Figure: Displaying Cluster Pages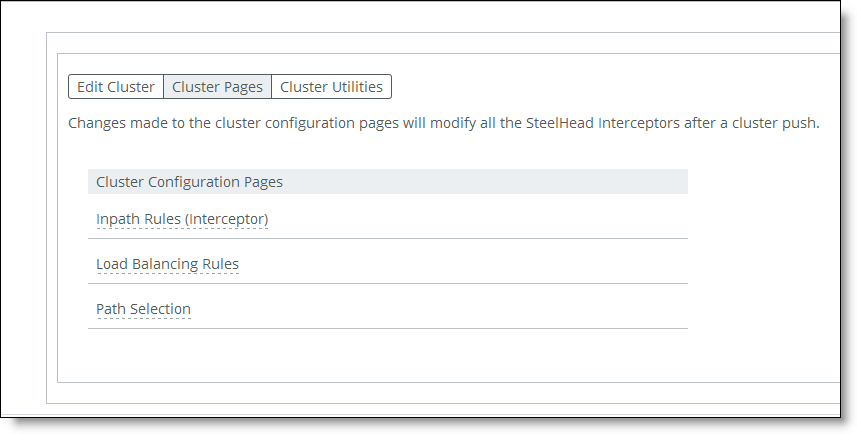


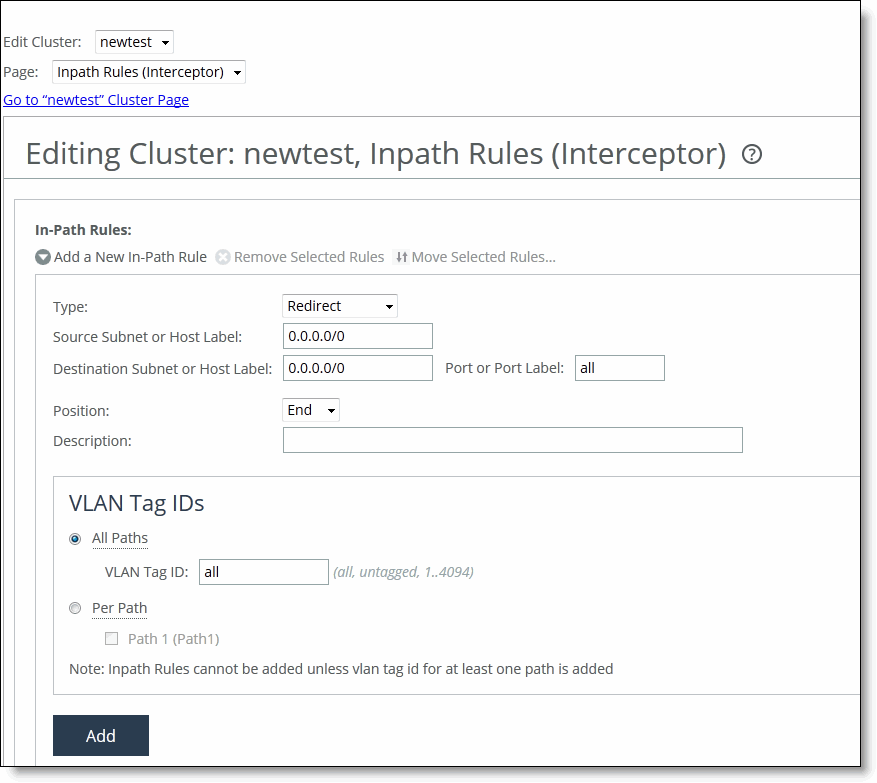
Control | Description |
Type | • Redirect - Redirects locally initiated TCP connections to be optimized by a SteelHead. Typically, you configure a redirect rule for source and destination addresses and ports you want to optimize in the Riverbed system. A separate set of load-balancing rules determines the SteelHead to which the connection is to be redirected. • Pass-Through - Allows the SYN packet to pass through the SteelHead unoptimized. No optimization is performed on the TCP connection initiated by this SYN packet. You define pass-through rules to exclude subnets from optimization. Traffic is also passed through when the SteelHead is in bypass mode. (Pass through of traffic might occur because of in-path rules or because the connection was established before the SteelHead was put in place or before the optimization service was enabled.) • Discard - Drops the SYN packets silently. The SteelHead filters out traffic that matches the discard rules. This process is similar to how routers and firewalls drop disallowed packets: the connection-initiating device has no knowledge that its packets were dropped until the connection times out. • Deny - Drops the SYN packets, sends a message back to its source, and resets the TCP connection being attempted. Using an active reset process rather than a silent discard allows the connection initiator to know that its connection is disallowed. |
Source Subnet or Host Label | Specify the subnet IP address and netmask for the source network: Use this format for an individual subnet IPv4 address and netmask: XXX.XXX.XXX.XXX/XX To configure a rule to apply to all source subnets, specify All. • Port or Port Label - Specify the source port number, port label, or All. |
Destination Subnet or Host Label | Specify the subnet IP address and netmask for the destination network: Use this format for an individual subnet IPv4 address and netmask: XXX.XXX.XXX.XXX/XX To configure a rule to apply to all source subnets, specify All. • Port or Port Label - Specify the destination port number, port label, or All. |
Position | Select Start, End, or a rule number from the drop-down list. Interceptors evaluate rules in numerical order starting with rule 1. If the conditions set in the rule match, then the rule is applied, and the system moves on to the next packet. If the conditions set in the rule do not match, the system consults the next rule. For example, if the conditions of rule 1 do not match, rule 2 is consulted. If rule 2 matches the conditions, it is applied, and no further rules are consulted. In general, list rules in this order: 1. Deny 2. Discard 3. Pass-through 4. Fixed-target 5. Auto-Discover Note: The default rule, Auto-Discover, which optimizes all remaining traffic that has not been selected by another rule, cannot be removed and is always listed last. |
Description | Describe the rule to facilitate administration. |
VLAN Tag ID | Specify a VLAN identification number from 0 to 4094, or All to apply the rule to all VLANs, or Untagged to apply the rule to nontagged connections. Pass-through traffic maintains any preexisting VLAN tagging between the LAN and WAN interfaces. To complete the implementation of VLAN tagging, you must set the VLAN tag IDs for the in-path interfaces that the Interceptor uses to communicate with other Interceptors. • All Paths - Specify a VLAN identification number from 0 to 4094, or All to apply the rule to all VLANs, or Untagged to apply the rule to nontagged connections. • Per Path - Select to configure a per path VLAN. – Path 1 - Select to specify a VLAN Tag ID from 0 to 4094, or All to apply the rule to all VLANs, or Untagged to apply the rule to nontagged connections. |
Add | Adds the rule to the list. |
Remove Selected Rules | Select the check box next to the name and click Remove Selected Rules. |
Move Selected Rules | Moves the selected rules. Click the rule you want to move and click Move Selected Rules, click-hold and drag the rule to the new position. |