About peering rule settings
Peering rules settings are under Optimization > Network Services: Peering Rules.
Peering Rules settings
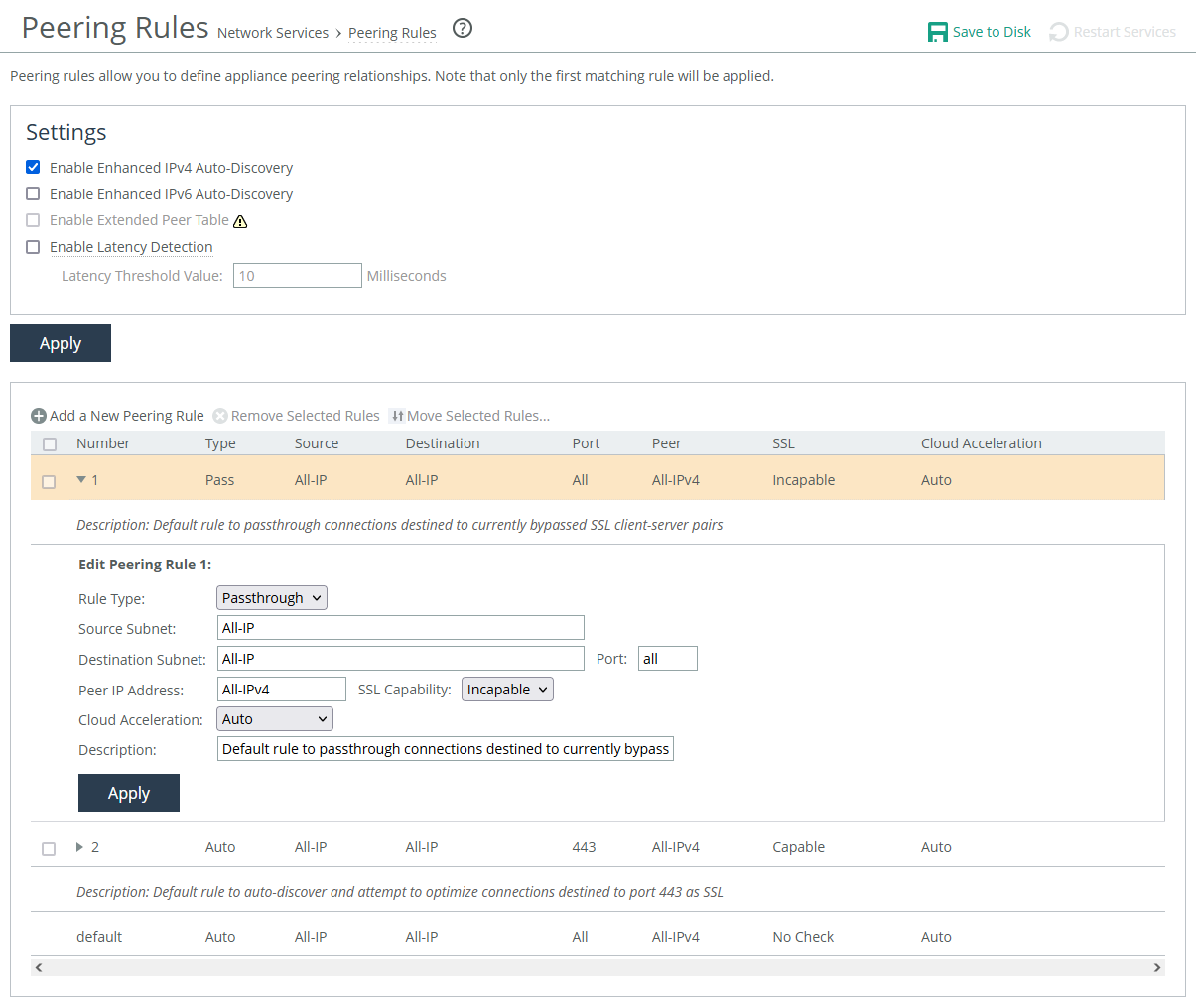
Rule Type determines which action the appliance takes on the connection.
• Auto allows built-in functionality to determine the response for peering requests (performs the best peering possible). If the receiving appliance is not using automatic autodiscovery, this has the same effect as the Accept action. If automatic autodiscovery is enabled, the appliance only becomes the optimization peer if it’s the last one in the path to the server.
• Accept accepts peering requests that match the source-destination-port pattern. The receiving appliance responds and peers.
• Passthrough allows pass-through peering requests that match the source and destination port pattern. The receiving appliance doesn’t respond to the probe and allows the SYN+probe packet to continue through the network.
Insert Rule At determines the order in which the system evaluates the rule.
Source Subnet and Destination Subnet specify IP addresses subnet mask for traffic sources and destinations. Wildcards supported.
Port specifies the destination port number, port label, or All.
Peer IP Address specifies the in-path IP address of the probing appliance. If more than one in-path interface is present on the probing appliance, apply multiple peering rules, one for each in-path interface. You can also specify wildcards.
SSL Capability enables an SSL capability flag, which specifies criteria for matching an incoming connection with one of the rules in the peering rules table. This flag is typically set on a server-side appliance.
• No Check performs no check to determine whether the server-side appliance is present at the specified destination IP address and port combination.
• Capable determines that the connection is SSL-capable if the destination port is 443 (irrespective of the destination port value on the rule) and the destination IP and port don’t appear on the bypassed servers list. The appliance accelerates SSL for traffic meeting those conditions.
• Incapable determines that the connection is SSL-incapable if the destination IP and port appear in the bypassed servers list. The service adds a server to the bypassed servers list when there’s no SSL certificate for the server or for any other SSL handshake failure. The appliance passes the connection through unoptimized without affecting connection counts.
Cloud Acceleration determines which connections coming from a client-side appliance (with the Cloud Accelerator enabled but with redirect disabled) should be optimized with the Cloud Accelerator. Use cloud acceleration in peering rules on a server-side SteelHead in a back-hauled deployment.
• Auto indicates the server-side SteelHead redirects connections to the cloud for acceleration.
• Pass Through indicates the server-side SteelHead doesn’t redirect connections to the cloud.
If the client-side SteelHead doesn’t have cloud acceleration enabled, or if it’s not trying to optimize cloud connections, the value of this field is irrelevant on the server-side SteelHead.
Description. Enter a description to help you identify the peering relationship.


