, check your settings. For details, see
About alarms. If your alarm thresholds are correct, reboot the controller. If more than 100 MB of data is moved through a controller while performing PFS synchronization, the CPU utilization might become high and result in a CPU alarm. This CPU alarm is not cause for concern. |
Disk Full | Indicates that the system partitions (not the Client Accelerator RiOS data store) are full or almost full. | |
Endpoint Datastore | Indicates whether the number of endpoint clients with data store errors has reached the rising threshold. By default, this alarm is enabled. | |
Endpoint Filesystem Full | Indicates whether the number of endpoint clients with File System Full errors has reached the rising threshold. By default, this alarm is enabled. | |
Endpoint Firewall | Indicates whether the number of endpoints with firewall status has reached the rising threshold. By default, this alarm is enabled. | |
Endpoint Gen Id Error | Indicates whether an Endpoint Gen Id error was detected. By default, this alarm is enabled. | |
Endpoint NFS | Indicates whether there has been an NFS error. By default, this alarm is enabled. | |
Endpoint Service | Indicates whether the number of endpoint clients with service errors has reached the rising threshold. By default, this alarm is enabled. | |
Endpoint SSL Error | Indicates whether there has been an SSL error. By default, this alarm is enabled. | |
Endpoint Version | Indicates whether there is a mismatch between software versions in your network. If a software mismatch is detected, resolve the mismatch by upgrading or reverting to a previous version of the software. By default, this alarm is enabled. | |
Endpoint License | Indicates whether the number of connected endpoint licenses (including desktop licenses) has exceeded the licensed limit. For details about updating licenses, see
Maintaining Client Accelerator Controller. | |
Hardware | Either Critical or Degraded, depending on the state | • Fan Error—Indicates that a fan is failing or has failed and must be replaced. • Flash Error—Flash Error - Indicates an error with the flash drive hardware. At times, the USB flash drive that holds the system images might become unresponsive; the controller continues to function normally. When this error occurs, you can’t perform a software upgrade, as the controller is unable to write a new upgrade image to the flash drive without first power-cycling the system. To reboot the appliance, go to the Administration > Maintenance: Reboot/Shut Down page or enter the CLI reload command to automatically power cycle the controller and restore the flash drive to its proper state. • IPMI—Indicates an Intelligent Platform Management Interface (IPMI) event. (Not supported on all appliance models.) This alarm triggers when there has been a physical security intrusion. These events trigger this alarm: – chassis intrusion (physical opening and closing of the appliance case) – memory errors (correctable or uncorrectable ECC memory errors) – hard drive faults or predictive failures – power cycle, such as turning the power switch on or off, physically unplugging and replugging the cable, or issuing a power cycle from the power switch controller By default, this alarm is enabled. • Memory Error—Indicates a memory error: for example, when a system memory stick fails. • Power Supply—Indicates that an inserted power supply cord does not have power, as opposed to a power supply slot with no power supply cord inserted. • RAID—Indicates that the system has encountered RAID errors (for example, missing drives, pulled drives, drive failures, and drive rebuilds). Provides status information for individual drives on the system. – RAID Disk 0 Status – RAID Disk 1 Status For drive rebuilds, if a drive is removed and then reinserted, the alarm continues to be triggered until the rebuild is complete. |
Licensing | Critical | Indicates whether a license on the controller is removed, is about to expire, has expired, or is invalid. This alarm triggers if the Client Accelerator has no license installed for its currently configured model. • Autolicense Critical Event—This alarm triggers when the Riverbed Licensing Portal can’t respond to a license request with valid licenses. • Autolicense Informational Event—This alarm triggers if the Riverbed Licensing Portal has information regarding the licenses for a controller. For example, this alarm displays when the portal provides a license that is associated with a token previously used on a different controller. • Licenses Expired—This alarm triggers if one or more features have at least one license installed, but all of them are expired. • Licenses Expiring—This alarm triggers if the license for one or more features is going to expire within two weeks. • Licensing—This alarm triggers if the controller has no BASE or MSPEC license installed for its currently configured model. The licenses expiring and licenses expired alarms are triggered per feature. For example, if you install two license keys for a feature, LK1-FOO-xxx (expired) and LK1-FOO-yyy (not expired), the alarms don’t trigger, because the feature has one valid license. |
Link Duplex | Enables an alarm and sends an email notification when an interface was not configured for half-duplex negotiation but has negotiated half-duplex mode. The alarm displays which interface is triggering the duplex alarm. • Interface aux Half-Duplex • Interface primary Half-Duplex | |
Link I/O Errors | Enables an alarm and sends an email notification when the error rate on an interface exceeds 0.1 percent while either sending or receiving packets. This threshold is based on the observation that even a small link error rate reduces TCP throughput significantly. A properly configured LAN connection experiences very few errors. The alarm clears when the rate drops below 0.05 percent. The alarm displays the interface with the link error. • Interface aux Link Error • Interface primary Link Error | |
Link State | Degraded | Indicates that the system has detected a link that is inoperable. You are notified through SNMP traps, email, and alarm status. • Interface aux Down—This alarm triggers if an Ethernet link is inoperable on the aux interface. • Interface primary Down—This alarm triggers if an Ethernet link is inoperable on the primary interface. By default, this alarm is disabled. |
Memory Paging | Degraded | Indicates that the system has reached the memory paging threshold. If 100 pages are swapped approximately every two hours, the SteelHead is functioning properly. If thousands of pages are swapped every few minutes, then reboot the controller. If rebooting does not solve the problem, contact Support. |
Process Dump Creation Error | Degraded | Indicates that the system has detected an error while trying to create a process dump. This alarm indicates an abnormal condition in which RiOS can’t collect the core file after three retries. It can be caused when the /var directory, which is used to hold system dumps, is reaching capacity or other conditions. When this alarm is raised, the directory is blacklisted. Contact Support to correct the issue. |
Secure Vault | Degraded | Indicates a problem with the secure vault. • Secure Vault Locked—Needs Attention—Indicates that the secure vault is locked. To optimize SSL connections or to use RiOS data store encryption, the secure vault must be unlocked. Choose Administration > Security: Secure Vault and unlock the secure vault. For details, see
Unlocking the secure vault. |
SSL | Indicates that an error has been detected in your SSL configuration. • SSL Certificates—Indicates that an SSL peering certificate has failed to reenroll automatically within the Simple Certificate Enrollment Protocol (SCEP) polling interval. • SSL Signing Certificate Validity—Indicates that an SSL peering certificate has failed to reenroll automatically within the Simple Certificate Enrollment Protocol (SCEP) polling interval. | |
Temperature | Critical or Warning | Indicates that the CPU temperature has exceeded or is approaching the critical threshold: • Critical Temperature—Indicates that the CPU temperature has exceeded the critical threshold. The default value for the rising threshold temperature is 70°C; the default reset threshold temperature is 67°C. • Warning Temperature—Indicates that the CPU temperature is about to exceed the critical threshold. |
Underprovisioned VM | Memory, data storage, or CPU resources are insufficient for the maximum number of endpoints. Does not apply to the controller. | |
Valid Platform | Indicates that the hardware platform does not support the controller. By default, this alarm is enabled. | |
Valid VM | Indicates that the virtual machine is unavailable. |
